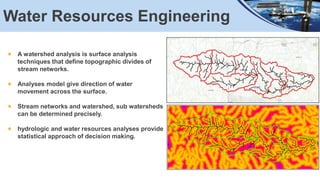
This document summarizes geospatial applications in civil engineering. It discusses how remote sensing and GIS techniques can be used for site investigations, terrain mapping and analysis, water resources engineering, town planning and urban development, transportation network analysis, and landslide studies. Specific applications are described, including using drones for site investigations, terrain analysis tools like slope and aspect maps, watershed and hydrologic modeling, and urban planning. Data sources, tools, and workflows are also outlined.