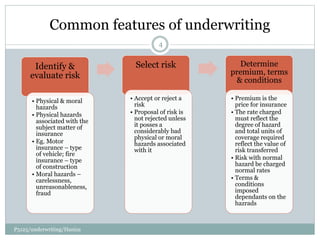
This document discusses the principles and process of underwriting in insurance. It defines underwriting as assessing and selecting risks to determine premiums, terms, and conditions. The key purposes of underwriting are to guard against applicants with high probability of loss and to charge premiums commensurate with risk. Common underwriting features include identifying hazards, selecting risks, and setting premiums, terms, and conditions accordingly. Risks with abnormal hazards may be accepted with risk improvements, warranties, exclusions, restricted coverage, excesses, or franchises. Premiums are set using individual, class, or merit rates and cover expected claims costs plus expenses.