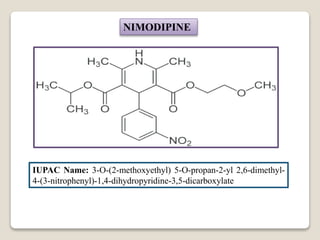
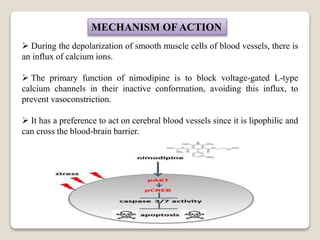
Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) are medications that lower blood pressure by preventing calcium from entering heart and arterial cells, leading to vessel relaxation and reduced heart contraction strength. Examples include amlodipine, diltiazem, and nifedipine, which are used to treat conditions like hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias. CCBs are available in short-acting and long-acting forms, affecting their duration of action.


![VERAPAMIL
IUPAC Name: 2-(3, 4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-[2-(3, 4-
dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl-methylamino]-2-propan-2-ylpentanenitrile](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calciumchannelblockers-200908054354/85/Calcium-channel-blockers-4-320.jpg)
![USES
Verapamil is used to treat high blood pressure and to
control angina (chest pain).
It is also used to treatment cerebral vasospasm and in cluster headache.
BEPRIDIL HYDROCHLORIDE
IUPAC Name: N-benzyl-N-
[3-(2-methylpropoxy)-2-
pyrrolidin-1-ylpropyl] aniline;
hydrochloride](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calciumchannelblockers-200908054354/85/Calcium-channel-blockers-6-320.jpg)
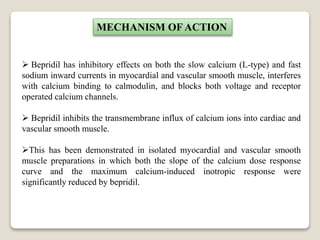
![USES
Bepridil (trade name Vascor) is an amine calcium channel blocker once used to
treat angina.
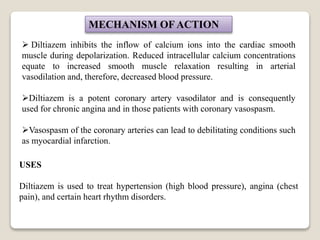
DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE
IUPAC Name: [(2S, 3S)-5-[2-
(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2-(4-
methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3-
dihydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-3-yl]
acetate; hydrochloride](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calciumchannelblockers-200908054354/85/Calcium-channel-blockers-8-320.jpg)
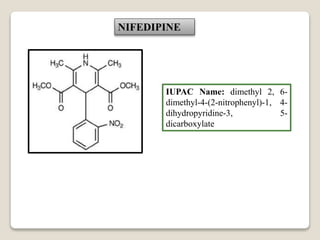

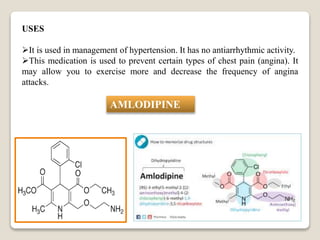
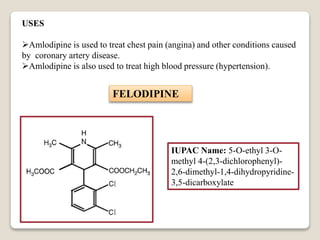

![NICARDDIPINE
IUPAC Name: 5-O-[2-[benzyl
(methyl) amino] ethyl] 3-O-methyl
2, 6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,
4-dihydropyridine-3, 5-
dicarboxylate; hydrochloride
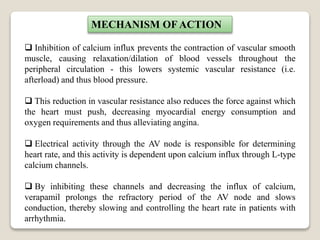
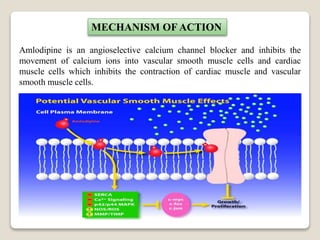
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Nicardipine hydrochloride capsules are a calcium entry blocker (slow
channel blocker or calcium ion antagonist) that inhibits the transmembrane
influx of calcium ions into cardiac muscle and smooth muscle without
changing serum calcium concentrations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calciumchannelblockers-200908054354/85/Calcium-channel-blockers-16-320.jpg)