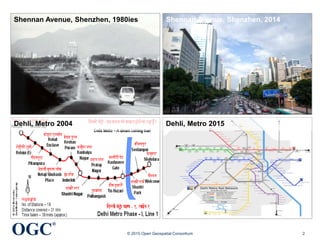
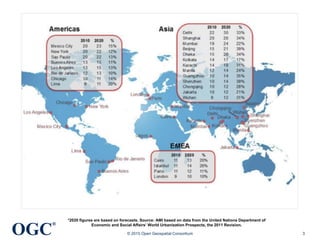
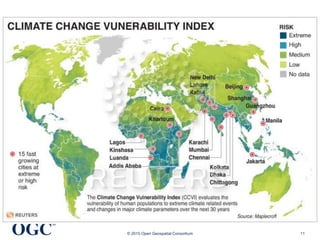
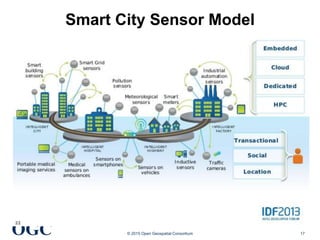
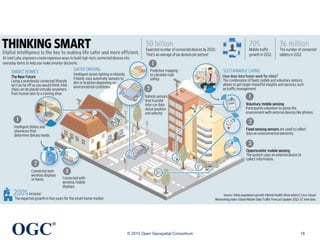
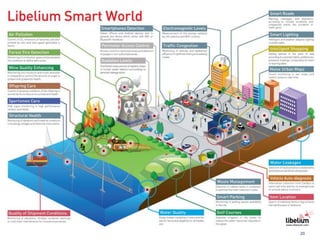
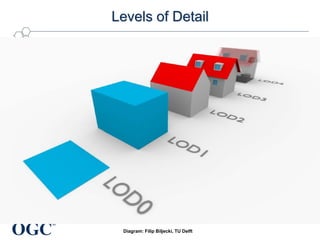
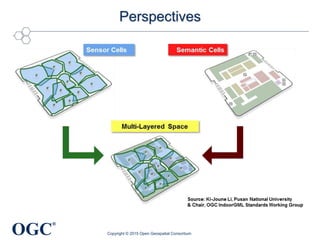
The document discusses the role of open geospatial standards in developing smart cities, emphasizing the need for unique solutions tailored to different urban environments as cities continue to grow. It highlights the advantages of standardization in promoting economic growth, improving trade, and facilitating interoperability across various sectors, thereby enhancing quality of life and sustainability. Furthermore, it details the impact of information and communication technology (ICT) in urban management, emphasizing its vital function in the realization of smart cities.