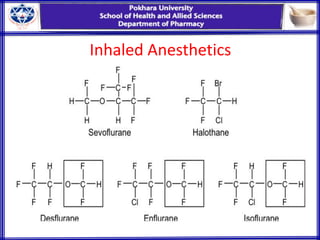
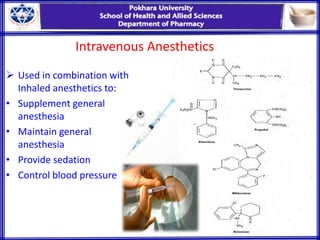
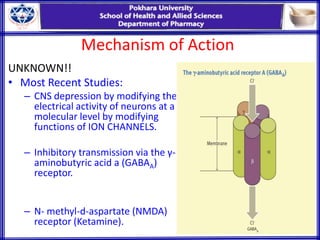
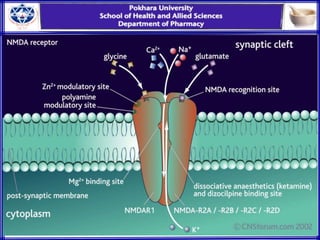
General anesthesia involves reversible loss of consciousness and sensation. It has allowed for modern surgery by creating patient comfort, immobility, and amnesia. The first widely used anesthetics were ether and chloroform in the 1840s. An ideal anesthetic has favorable physical properties like non-flammability and biological properties like rapid onset and offset without side effects. Anesthetics are classified as inhaled gases, volatile liquids, or intravenous agents. Their mechanism of action involves modifying ion channels in the central nervous system, especially GABA receptors. Stages of anesthesia include induction, excitement, surgical anesthesia, and potentially lethal medullary paralysis. Complications can occur during or after anesthesia and include respiratory depression, arrhythmias,