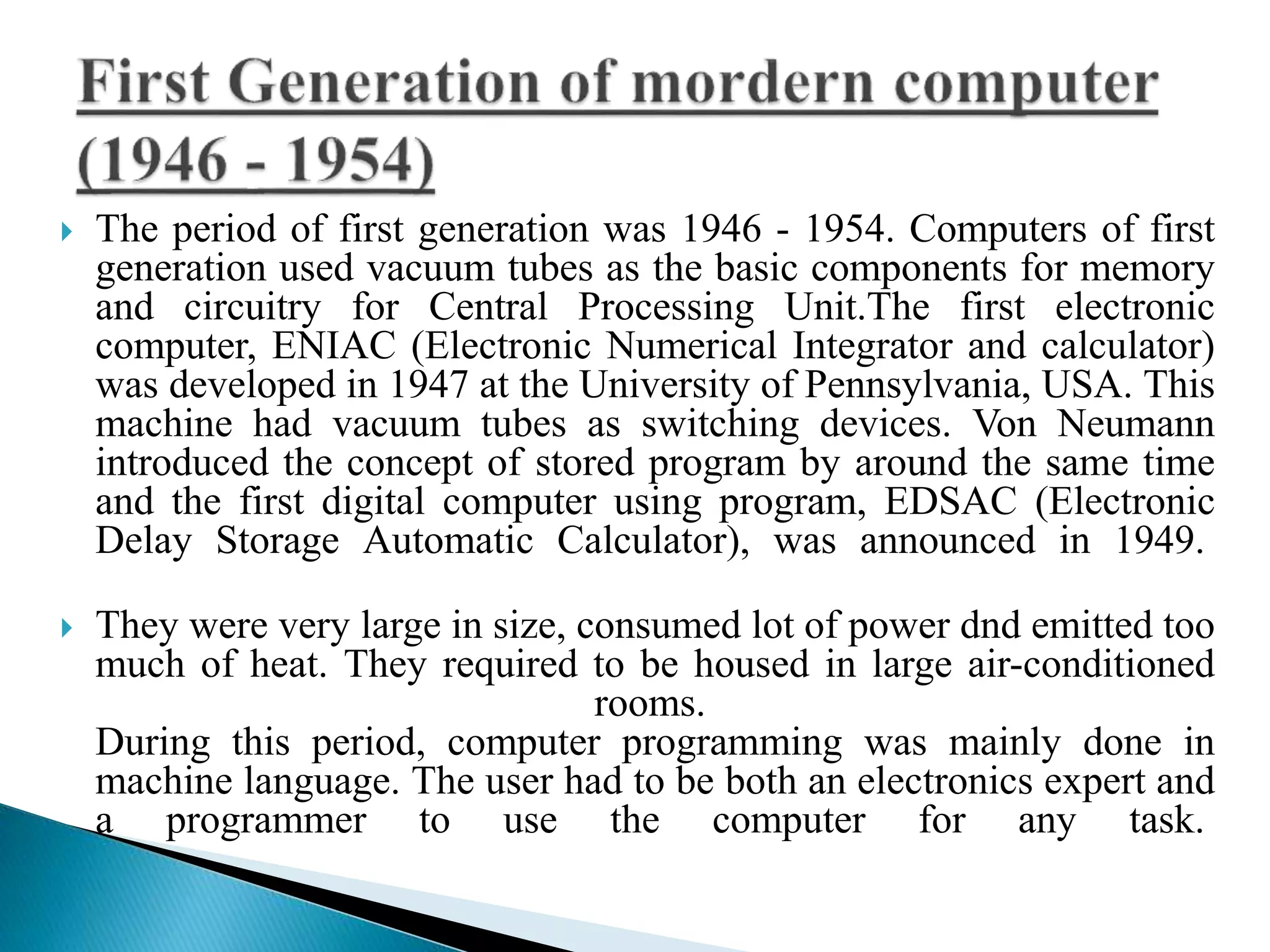
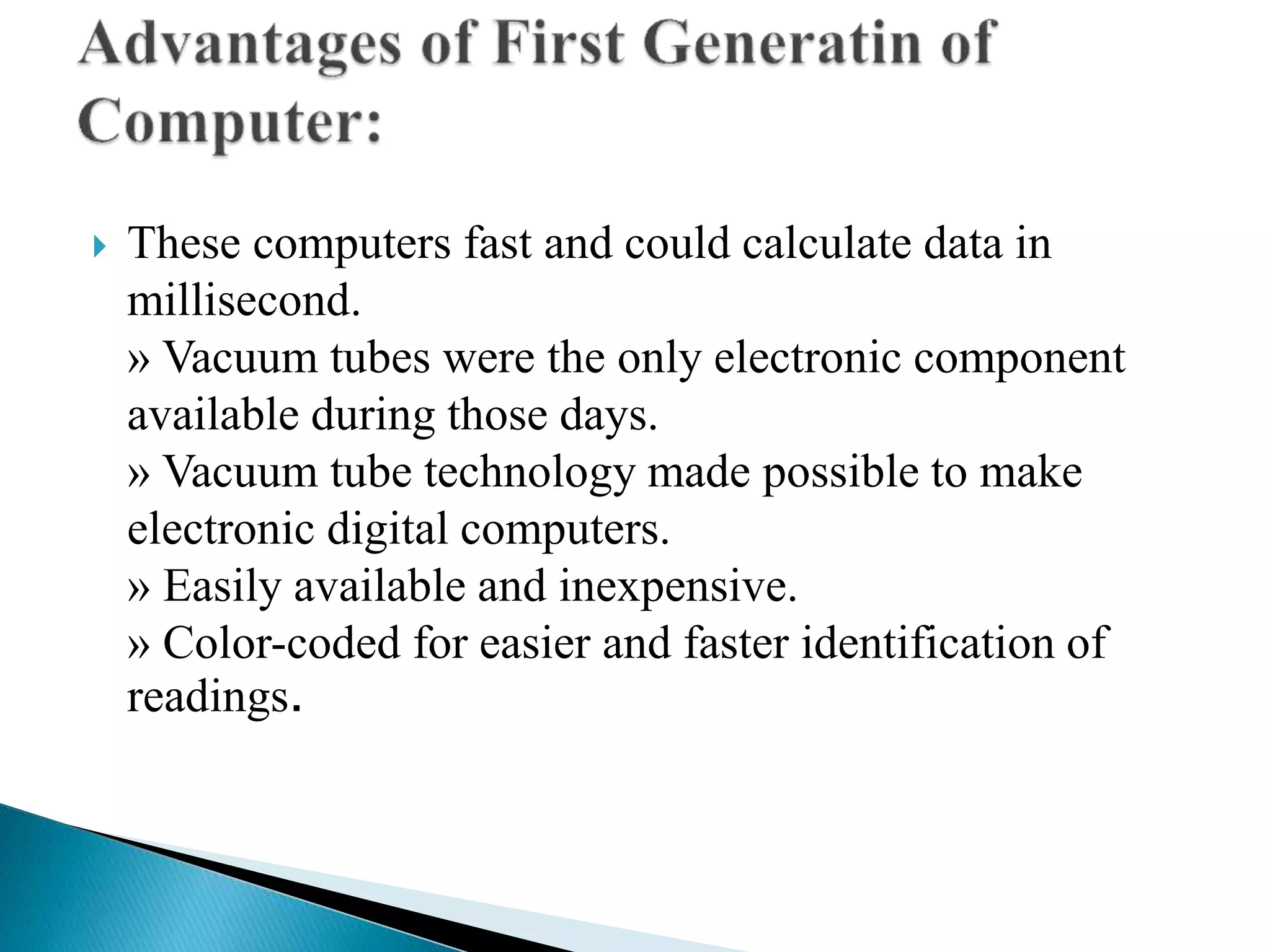
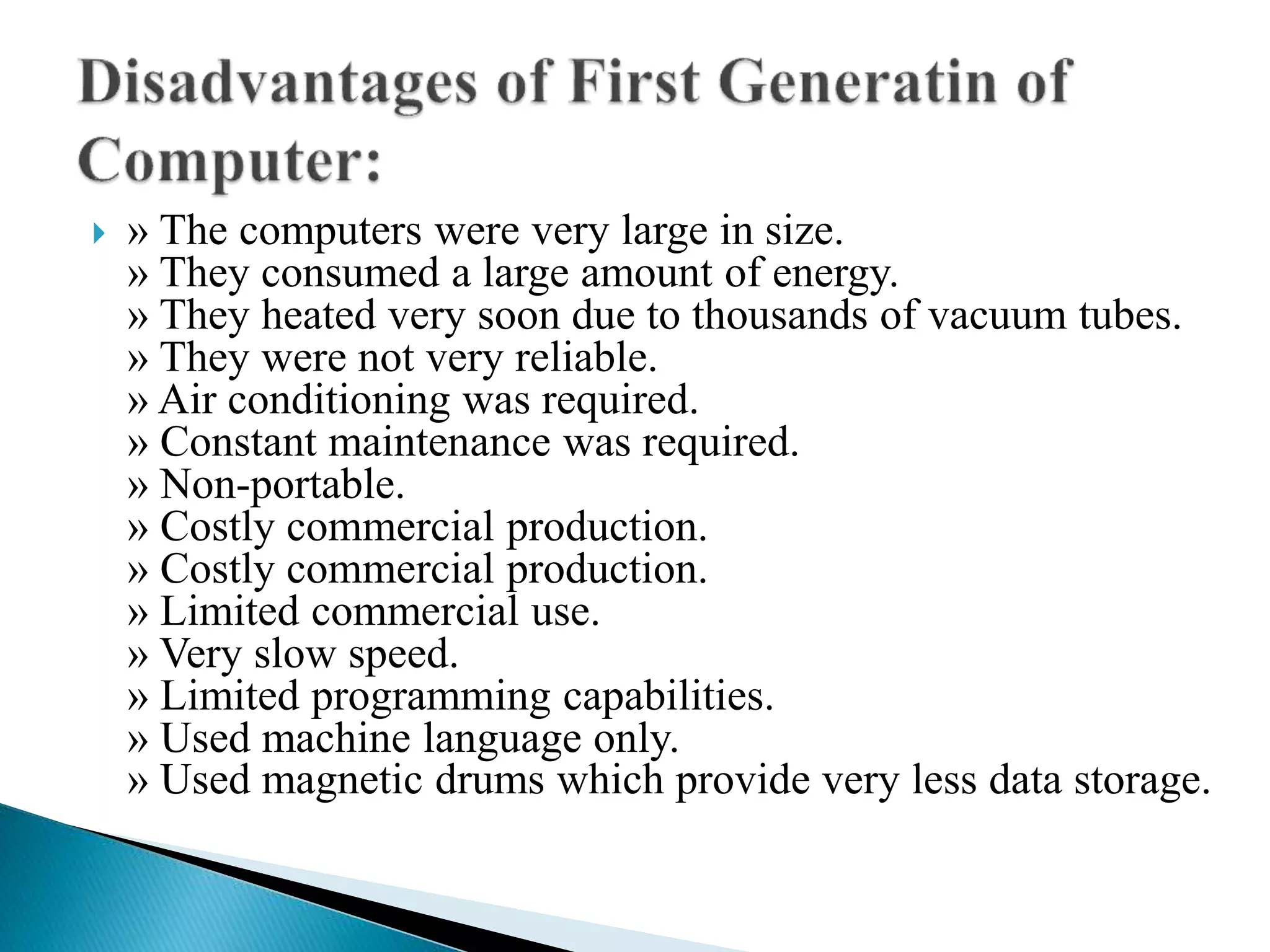
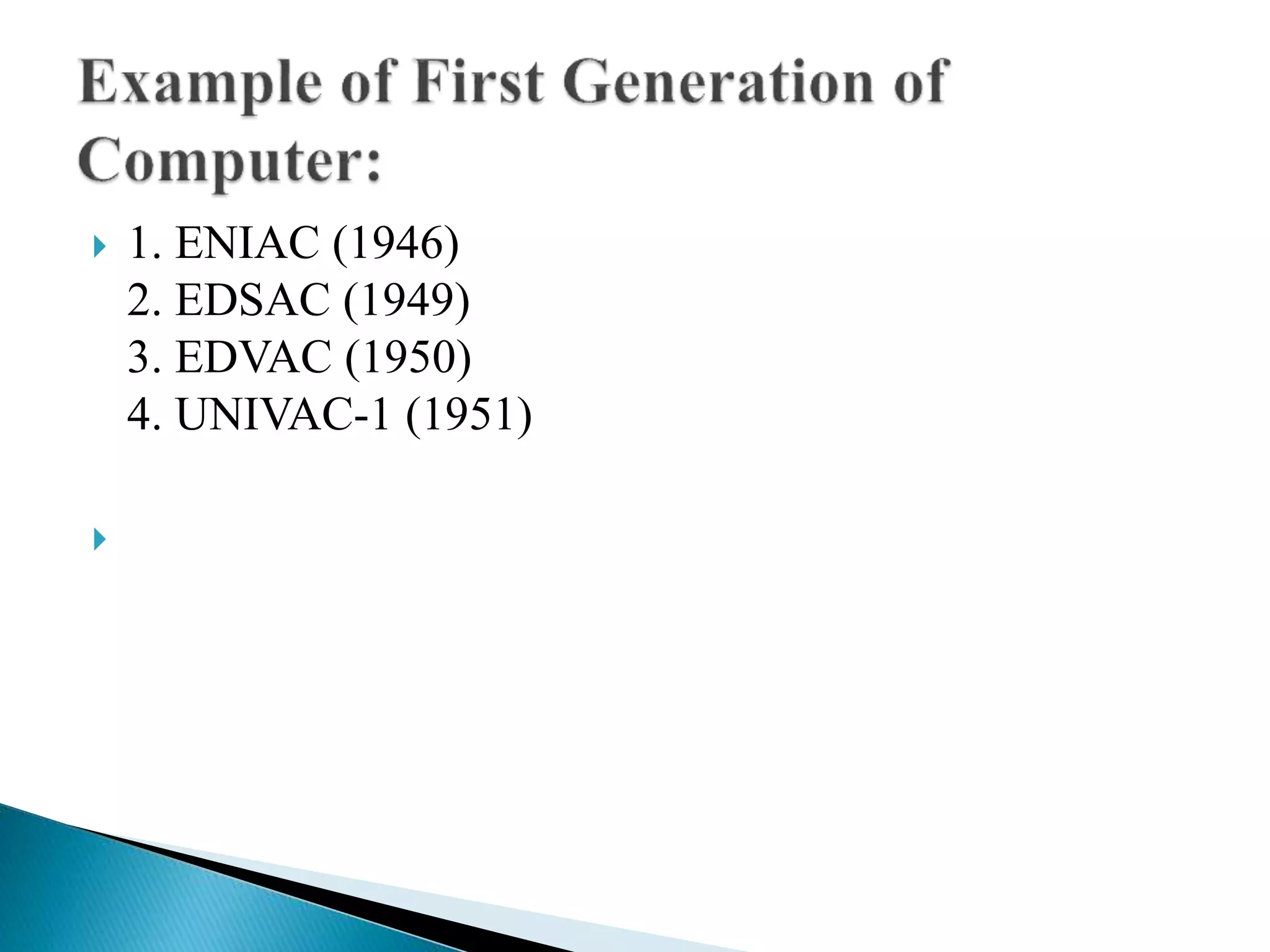
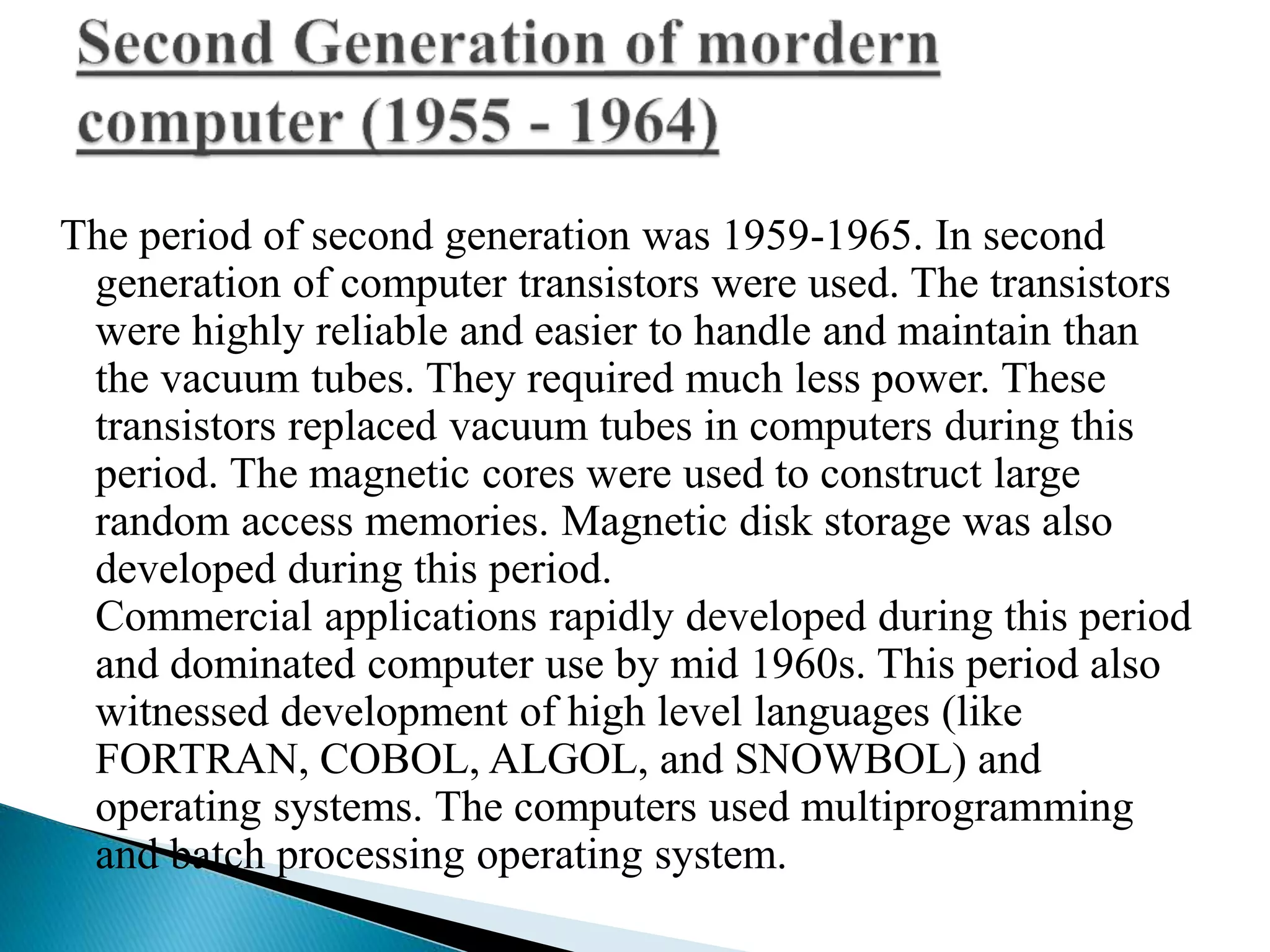
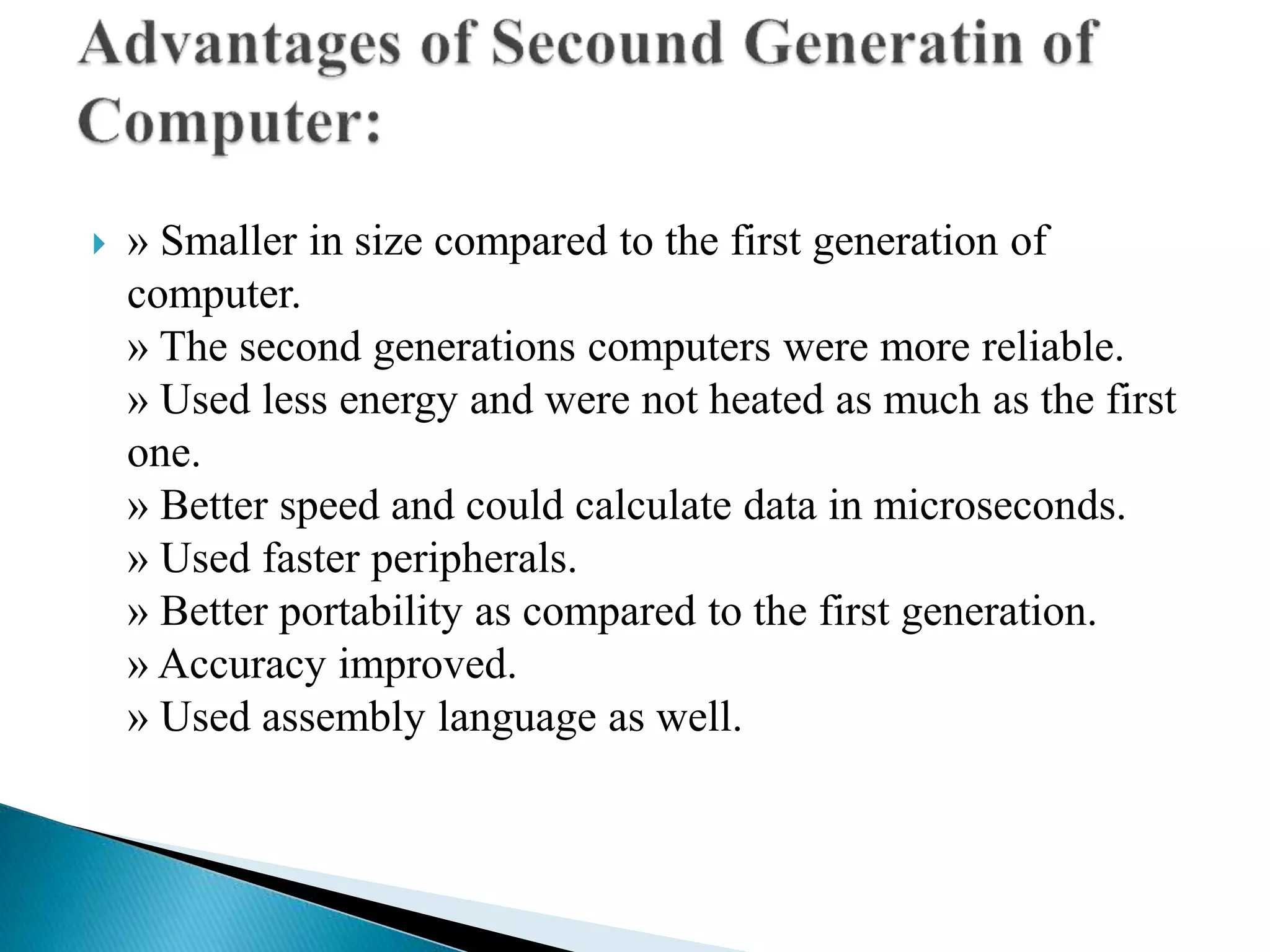
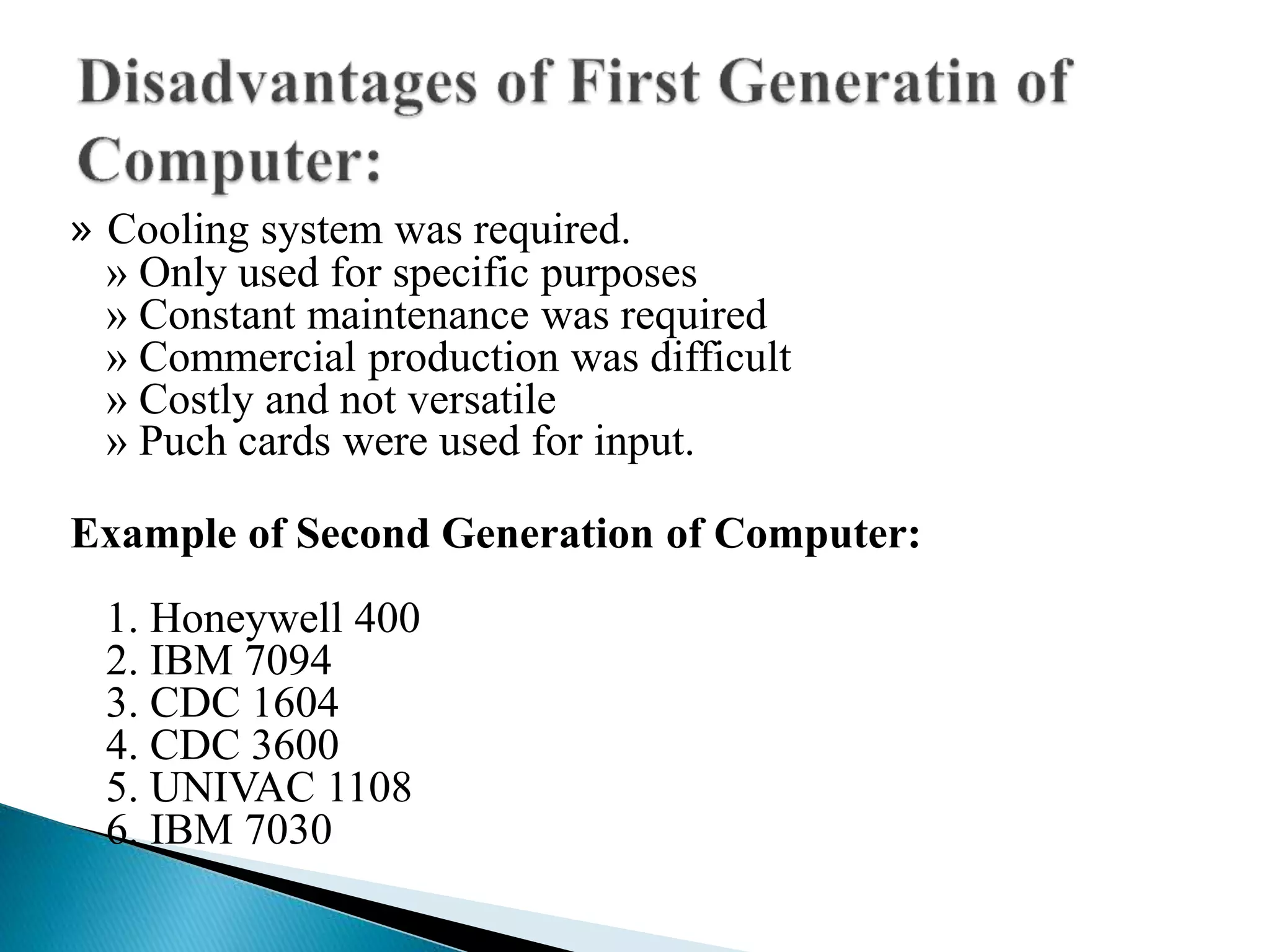
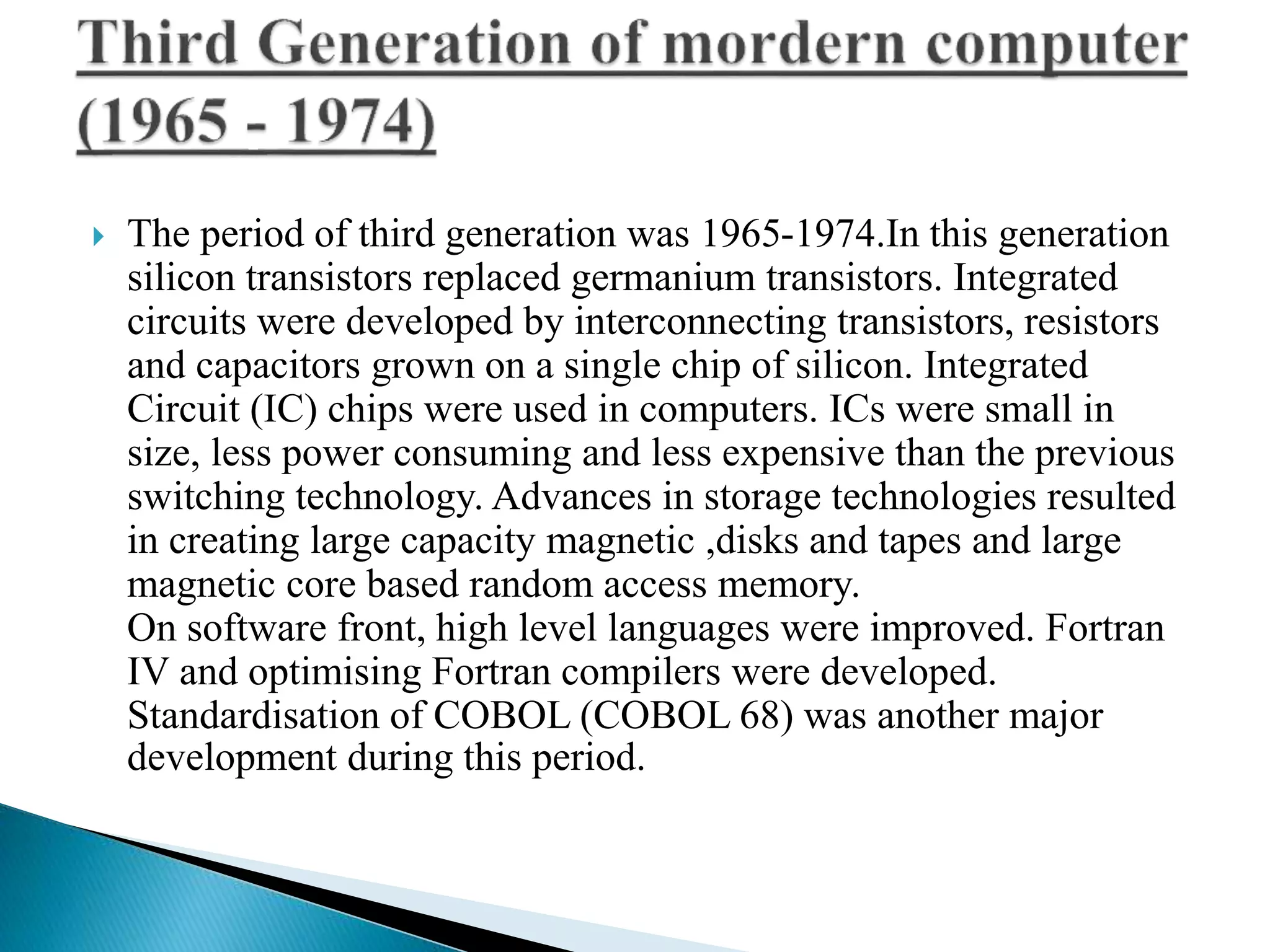
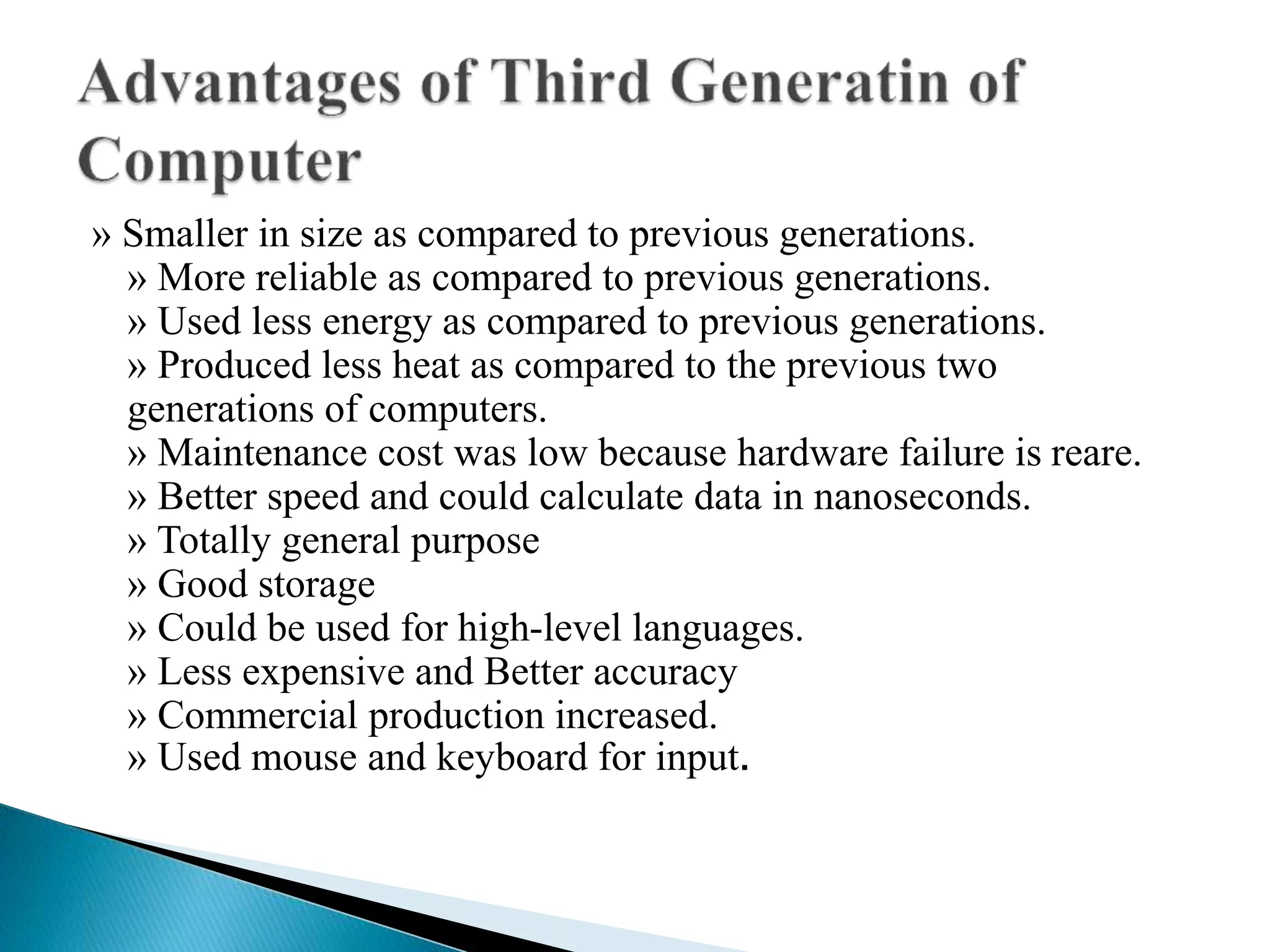
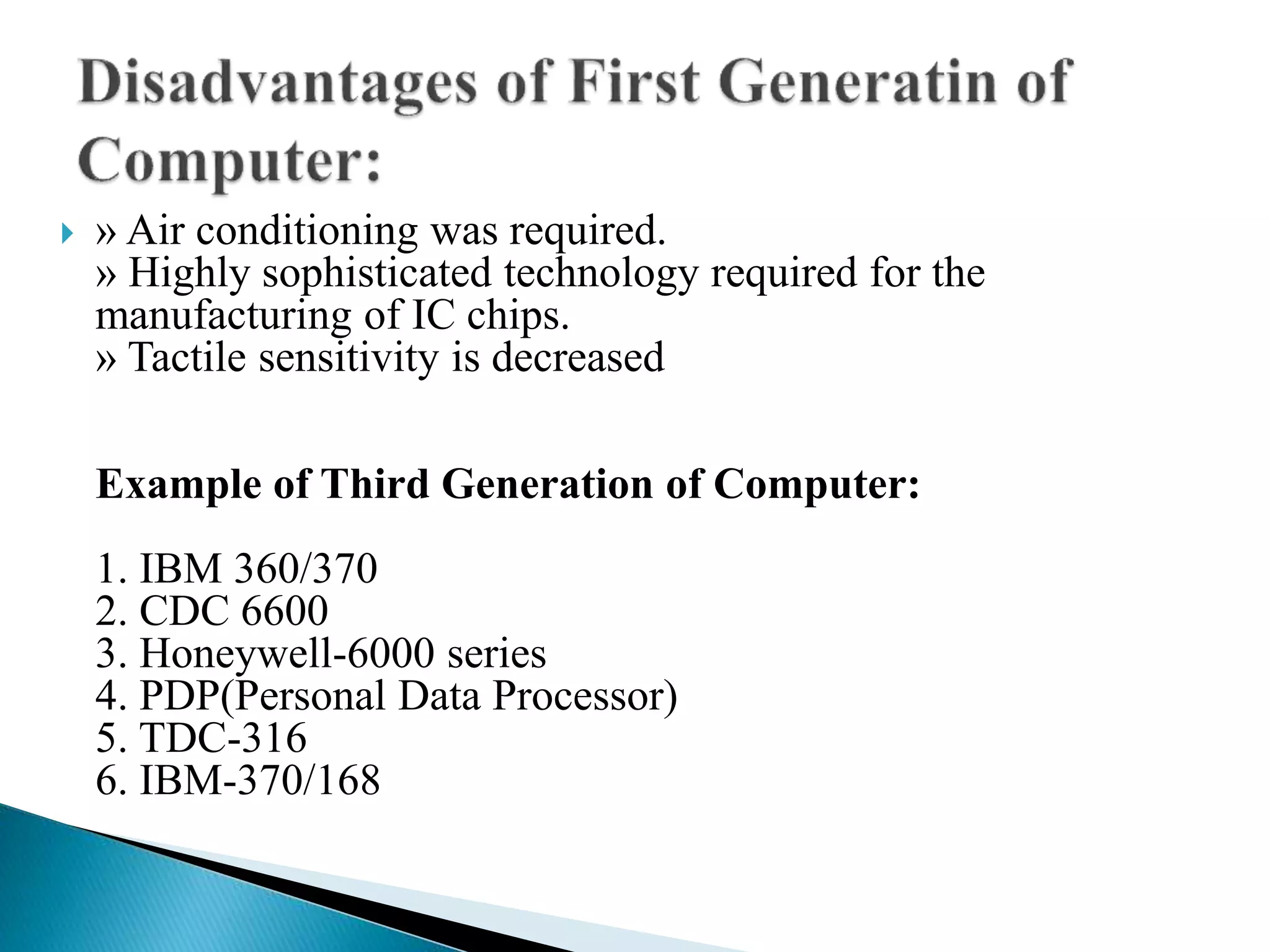
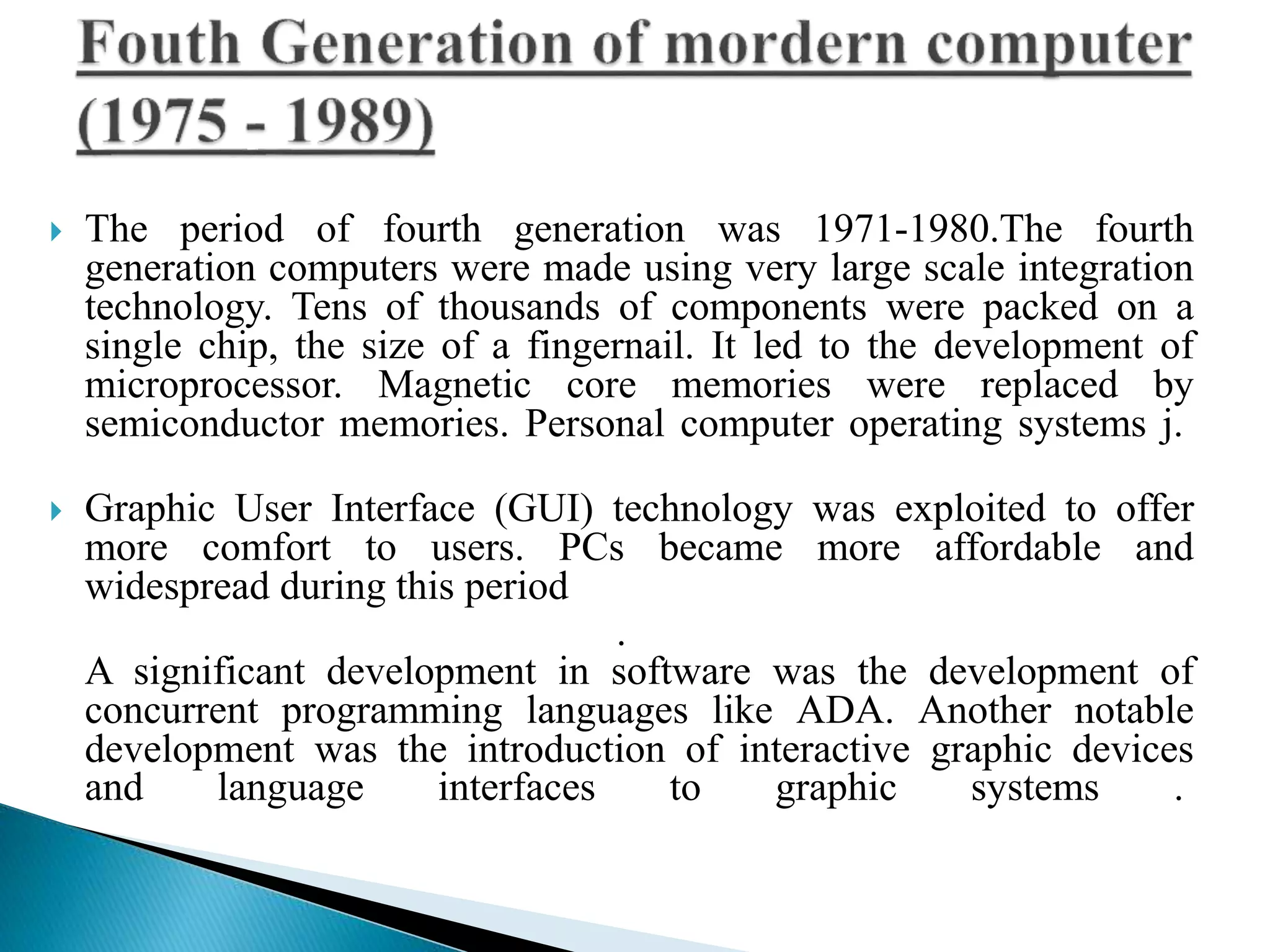
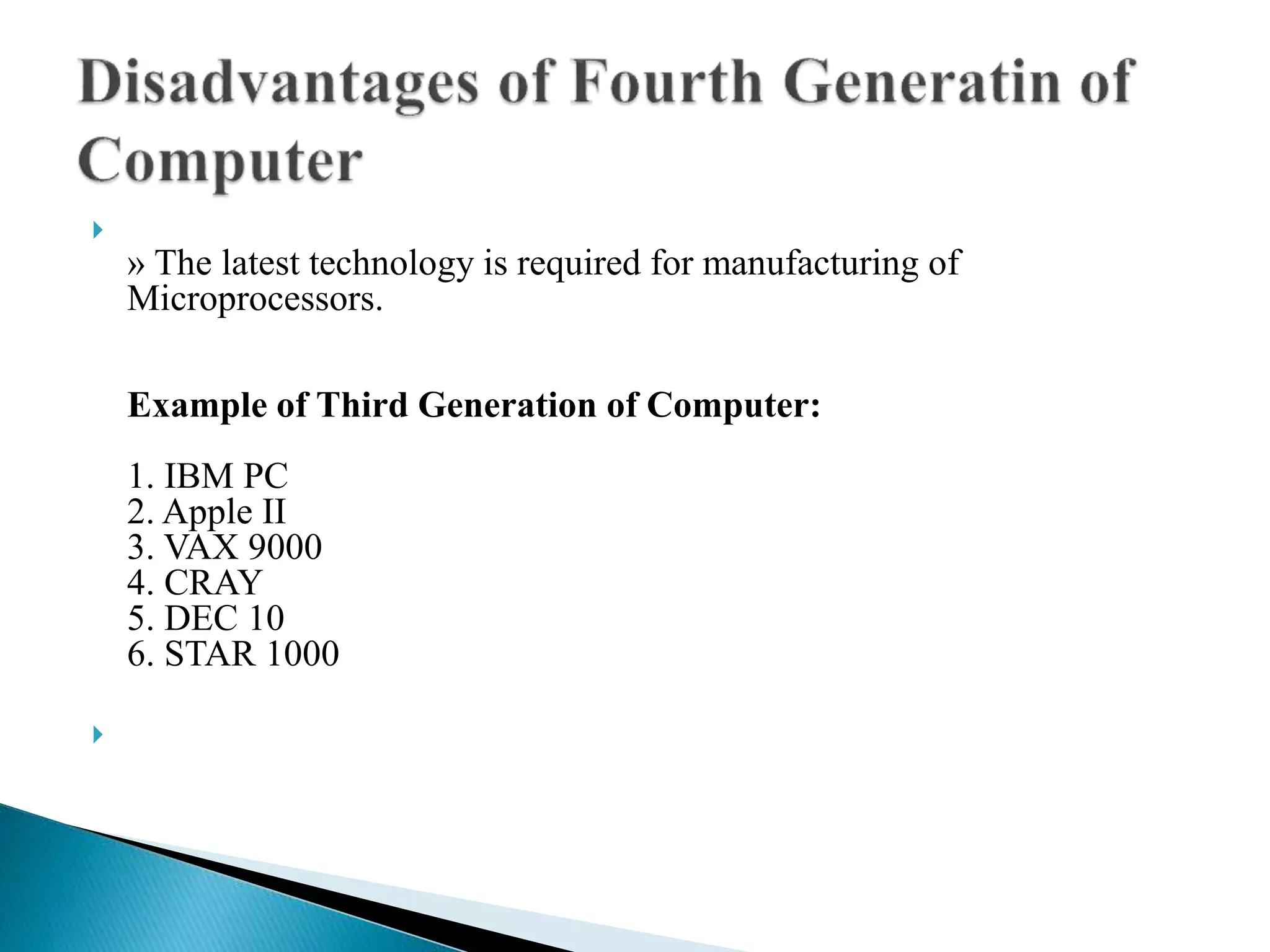
The document discusses the five generations of computers from 1946 to present. Each generation is distinguished by the type of switching circuits used and improvements in size, speed, reliability and capabilities. The first generation used vacuum tubes, the second used transistors, the third used integrated circuits, the fourth used microprocessors, and the fifth aims to develop true artificial intelligence using parallel processing. Each generation saw improvements in performance, cost, and applicability of computers.