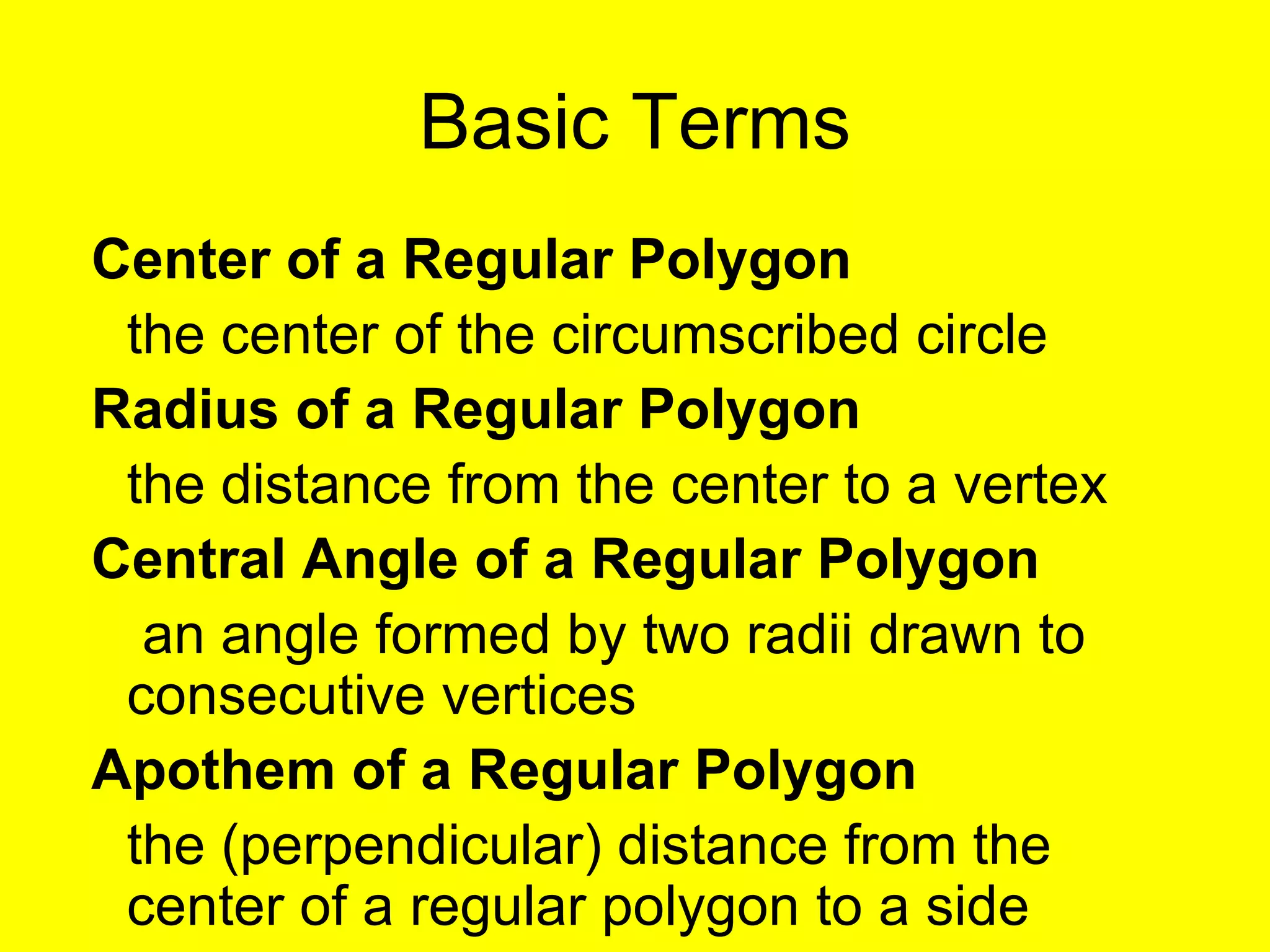
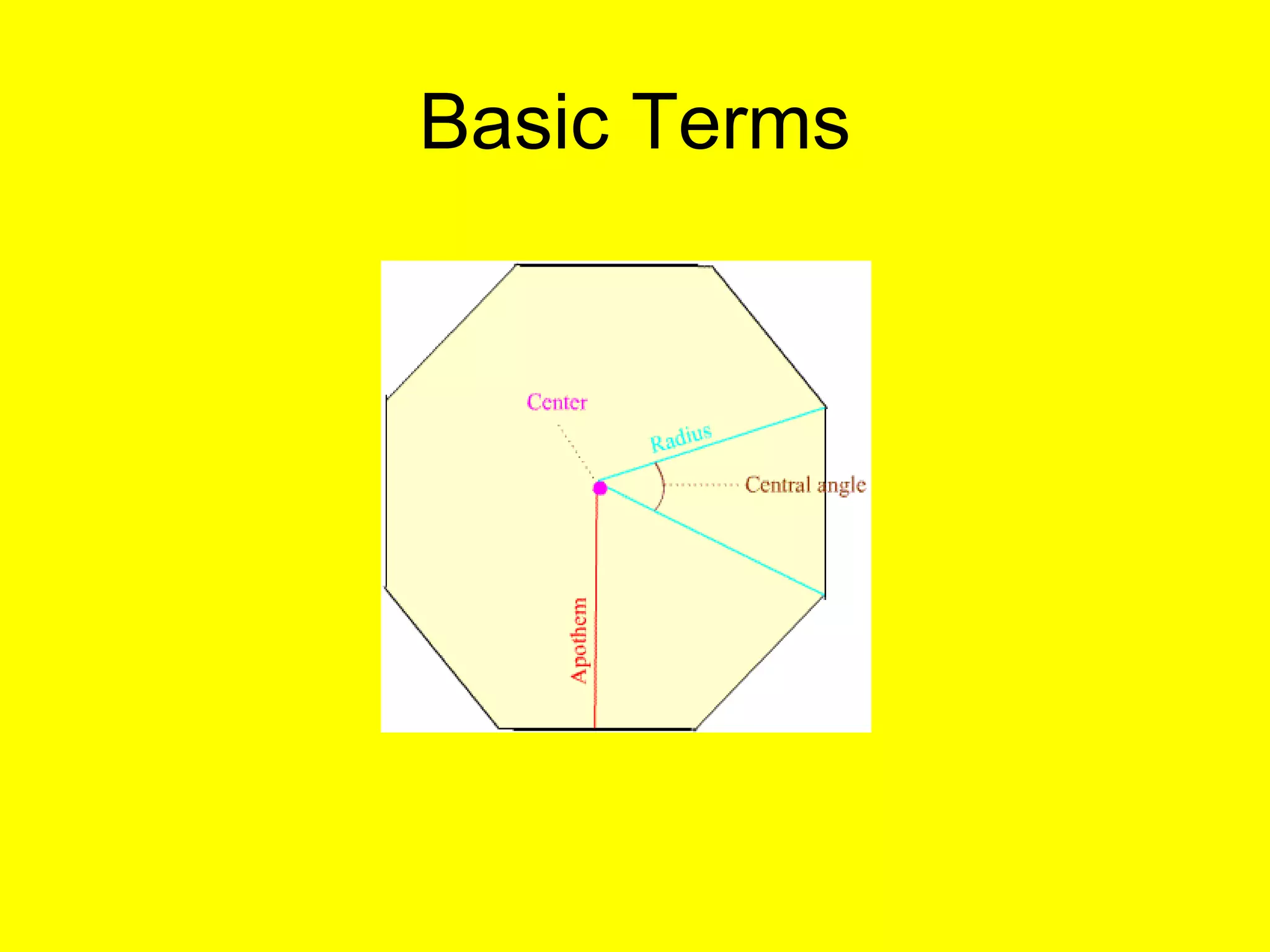
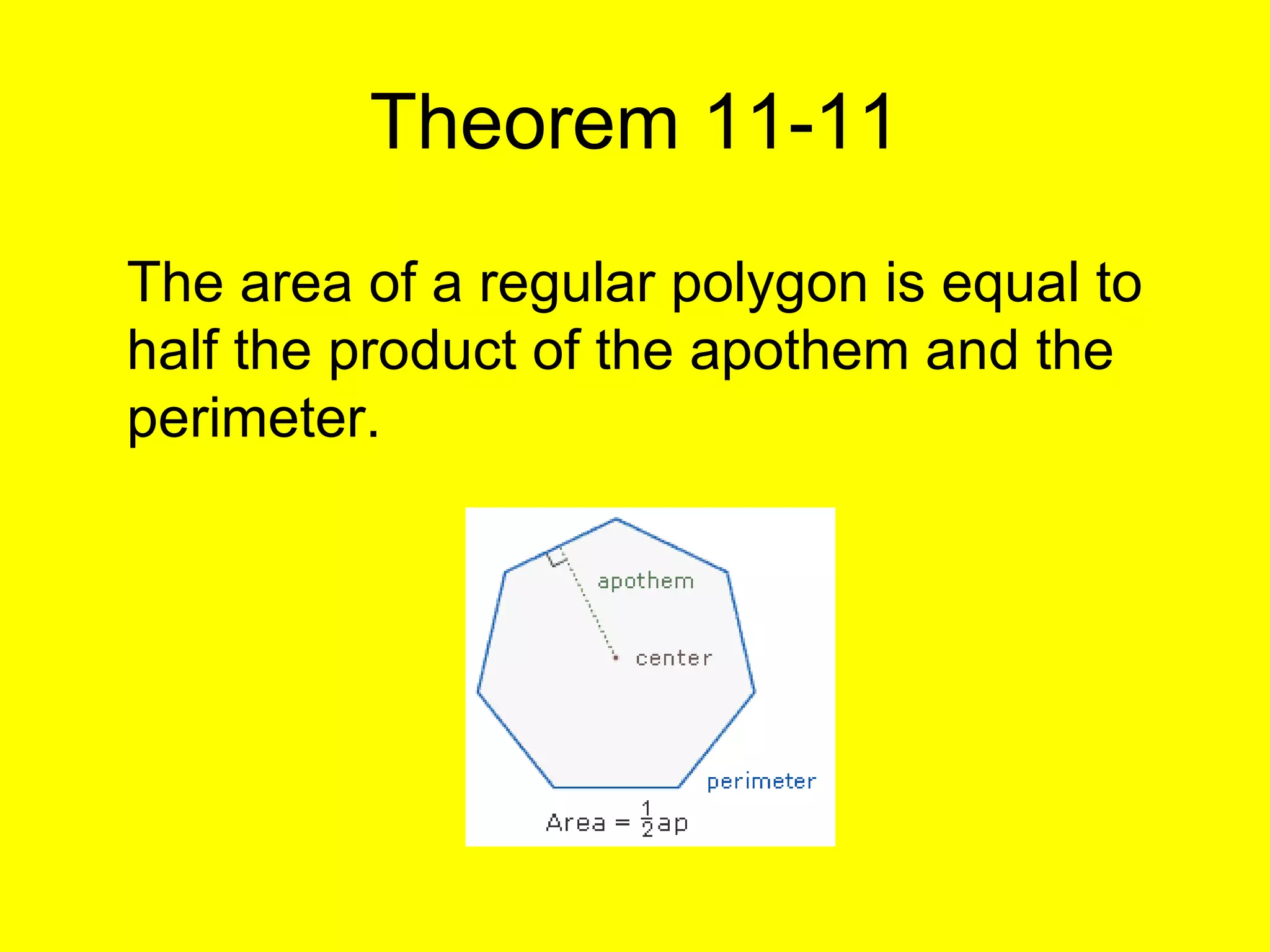
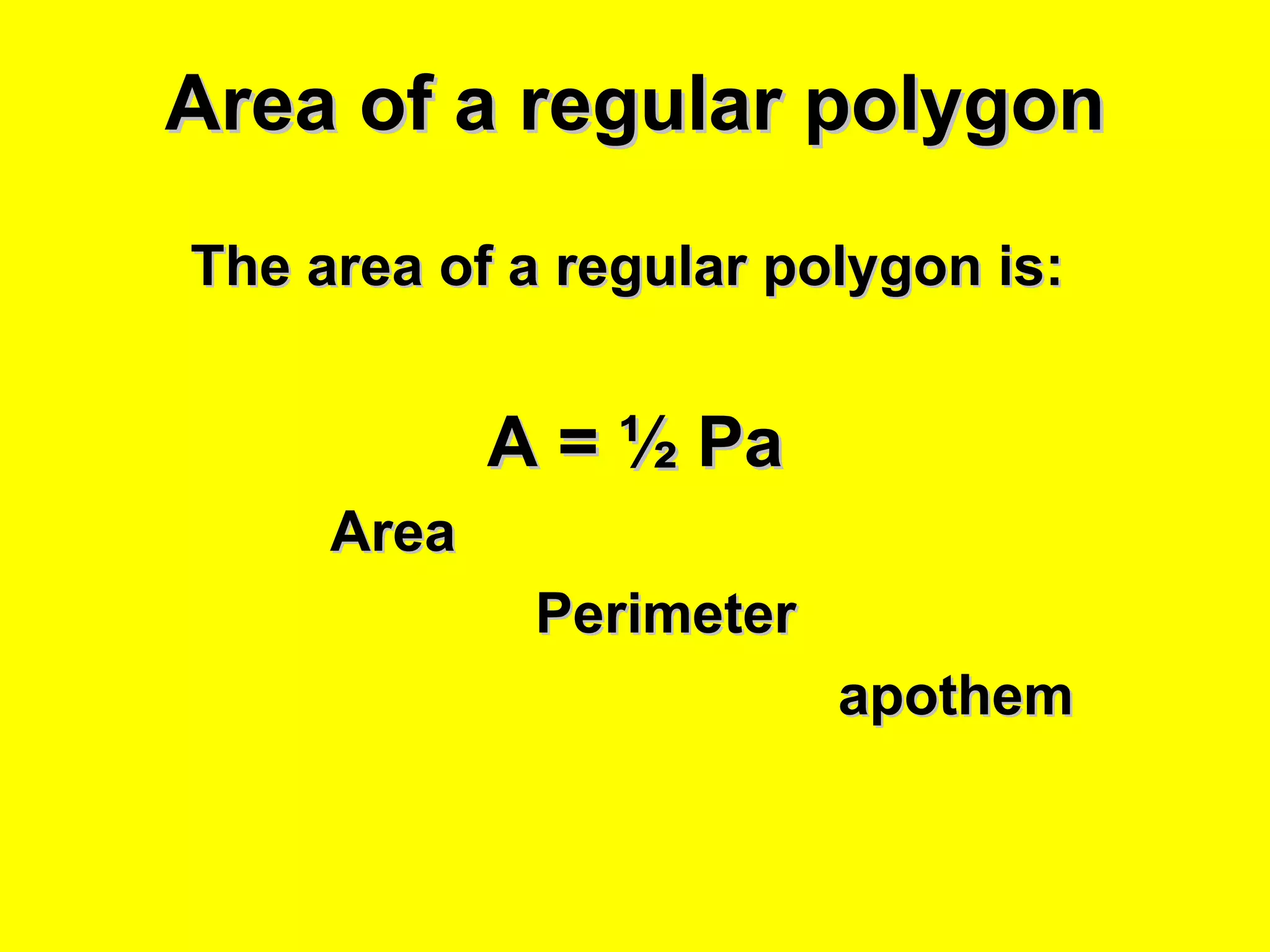
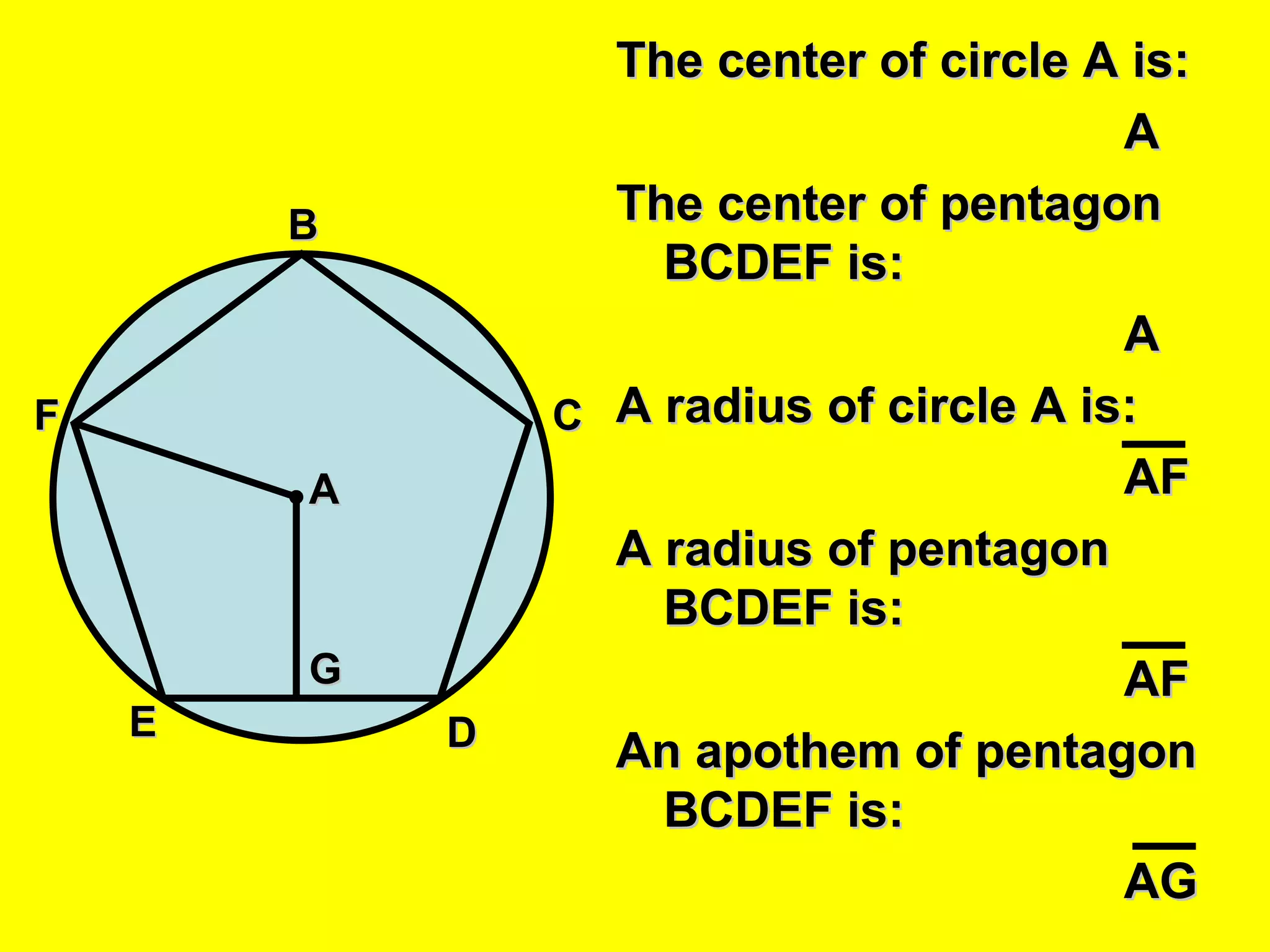
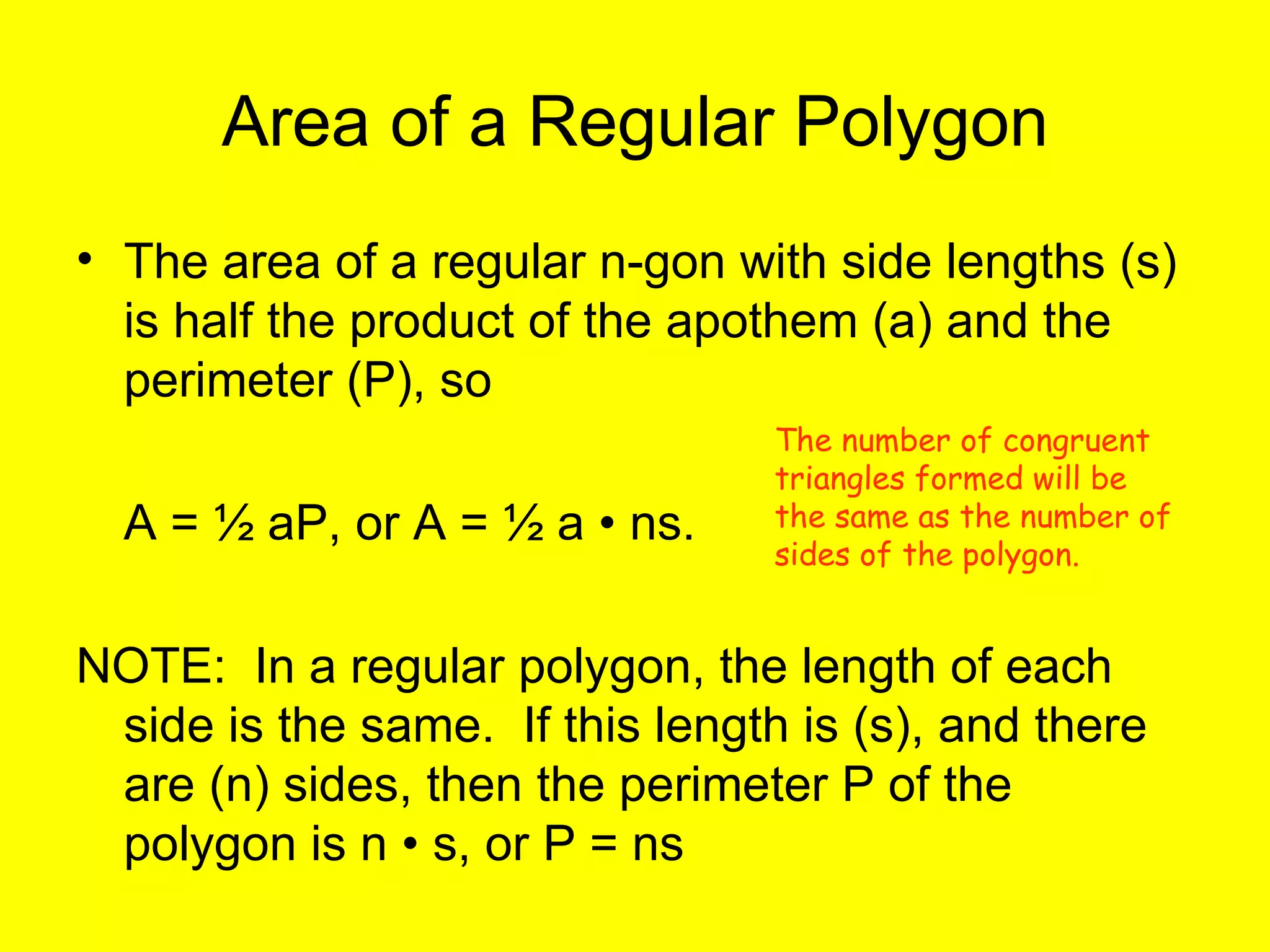
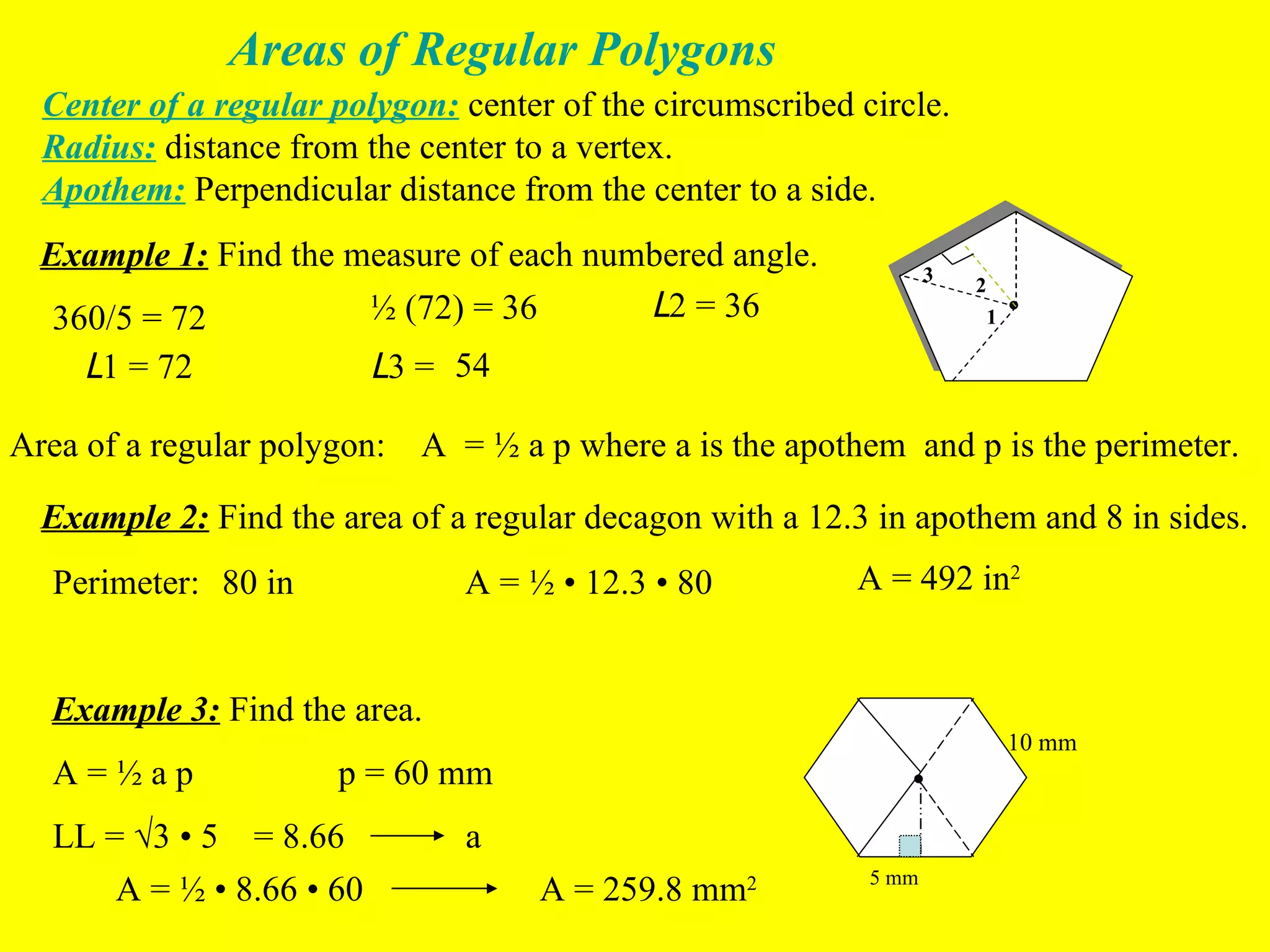
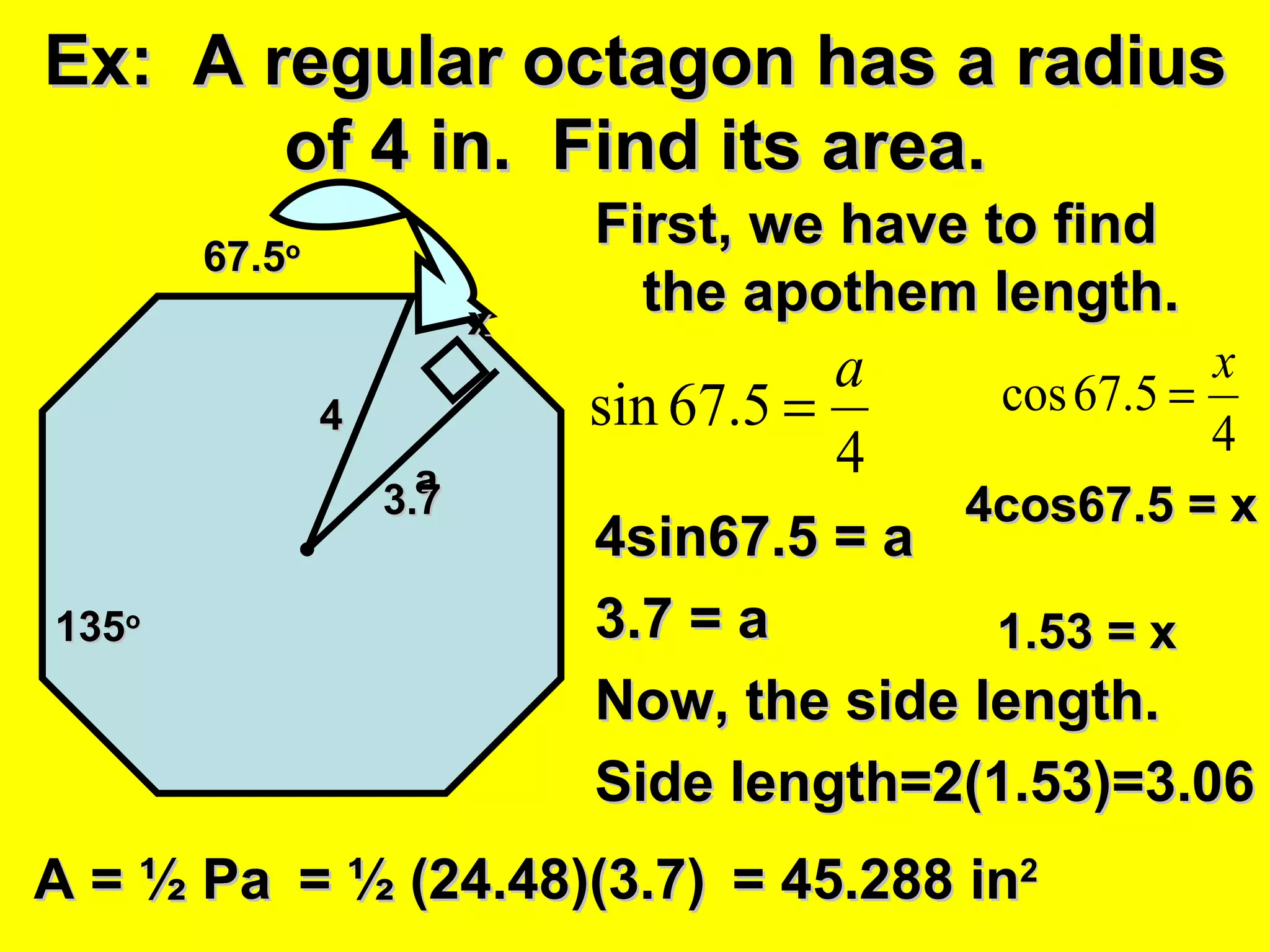
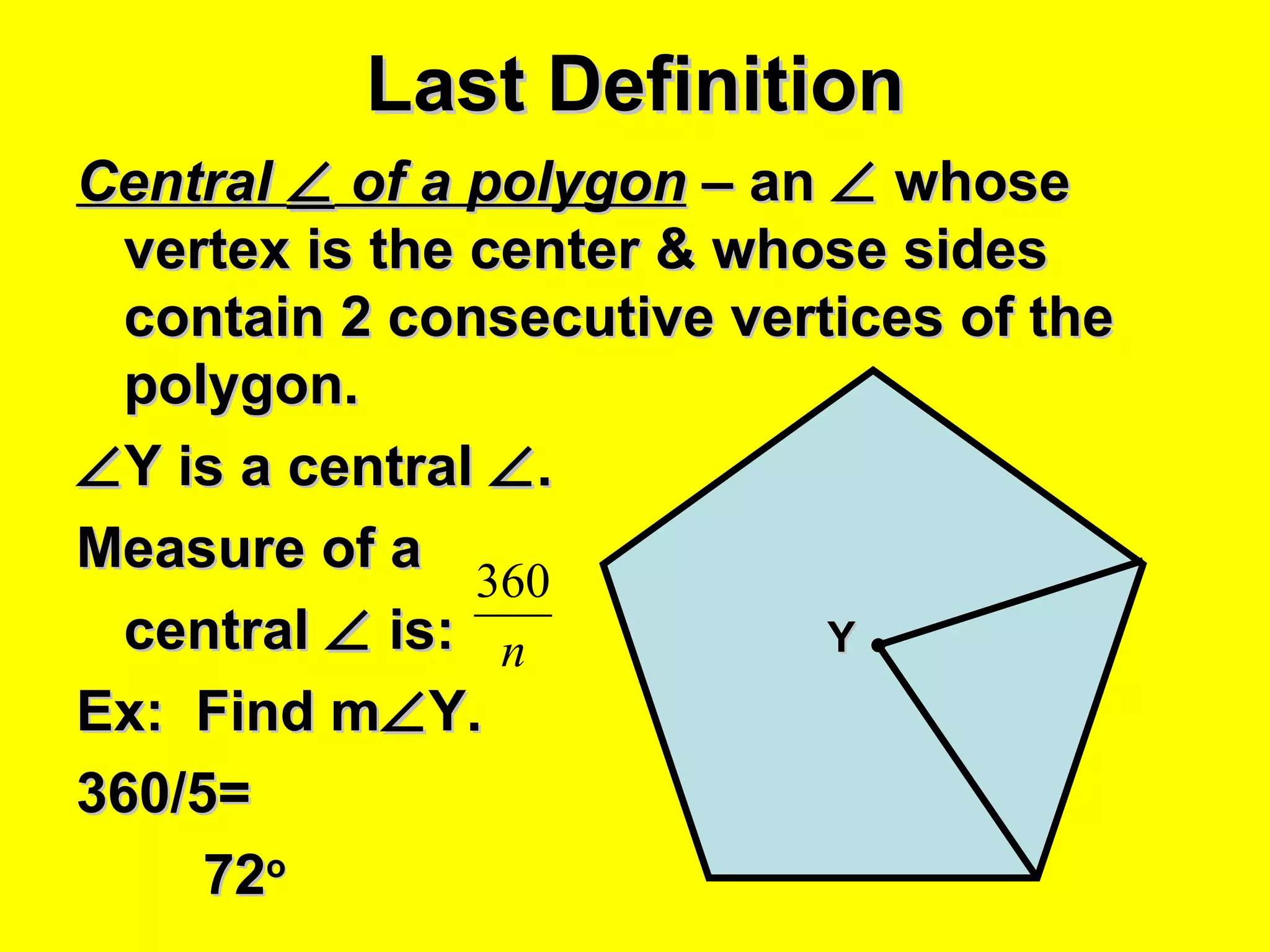
The document discusses the formulas and methods for calculating the area of regular polygons. It defines key terms like the center, radius, apothem, and central angle. It presents the theorem that the area of a regular polygon is equal to half the product of the apothem and perimeter. Examples are given of calculating areas of regular polygons by using the apothem, perimeter, and this area formula. Methods are described for finding the apothem or side length when they are not given.