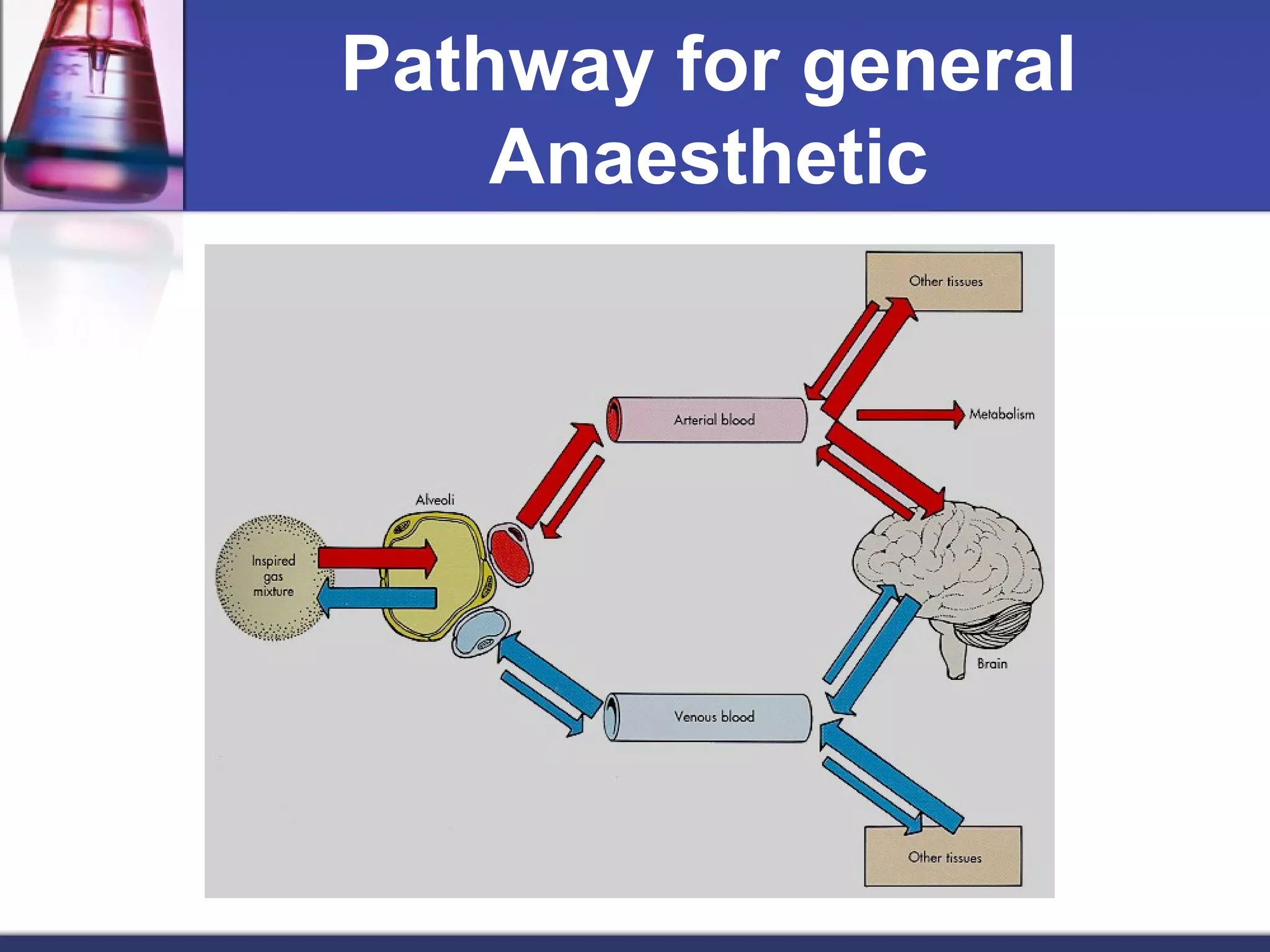
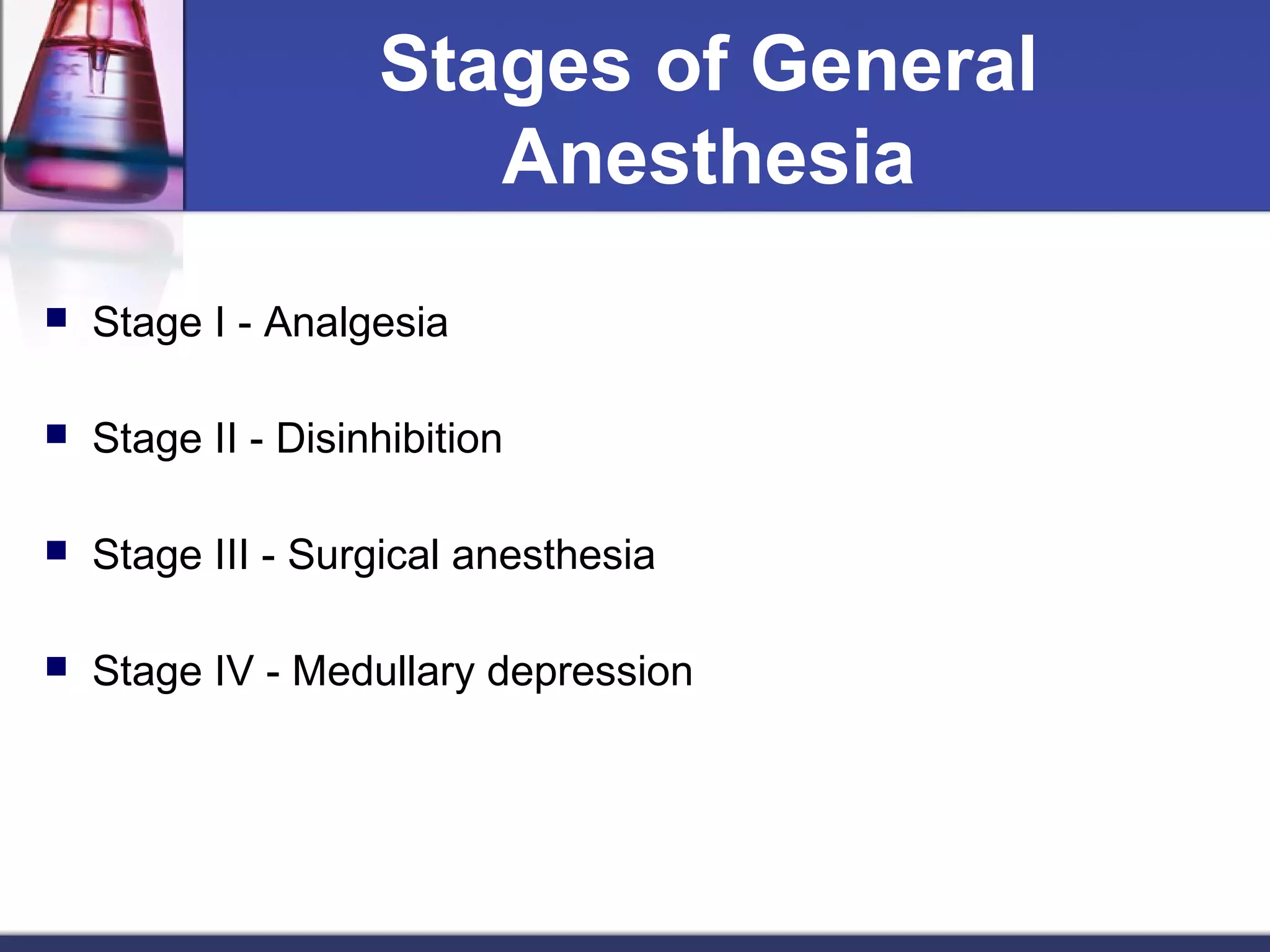
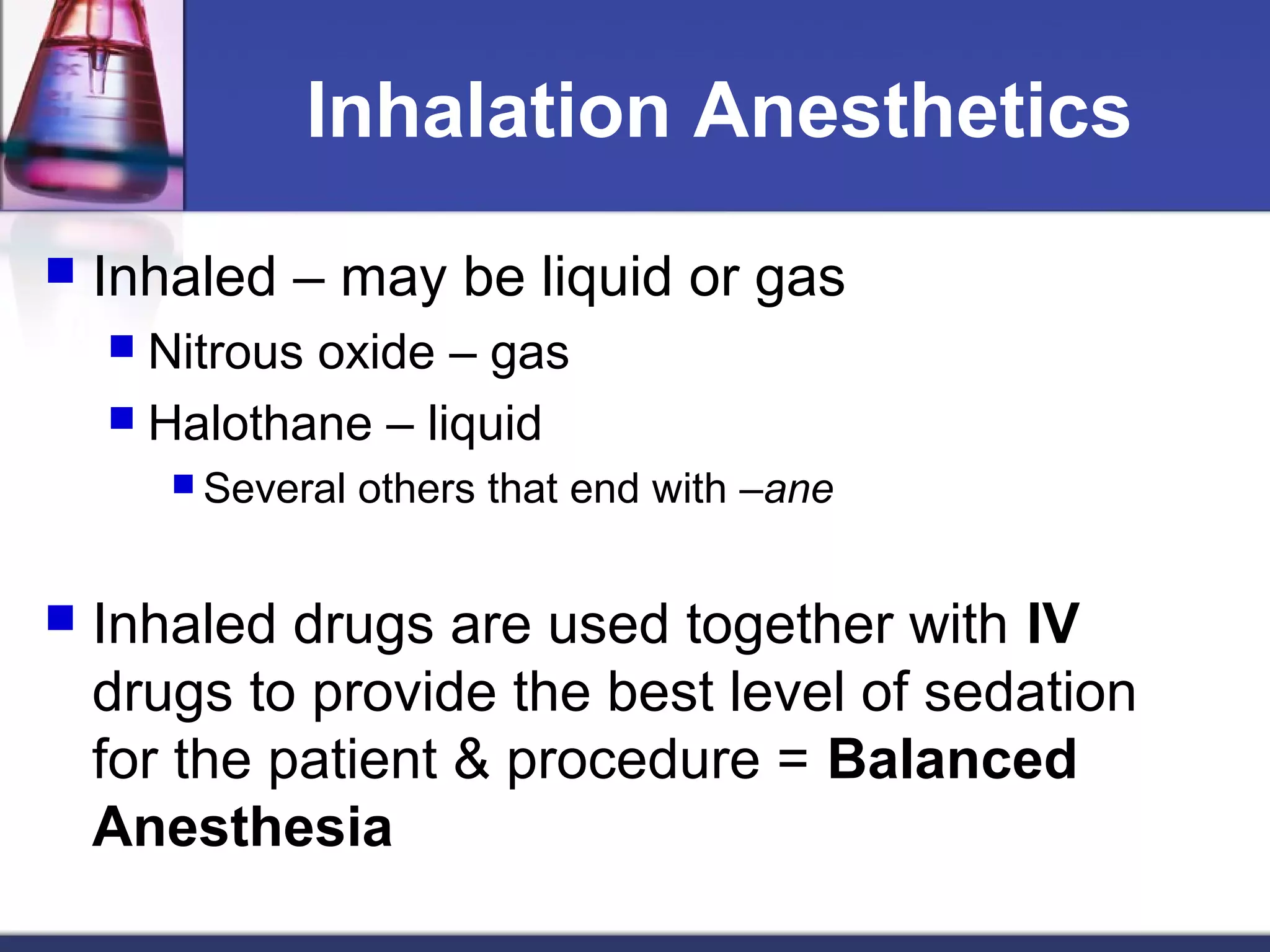
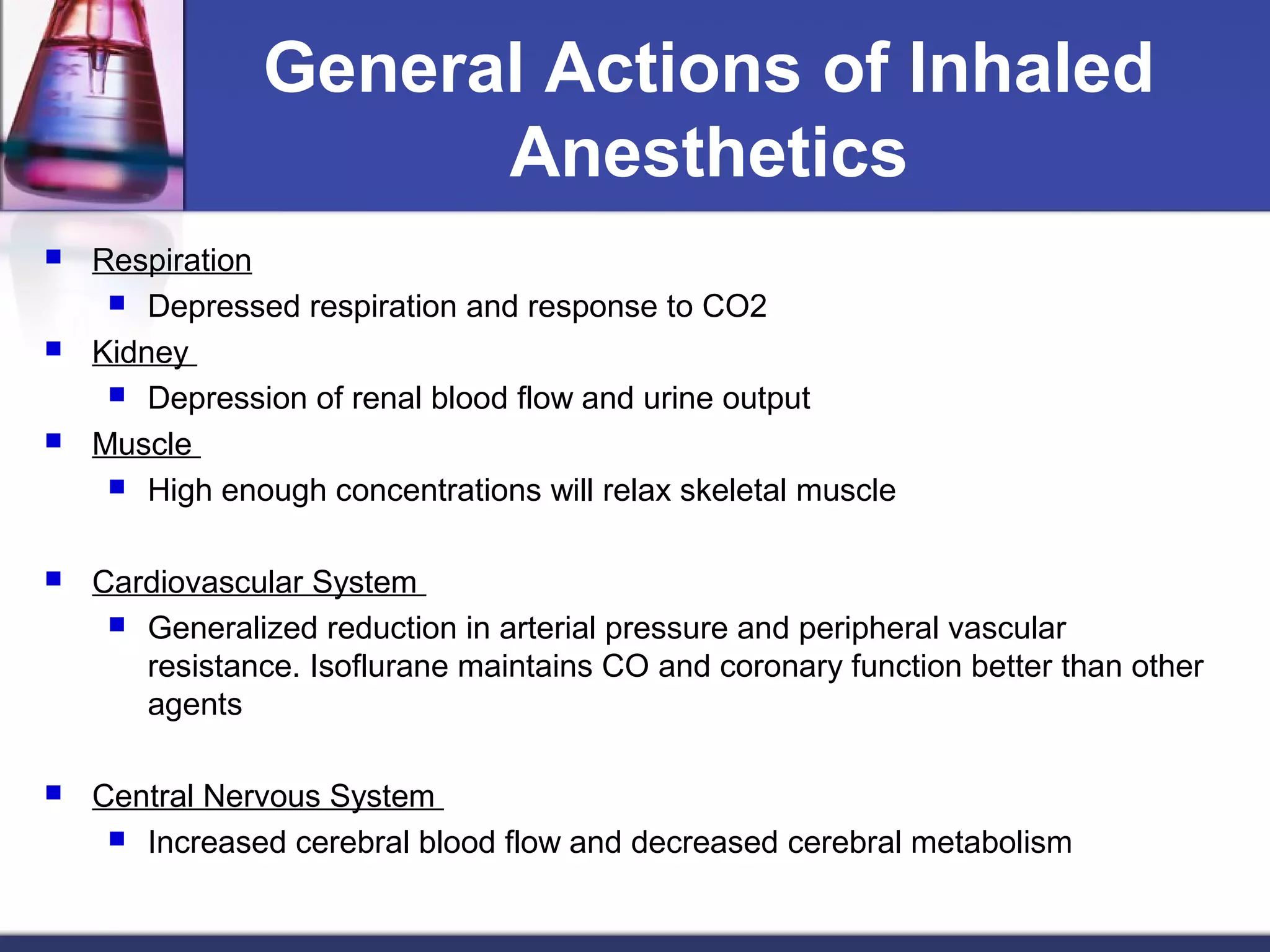
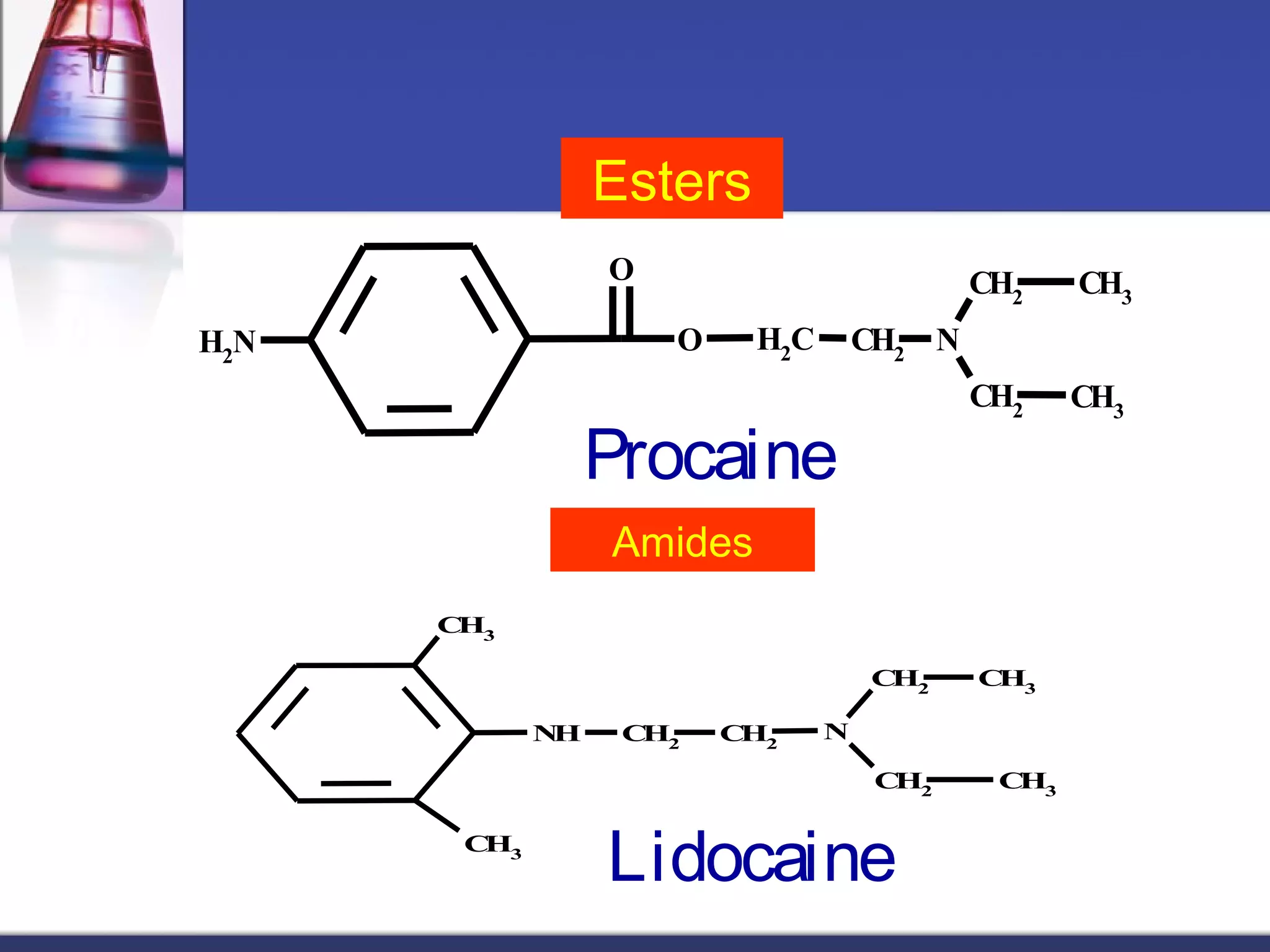
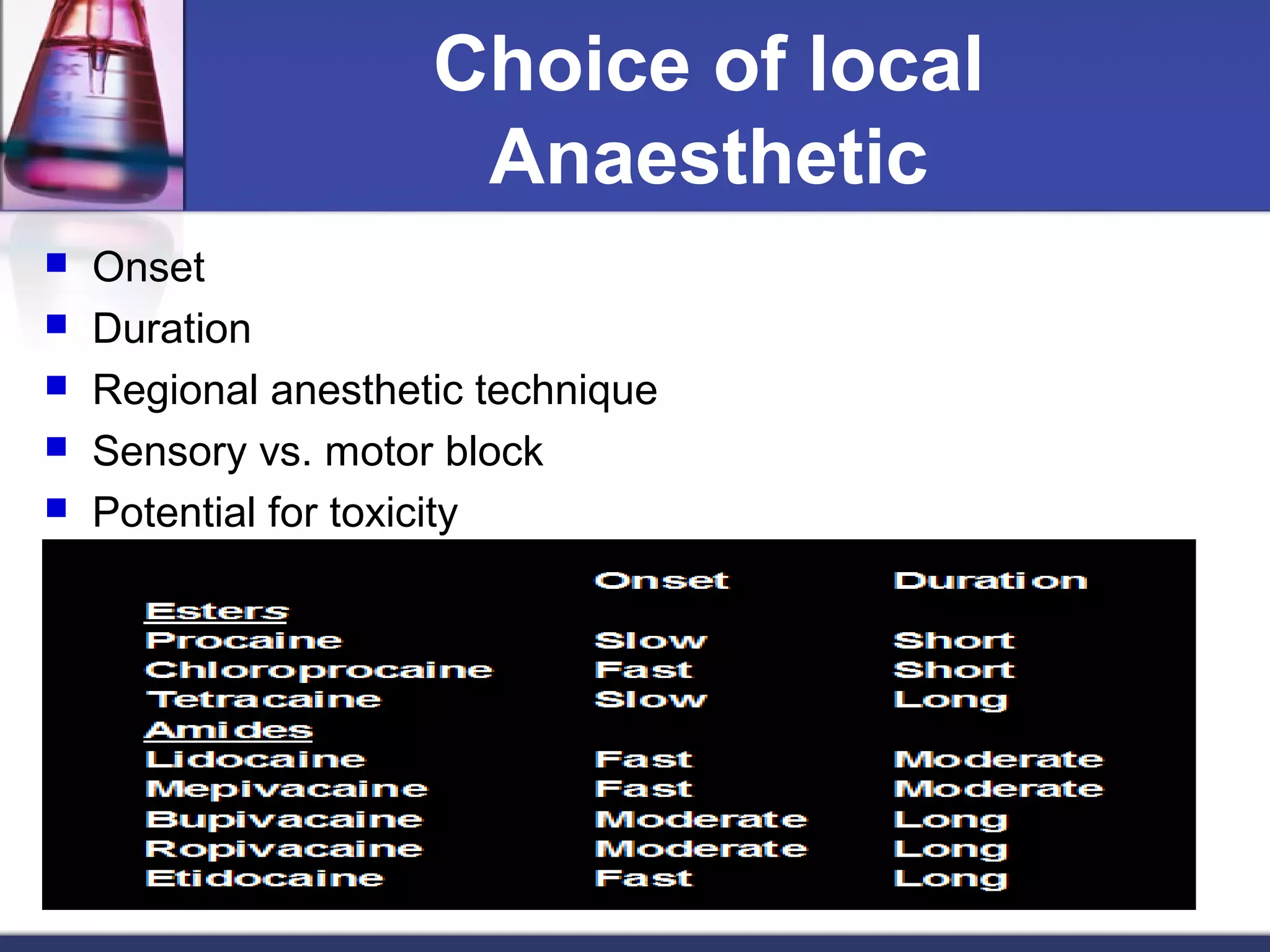
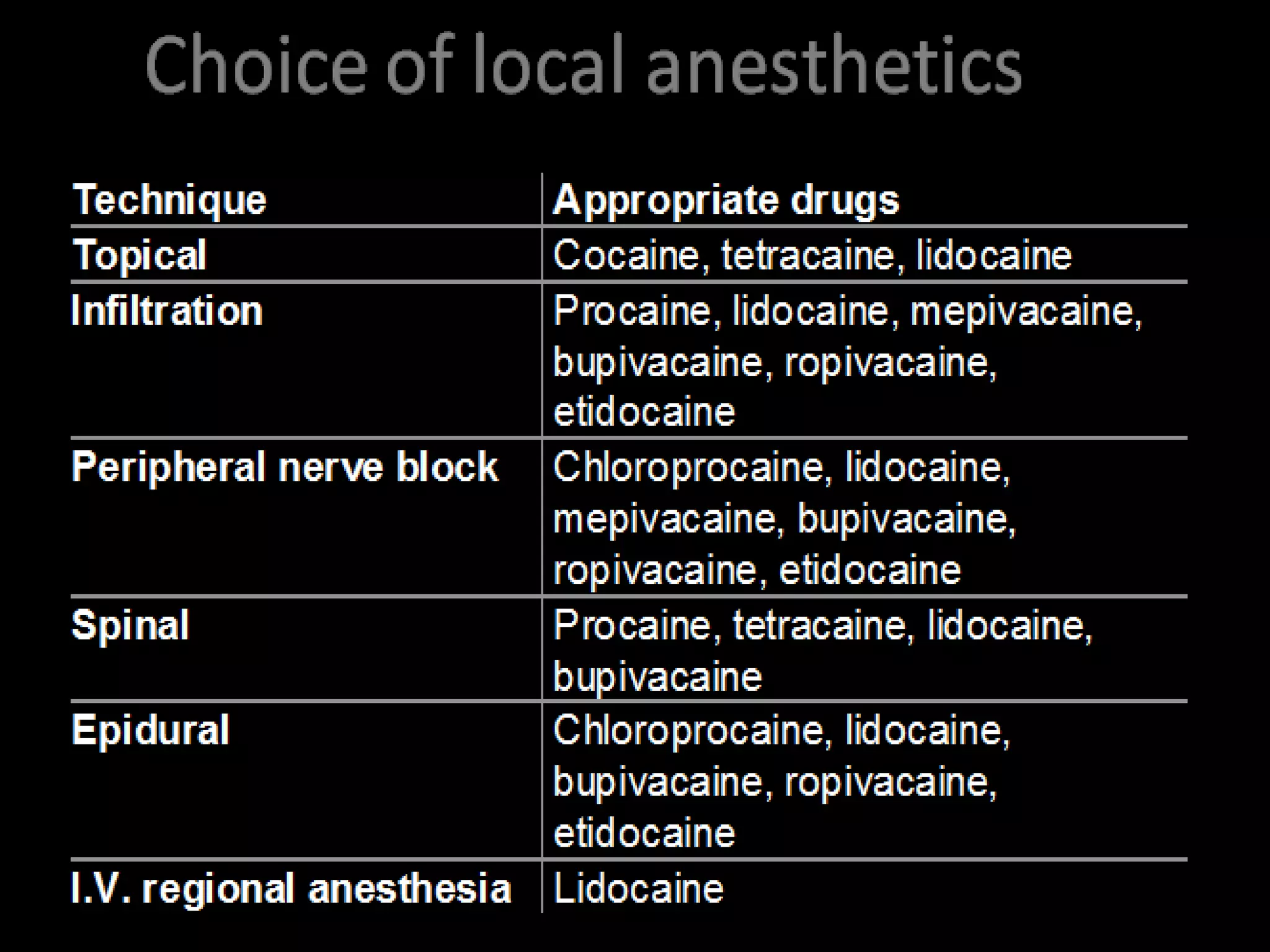
General anesthetics cause reversible loss of consciousness through pain relief, muscle relaxation, relaxation of reflexes, and induced deep sleep. They are commonly used during surgery. There are four stages of general anesthesia: analgesia, disinhibition, surgical anesthesia, and medullary depression. The main categories of anesthetics are inhalation agents (gases or vapors, usually halogenated) and intravenous agents (injections of anesthetics or induction agents). Inhalation anesthetics are inhaled as liquids or gases and act by activating potassium channels and blocking sodium channels. Intravenous anesthetics like propofol and thiopental sodium exert their actions by potentiating GABA-A receptors. Both inhalation and