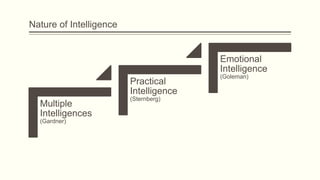
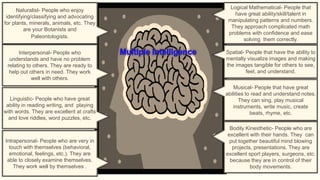
Howard Gardner developed the theory of multiple intelligences which suggests that there are different types of intelligence and people have varying strengths in each type. The types include linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalist intelligences. Applying multiple intelligences in adult education helps learners utilize their strengths and improves participation and learning outcomes by addressing different learning styles. Sternberg's theory of practical intelligence refers to the ability to apply knowledge to everyday tasks and problems. Culture influences what skills and knowledge are valued as practical intelligence. Emotional intelligence involves self-awareness, managing emotions, motivating oneself, recognizing emotions in others, and handling relationships. Culture shapes









![Reference
Hokagevigo. (Year). Carter Burtwell- Bella's lullaby extended [Video file]. Retrieved
YouTube website: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a1FMDOWJF58
from
Sternberg, R.J. (2002).
Culturalexplorationsofhumanintelligencearoundtheworld.InW.J.Lonner,D.L.Dinnel,S.A.Hayes,&D.N.
Suttler(Eds),OnlineReadingsinPsychologyandCulture (Unit5,Chapter1),CenterforCrossCulturalResearchWesternWashingtonUniversity,Bellingham,Washington.USA.
Capotosto, L. (2005). How to appeal to the multiple intelligences of your adult
learner. Retrieved from http://voices.yahoo.com/how-appeal-multiple- intelligences-your8826.html
Sarmiento, J. (2013, September 27). Howard Gardner theory of multiple intelligences
video
[Video file]. Retrieved from YouTube website: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bBE0Hwfpz2o](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/natureofintelligence-140119211250-phpapp02/85/Nature-of-intelligence-12-320.jpg)
![Reference
Sternberg’sTriarchicTheoryofIntelligence.(2014). Retrieved January, 19, 2014, from
http://wilderdom.com/personality/L2-2SternbergTriarchicTheory.htm
Merriam, S. B., Caffarella, R. S., & Baumgartner, L. M. (2007). Learning in adulthood: A
comprehensive guide (3rd ed.). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Mayer, J. D. & Salovey, P. (1997). What is emotional intelligence? In P. Salovey & D. Sluyter
(Eds). Emotional Development and Emotional Intelligence: Implications for Educators (pp. 331). New York: Basic Books.
Sengupta, Mousumi & Sengupta, Nilanjan. (2007). Emotional intelligence, New Delhi:
Excel Books. [ISBN 81-7446-543-X]
Ekman, P. & Oster, H. Facial Expressions On Emotion. Annual Review of Psychology. 1979,
30, 527-554. Vol. 30: 527-554 (Volume publication date February 1979) DOI:
10.1146/annurev.ps.30.020179.002523
Knowles, M. S., Holton, E. F., & Swanson, R. A. (2011). The adult learner/The definitive
classic in adult education and human resource development
(7th ed.). Burlington,
MA: Elsevier Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/natureofintelligence-140119211250-phpapp02/85/Nature-of-intelligence-13-320.jpg)