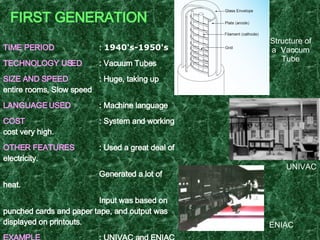
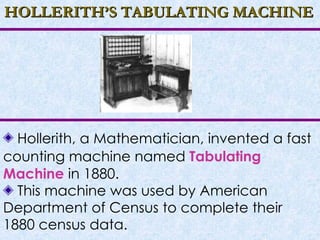
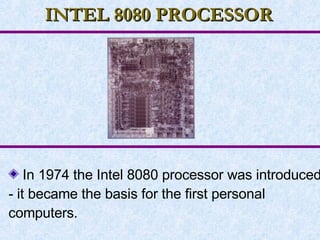
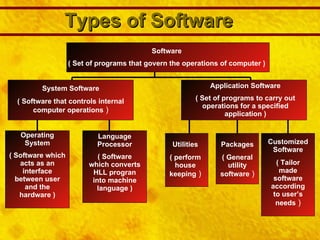
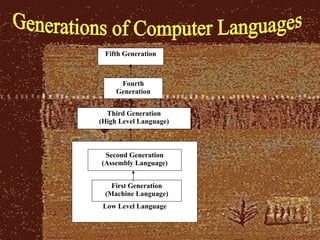
The document provides an overview of computer systems, including definitions, characteristics, hardware and software components, operating systems, and the evolution of computers through different generations. It discusses how computers have become faster, more powerful and efficient over time as the underlying technologies have advanced from vacuum tubes to integrated circuits and microprocessors. The document also summarizes the key features of different types of computers like supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, and personal computers.