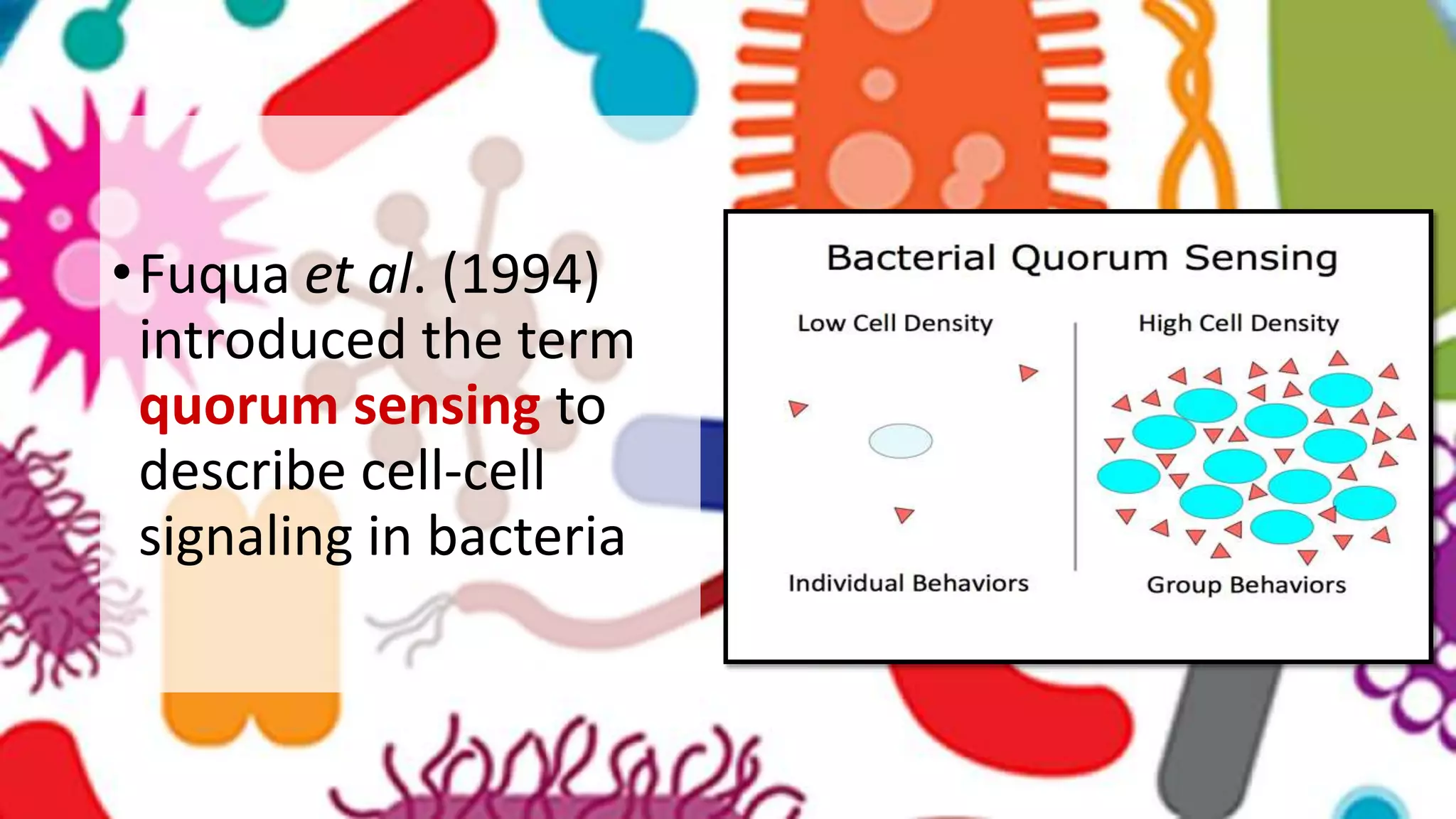
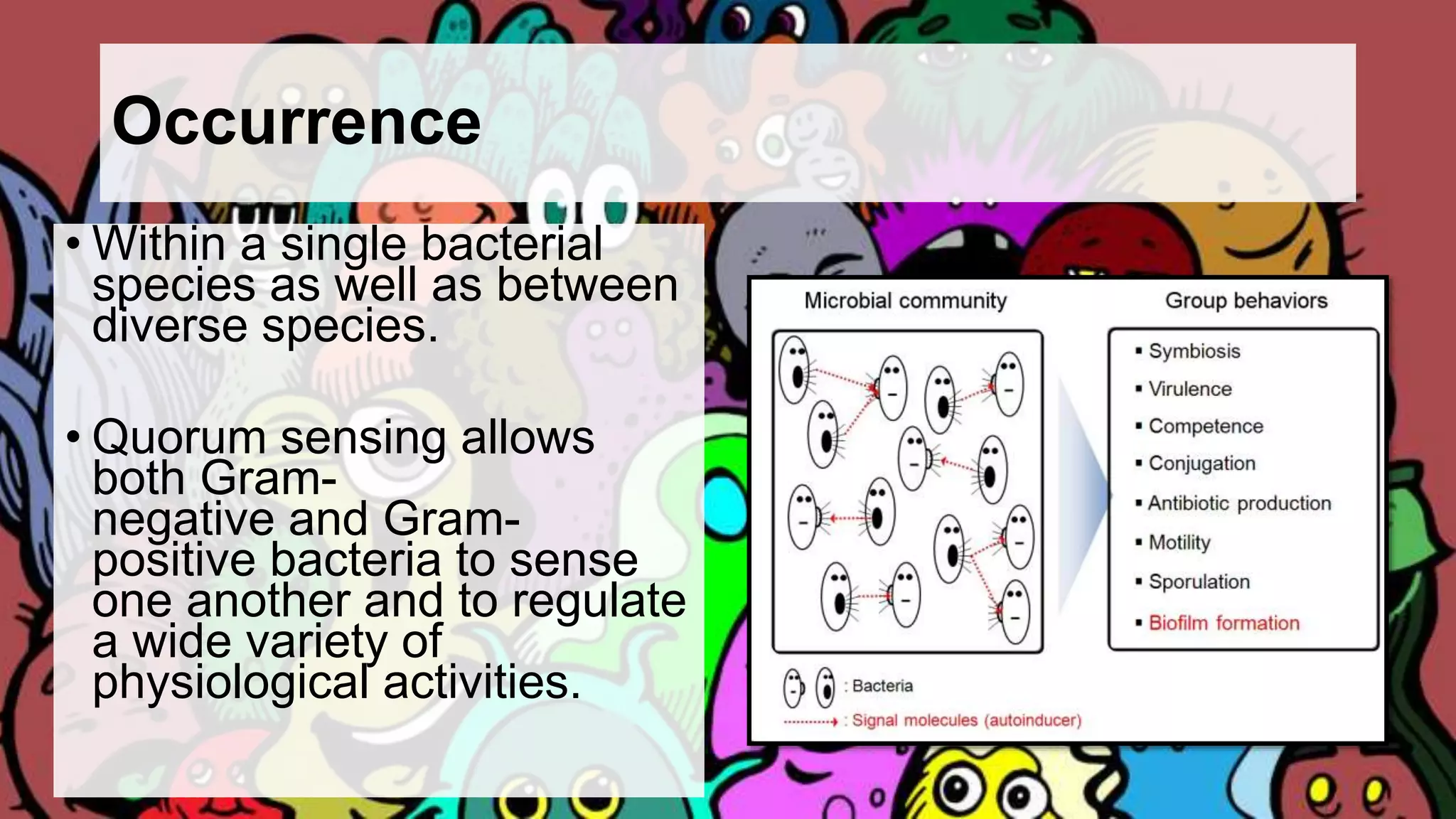
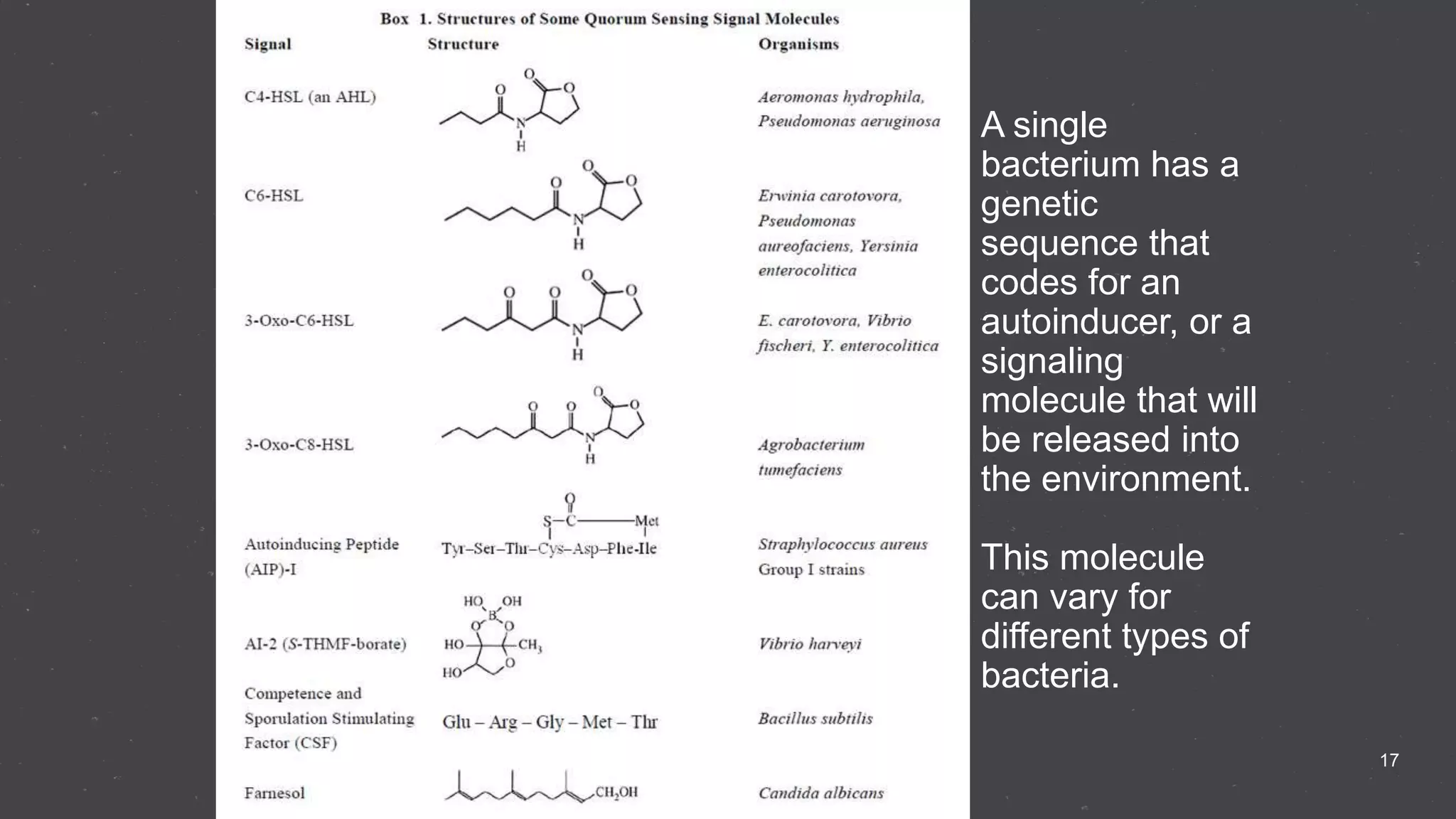
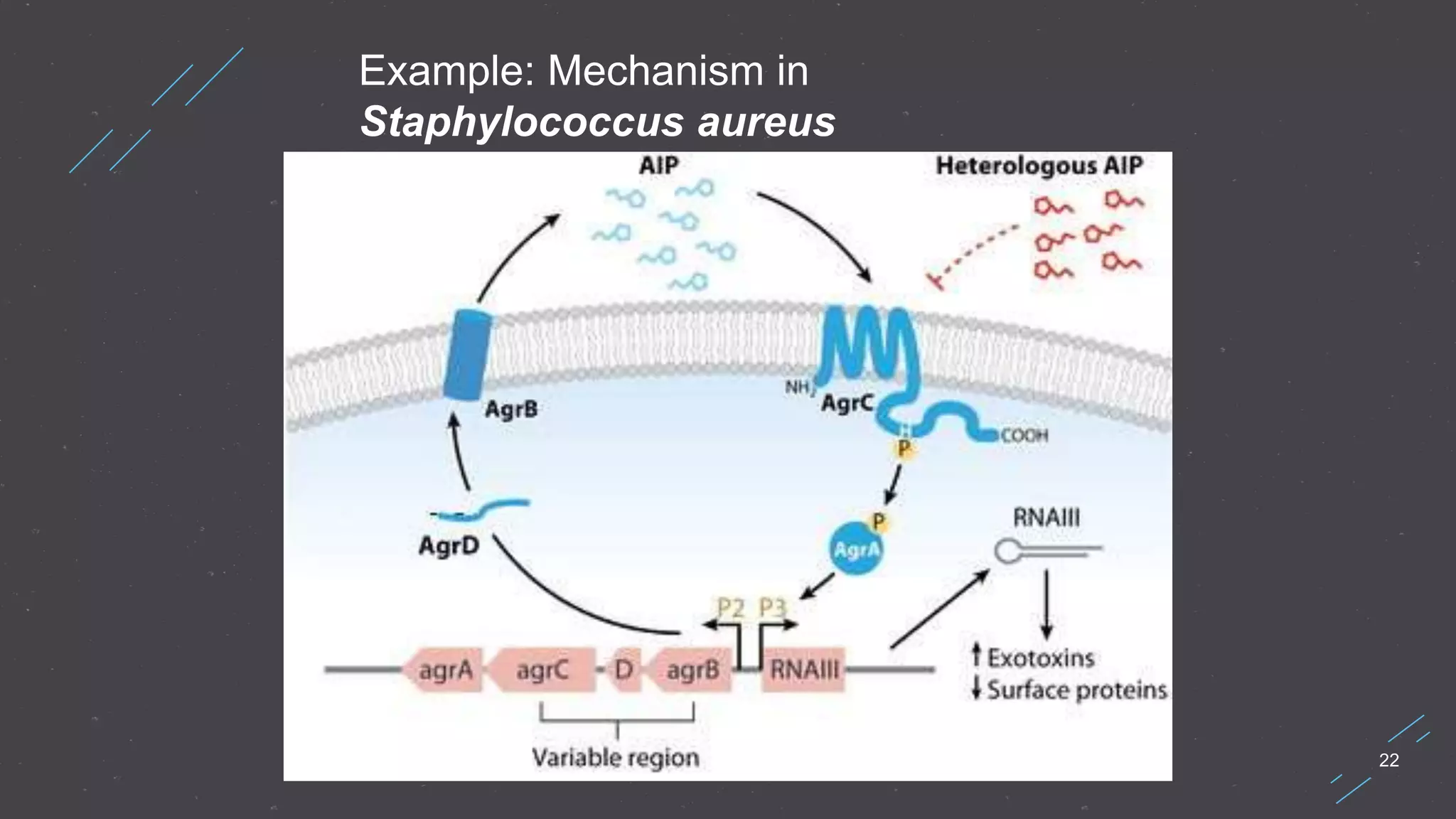
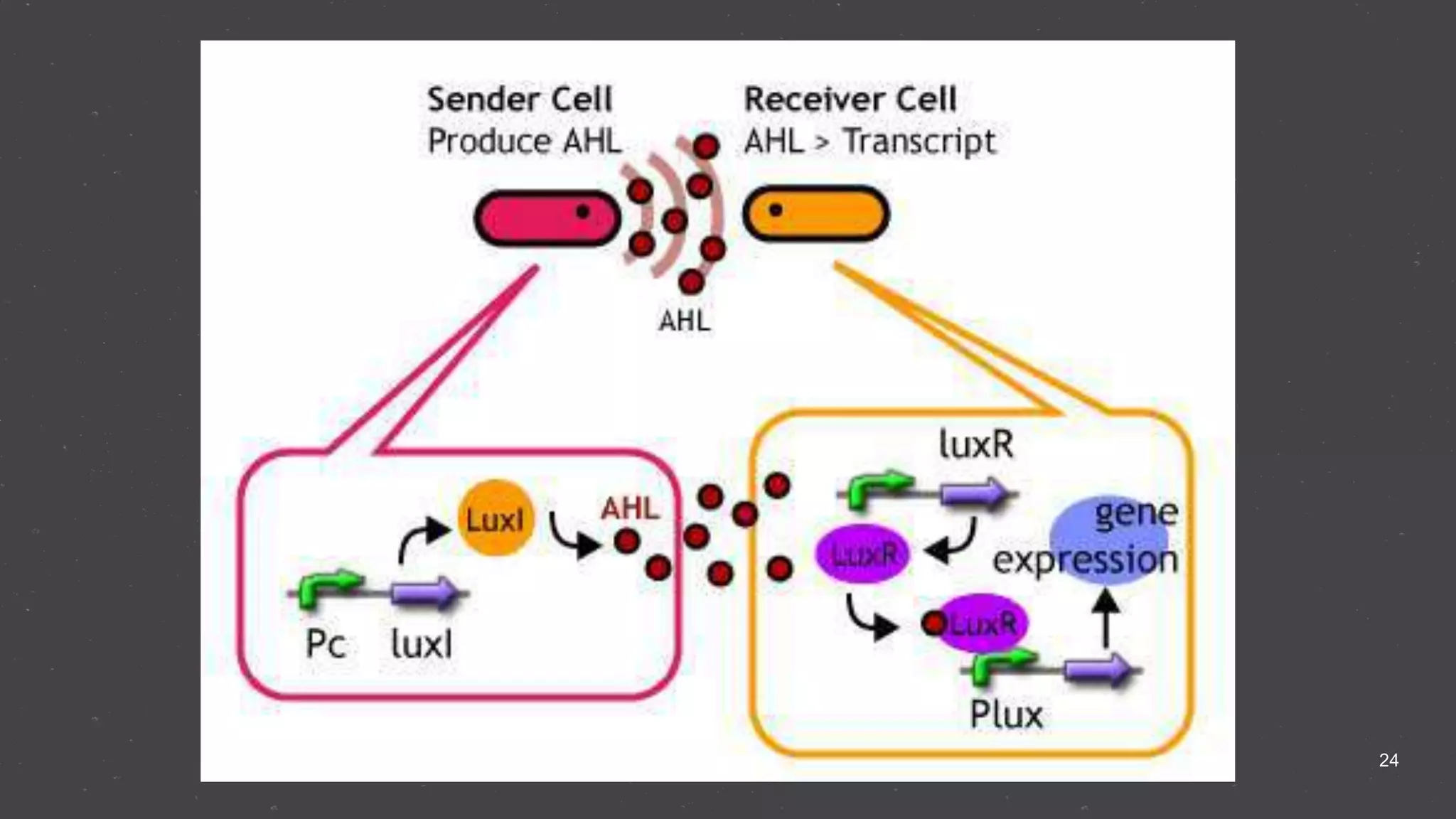
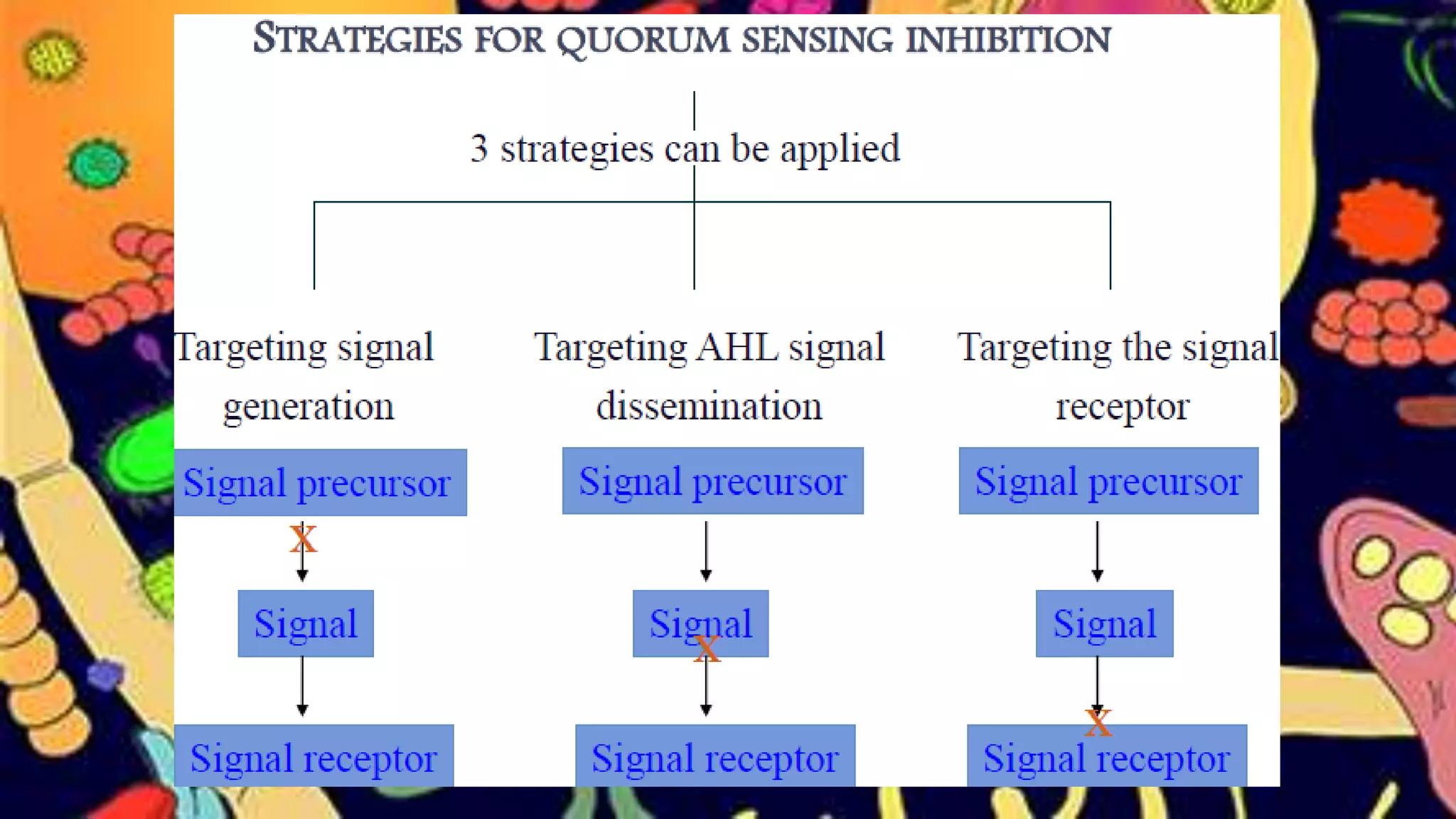
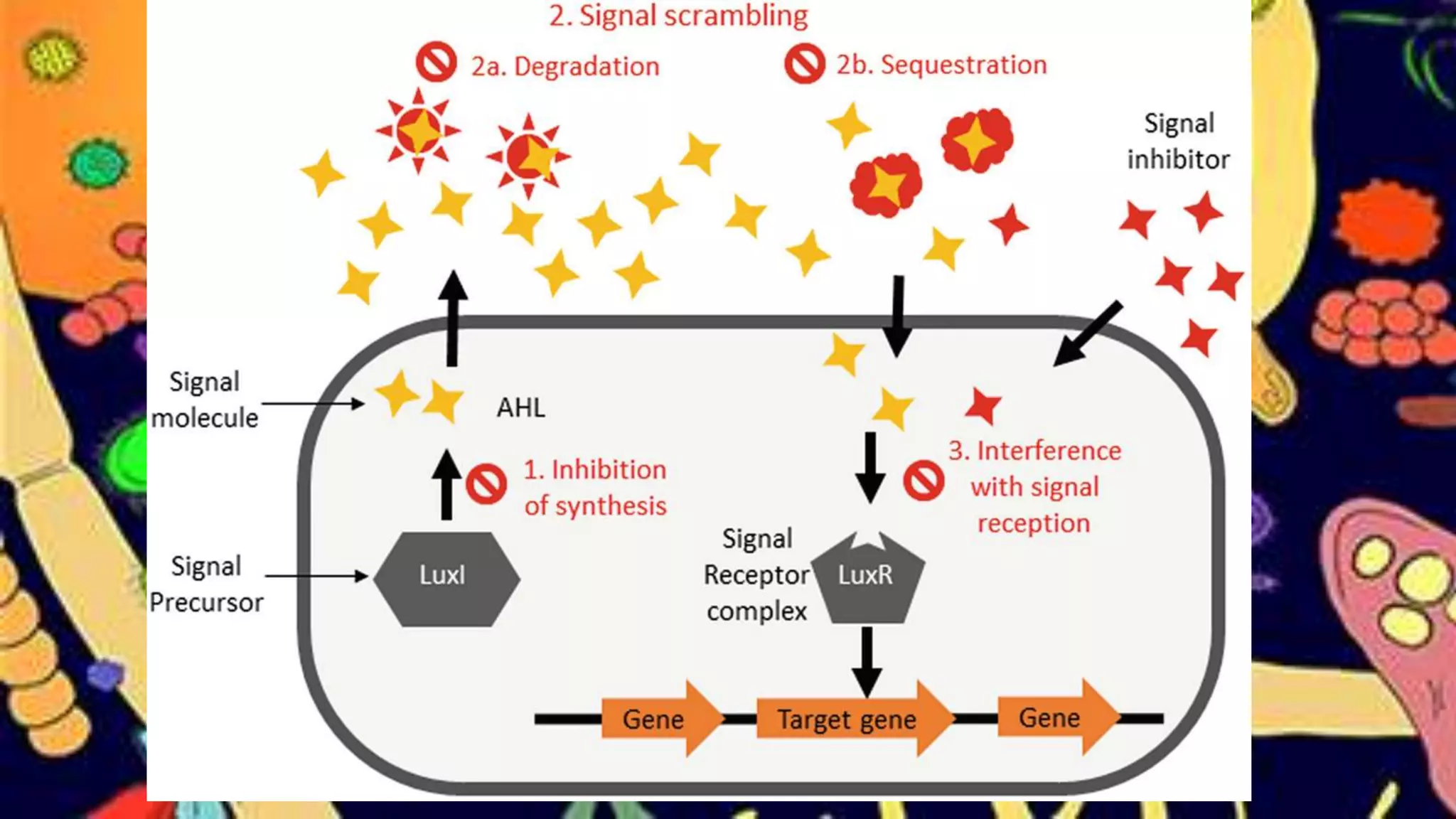
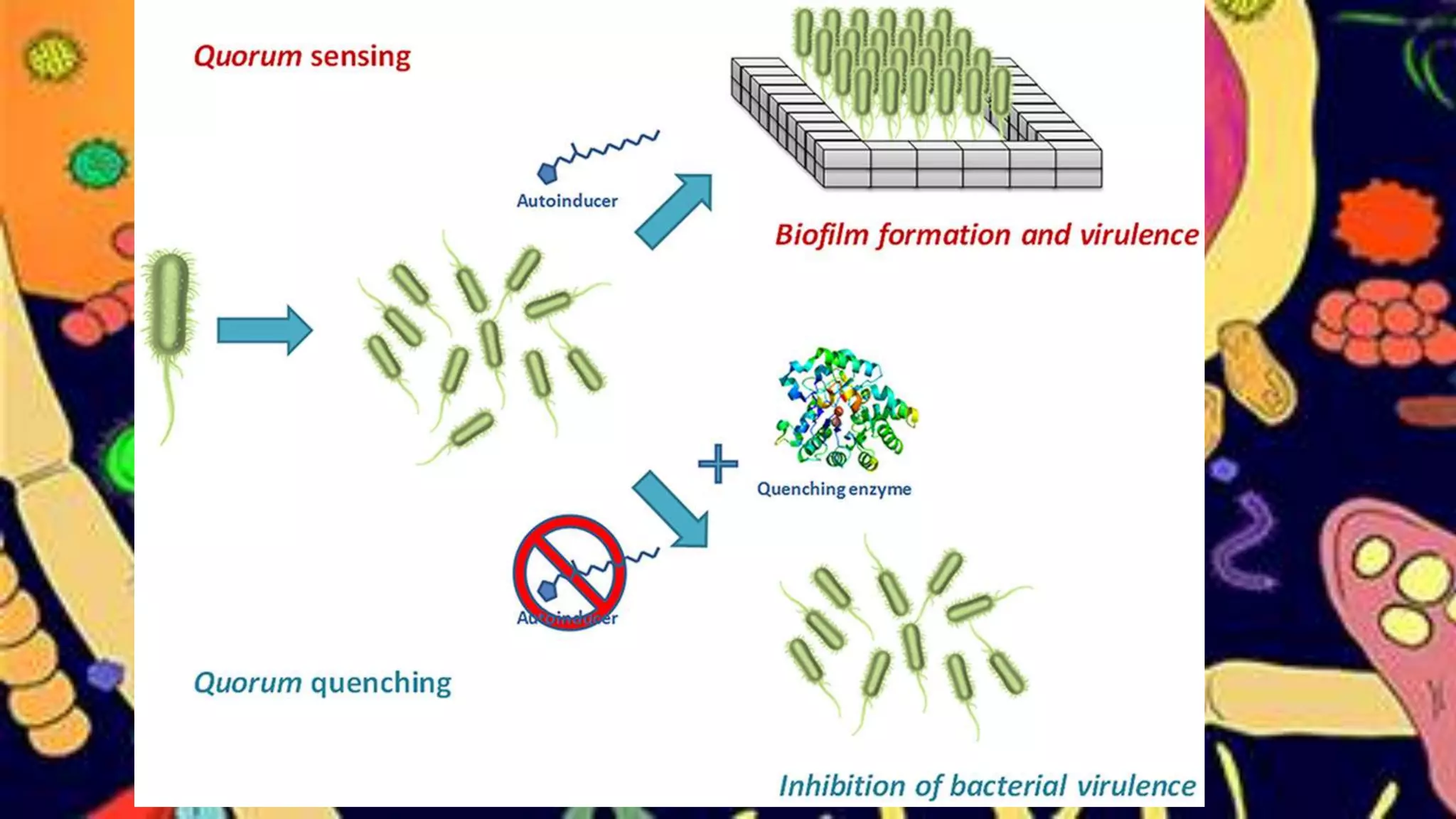
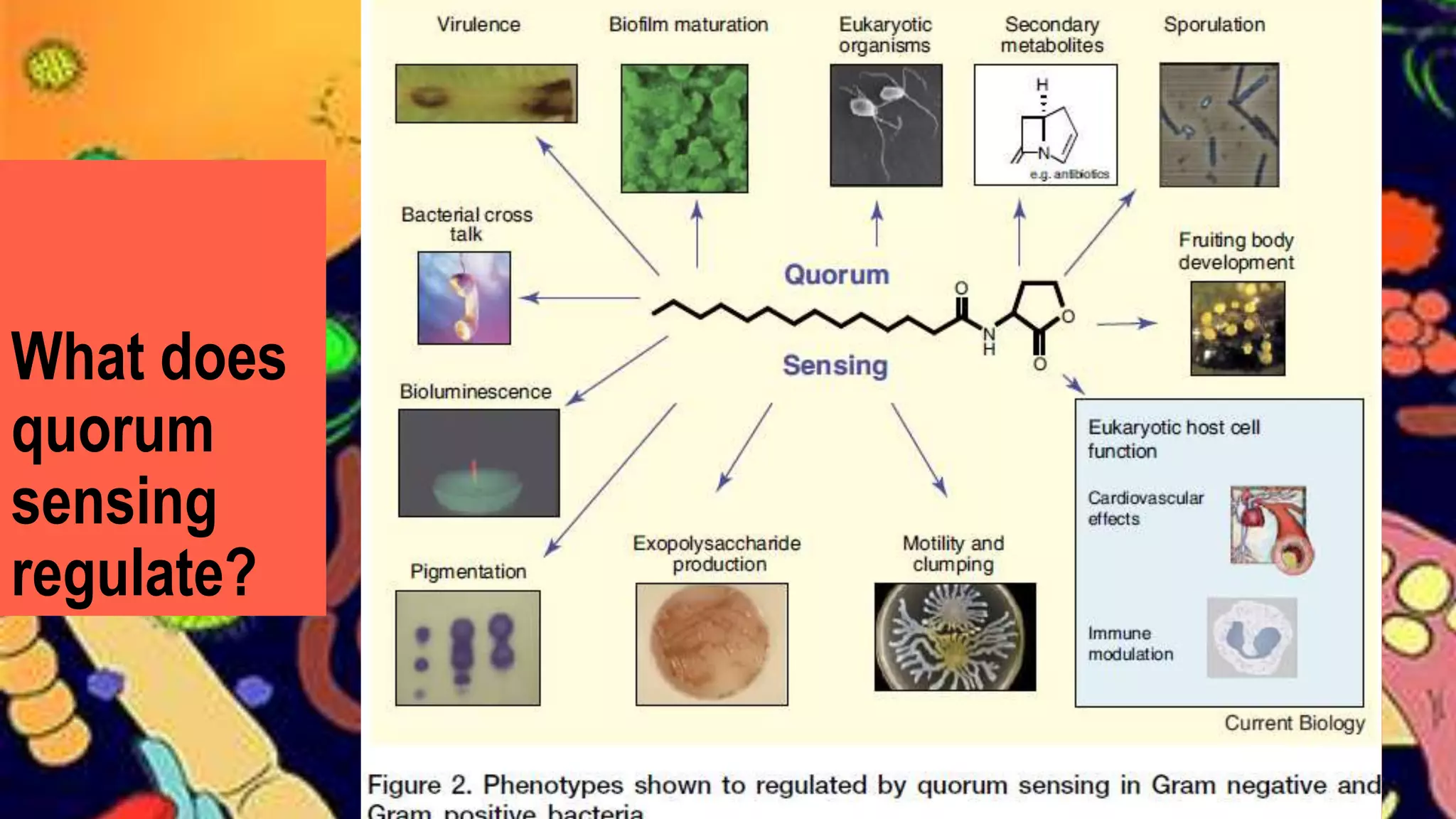
Quorum sensing is a bacterial communication process involving the production and detection of signaling molecules called autoinducers, which regulate gene expression based on bacterial population density. It allows bacteria to coordinate behaviors such as virulence and bioluminescence and occurs in both gram-negative and gram-positive species. Quorum quenching, mechanisms that disrupt this communication, can prevent pathogenic bacteria from successfully colonizing hosts.