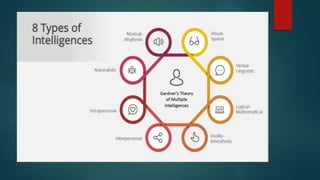
The document discusses Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, which proposes that people have different kinds of intelligences and learn in different ways. It describes eight types of intelligence: musical, visual, verbal, logical, physical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic. The document advocates for inclusive classrooms that incorporate strategies to engage students with different intelligences, such as using music, images, group work, individual reflection, and natural examples. This allows all students to learn in a way that suits their strengths and needs.