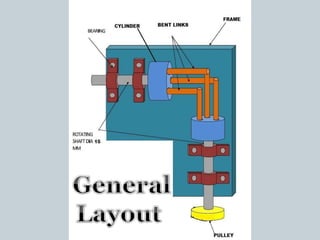
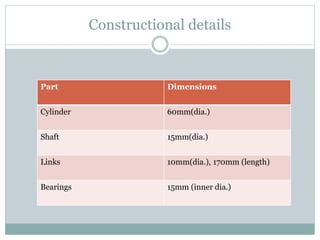
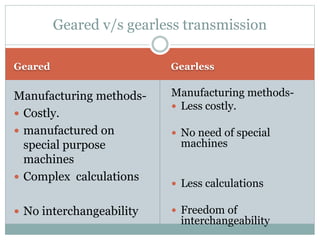
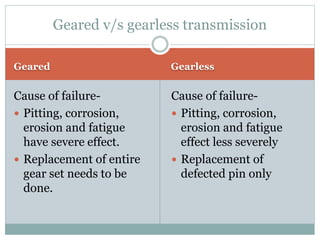
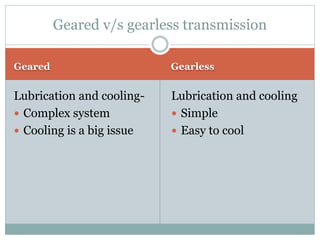
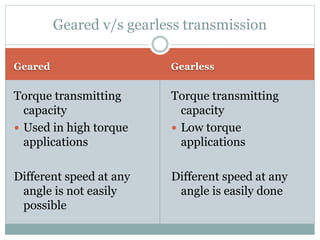
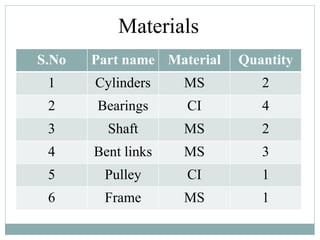
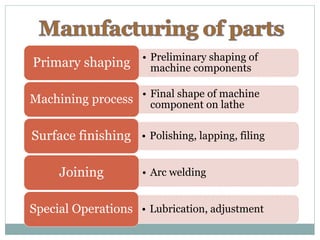
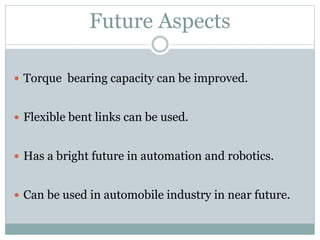
This document describes the development of a working model of a gearless transmission. It discusses the need for gearless transmission to increase efficiency. The working principle involves using bent links to transmit power between shafts at 90 degrees without using gears. Construction details and materials used are provided. Advantages include lower cost and ability to transmit power at any angle, while limitations include lower torque capacity and fixed speed ratio. Possible future applications are in automation and robotics.