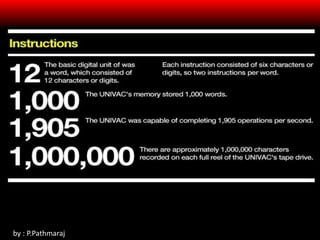
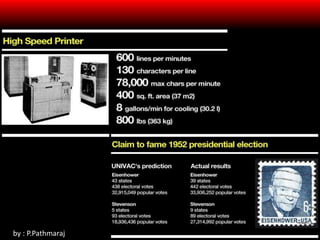
Mainframes first appeared in the 1940s and were large, powerful computers used by organizations for critical applications. They had reliability, capacity for high volumes of data, and ability to host multiple operating systems. In the 1950s and 1960s, mainframes like UNIVAC and IBM 360 drove commercial use and timesharing. Minicomputers like DEC's PDP series beginning in 1960 were smaller and cheaper alternatives. The IBM 360 was the first mainframe to support advanced functions and widespread business/government use through the 1960s.