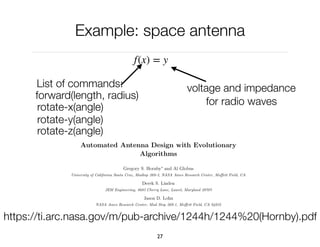
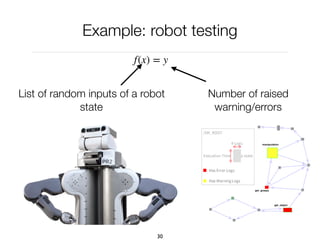
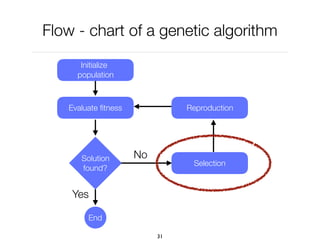
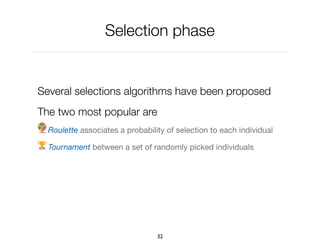
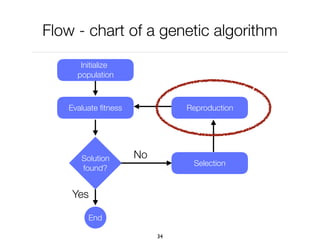
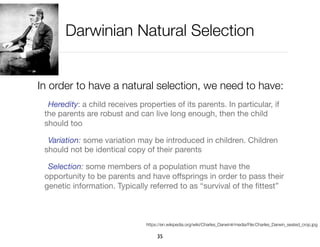
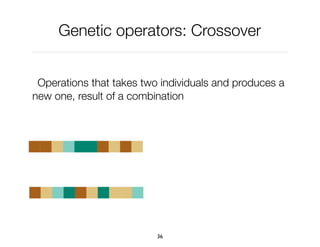
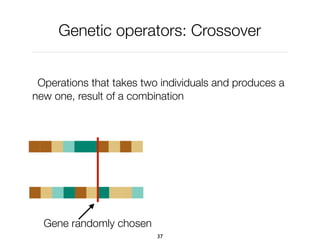
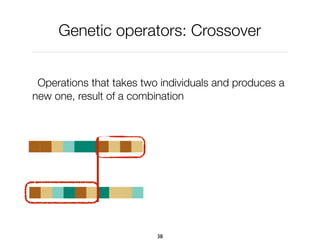
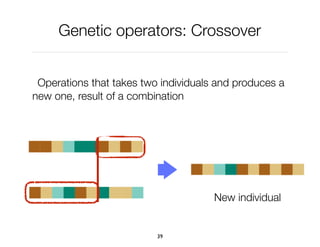
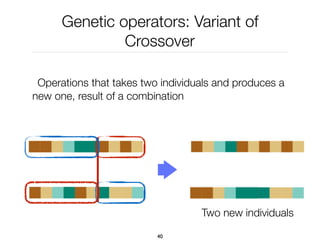
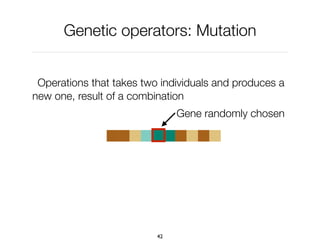
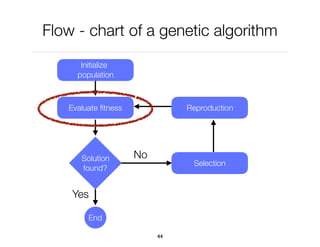
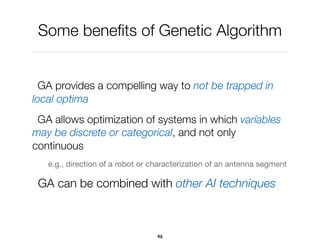
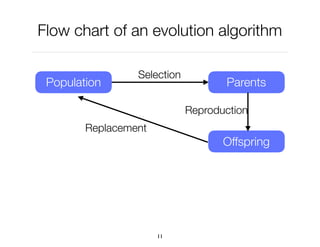
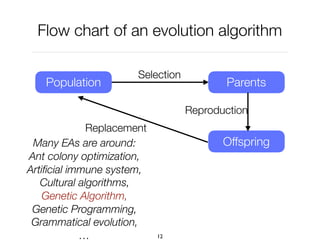
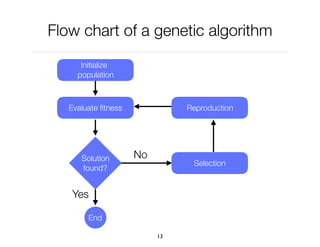
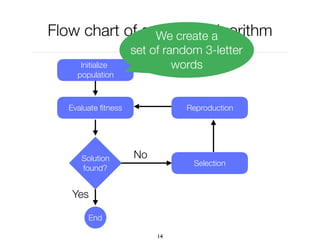
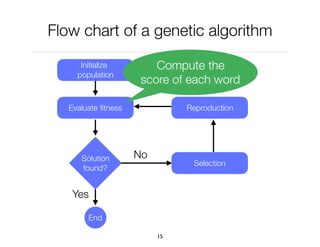
The document discusses genetic algorithms, which are computational models inspired by natural selection, to solve optimization problems without predefined structures. It outlines concepts such as population, fitness function, and genetic operators including selection, crossover, and mutation that drive the algorithm's evolution process. Examples highlight applications in software testing, server optimization, and antenna design, emphasizing the flexibility and effectiveness of genetic algorithms in various fields.






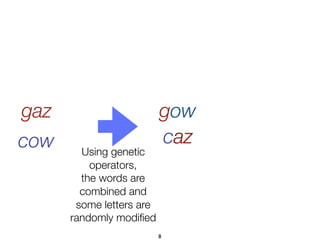
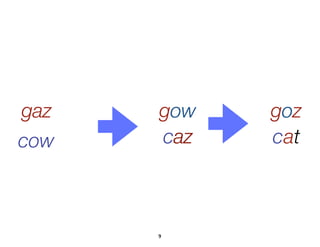
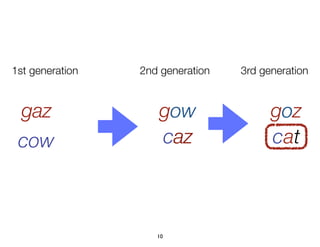
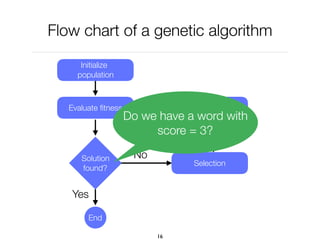
![Example: optimizing a server
Consider a server running in Java
The Java virtual machine, which has over 200 options
What are the options that consume the least amount
of memory to answer HTTP requests
is a set of options, e.g., [ -Xgc:parallel, -ms32m,
-mx200m]
is the amount of memory (in bytes)
is computed by launching the server using the
options and sending 1000 requests
24
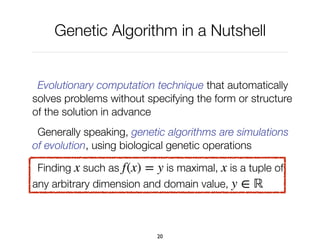
f(x) = y
x
y
f(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-geneticalgorithm-esug-190910144245/85/Genetic-Algorithm-24-320.jpg)
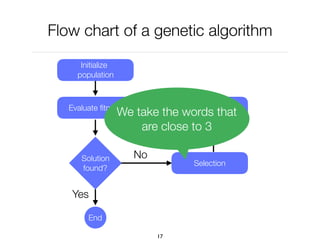
![Example: optimizing a server
Consider a server running in Java
The Java virtual machine, which has over 200 options
What are the options that consume the least amount
of memory to answer HTTP requests
is a set of options, e.g., [ -Xgc:parallel, -ms32m,
-mx200m]
is the amount of memory (in bytes)
is computed by launching the server using the
options and sending 1000 requests
25
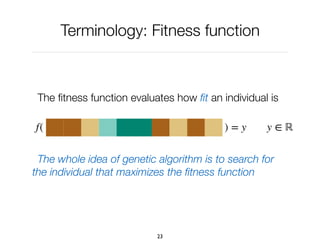
f(x) = y
x
y
f(x)
We look for the optimal x
that minimize f(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-geneticalgorithm-esug-190910144245/85/Genetic-Algorithm-25-320.jpg)