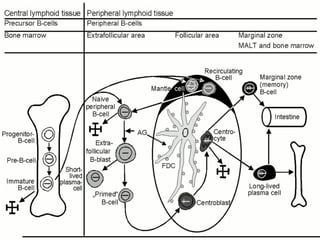
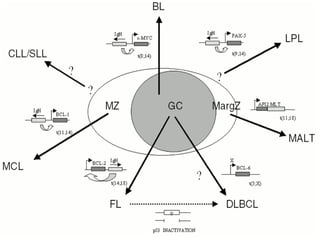
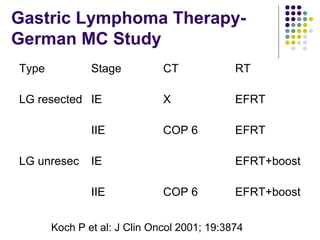
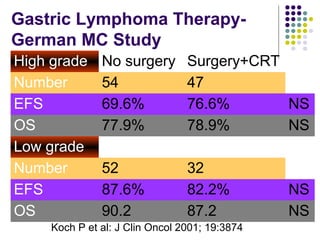
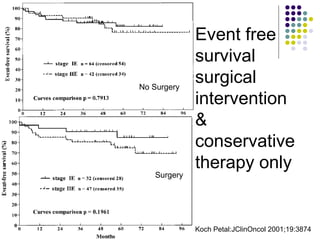
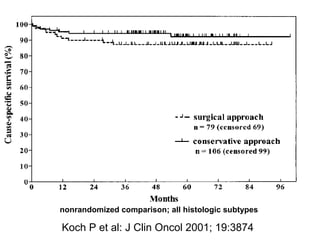
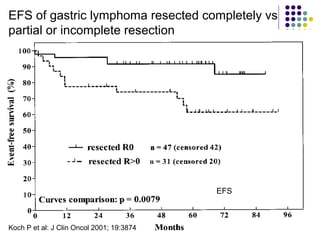
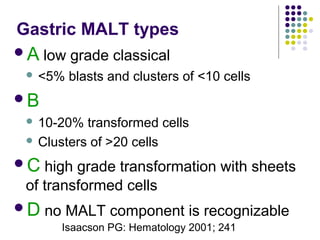
1. Gastrointestinal lymphomas, especially those of B-cell origin, commonly involve the stomach and small intestine. Complete surgical resection of early stage disease may improve survival outcomes.
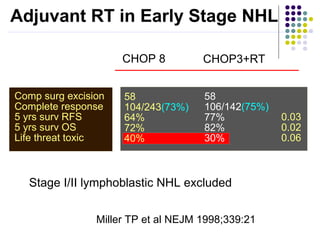
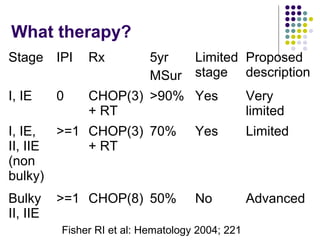
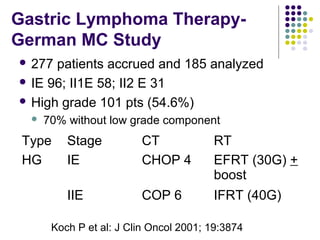
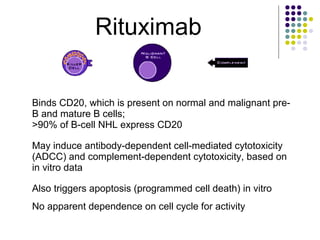
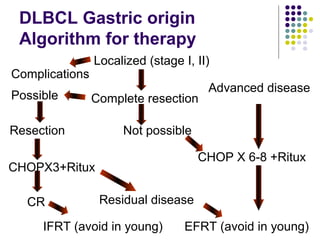
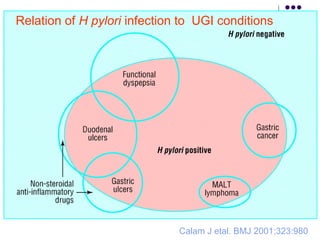
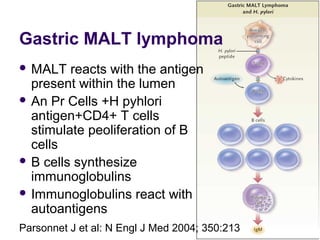
2. Treatment approaches for gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma typically involve chemotherapy such as CHOP, with or without radiation therapy or surgery based on disease extent and patient factors. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori can induce remission in gastric MALT lymphomas.
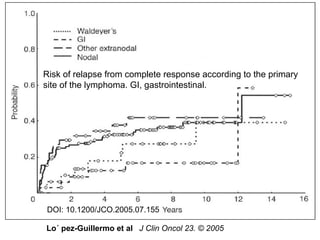
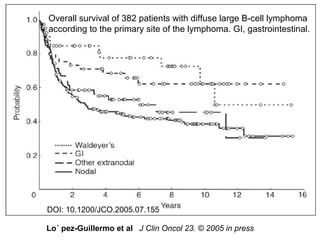
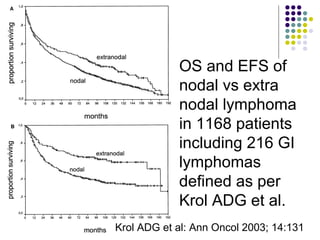
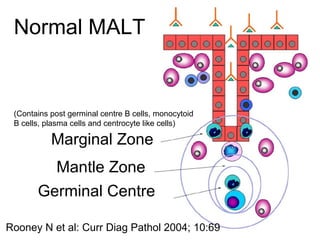
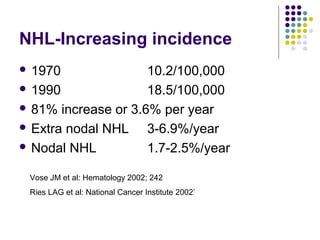
3. Prognosis depends on disease stage and histological subtype. Extra-nodal lymphomas generally carry a better prognosis than nodal disease, though intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas have a poorer outlook than gastric forms.







![ ? X to denote the organ of origin
X [stomach] II (gastric NHL with local nodes
involved)
X [stomach, colon] II
Addition of IP index as in AJCC Cancer
Staging Manual 6th
Edition?
GI NHL- Staging
Suggested modifications
Armitage JO; N Engl J Med 2005; 352:1250
Grothus-Pinke B et al: Ann Oncol 1996; 7:S126](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastrointestinaltractlymphoma-161216164614/85/Gastrointestinal-tract-lymphoma-13-320.jpg)