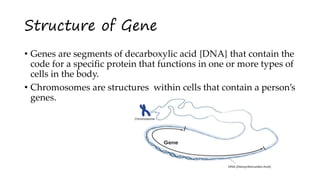
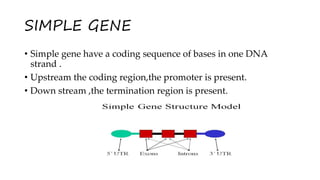
Genes are the basic physical and functional units of heredity that are made up of DNA. A gene typically consists of coding regions called exons that specify amino acid sequences, non-coding regions called introns, and regulatory sequences that determine when and where a protein is made. There are different types of genes, including simple genes with one coding sequence, variable genes where a polypeptide is coded by multiple genes, and transposon genes which are sequences of DNA that can move to different locations in the genome.








![TRANSPOSONE GENE
• Transposable elements [TEs] also known as “Jumping Genes” or
Transposons are sequence of DNA that move or jump from one
location in the genome to another.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genestructureppt-200727141009/85/Gene-structure-11-320.jpg)
