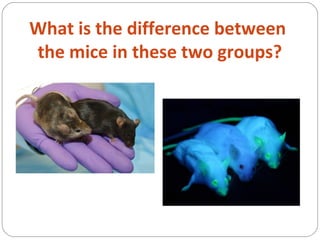
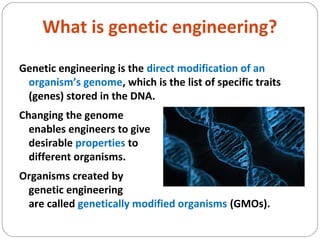
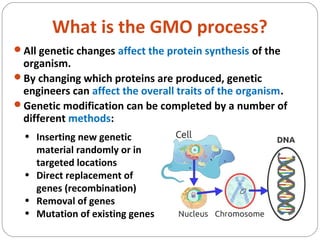
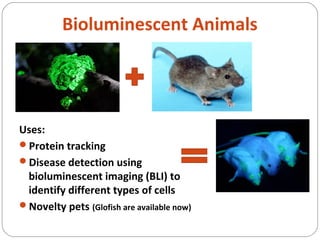
The document discusses genetic engineering and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). It defines genetic engineering as the direct modification of an organism's genome through techniques like inserting, replacing or removing genes. This allows scientists to modify traits. Some key points:
- The first GMOs were bacteria in 1973, mice in 1974, and commercial GMO development began with insulin-producing bacteria in 1982.
- Common GMO crops include 93% of soybeans, 93% of cotton and 86% of corn grown in the US. One example is Bt-corn which produces a toxin harmful to insects.
- GMOs can be engineered for traits like insect or herbicide resistance, increased yield, or improved nutrition. Concer