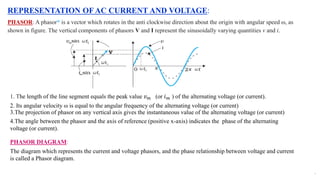
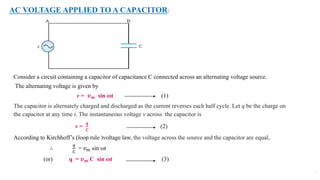
1. An alternating current leads or lags an alternating voltage by a phase angle depending on whether it is flowing through an inductor or capacitor. Current through an inductor lags voltage by 90 degrees, while current through a capacitor leads voltage by 90 degrees.
2. The average power consumed by an inductor or capacitor over one full cycle of AC is zero, since the product of the alternating current and voltage is always positive in one half cycle and negative in the other half cycle.
3. RMS values are used to calculate the effective or heating value of alternating currents and voltages, since they fluctuate between positive and negative values. The RMS value of an AC is 70.7% of its peak value.