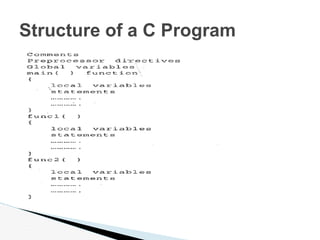
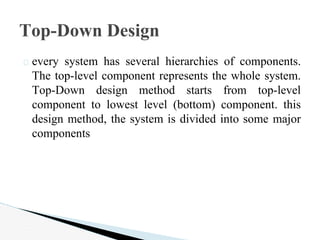
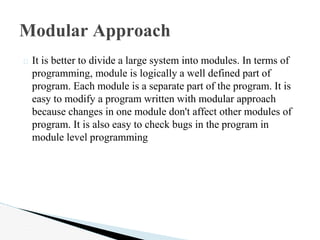
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, including its history, characteristics, and structure. It discusses how C was developed in the 1970s at Bell Labs to program the UNIX operating system. It also summarizes key aspects of C like it being a middle-level language suitable for both systems and applications programming, its use of control structures for selection, repetition and loops, and its portability across operating systems.