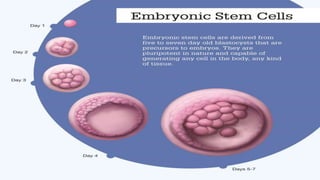
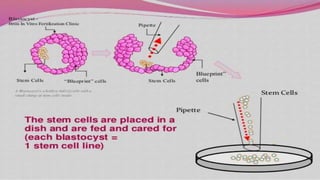
The document discusses embryonic stem cells, which are unspecialized precursor cells capable of developing into various specialized cell types, and their role in tissue repair and regenerative medicine. It highlights research on the early developmental stages of embryos, with findings indicating that the formation of body structures, such as the head and spinal cord, is influenced by genetic switches and hydrodynamic forces. While embryonic stem cells exhibit higher proliferative potential compared to adult stem cells, their limitations include potential differences in maturation and the need for proper characterization.