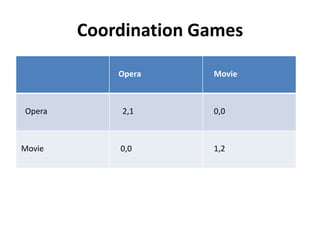
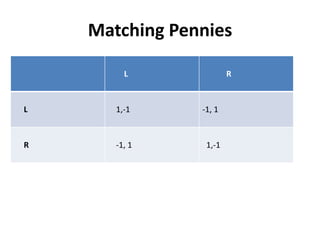
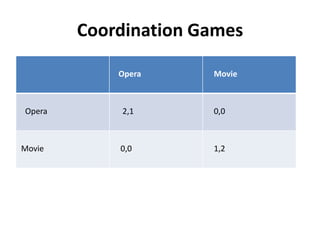
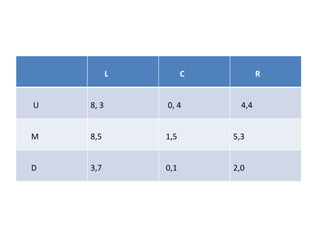
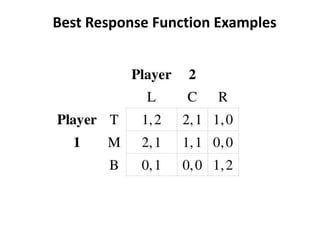
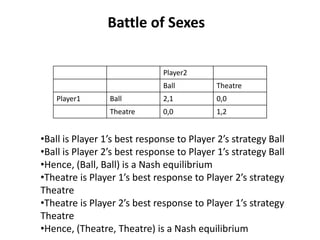
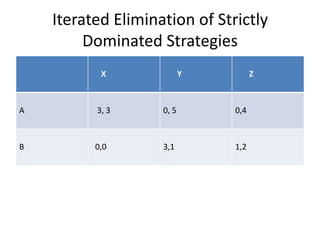
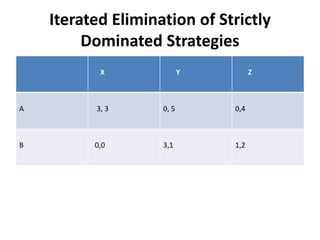
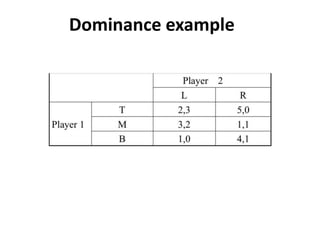
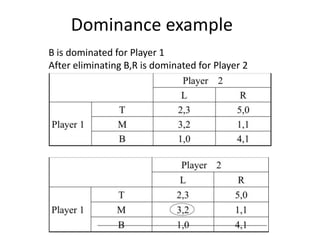
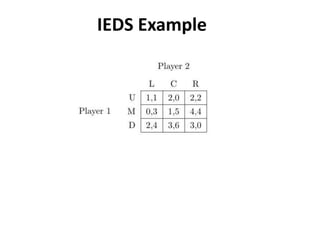
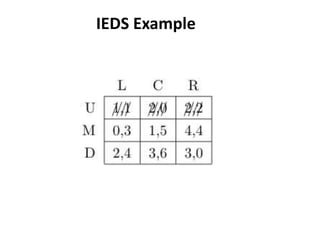
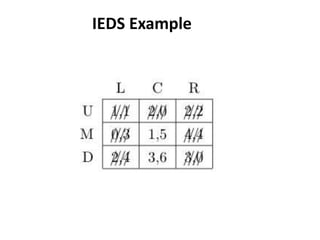
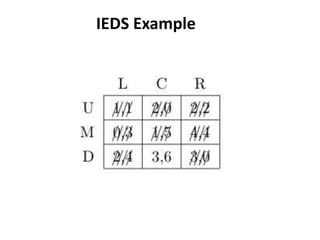
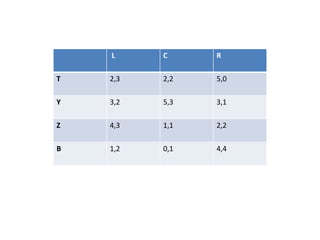
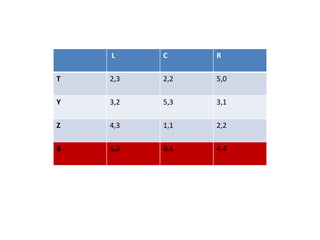
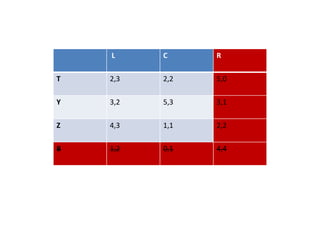
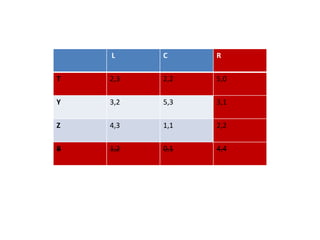
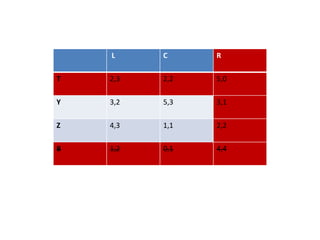
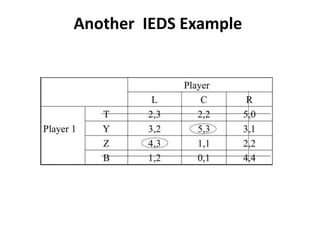
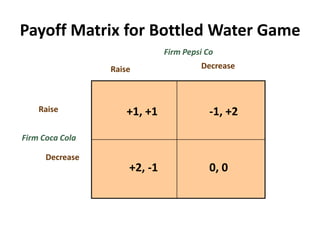
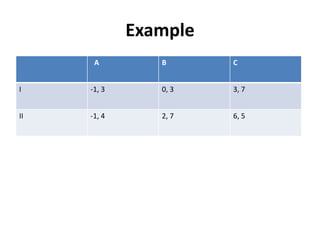
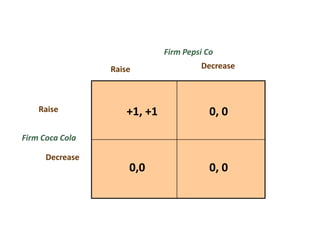
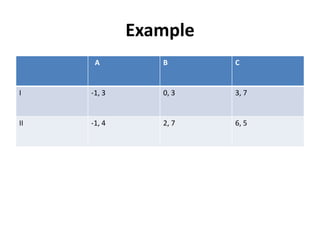
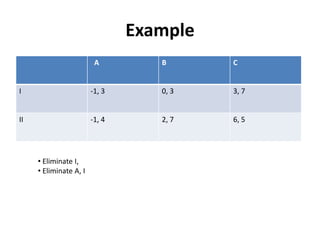
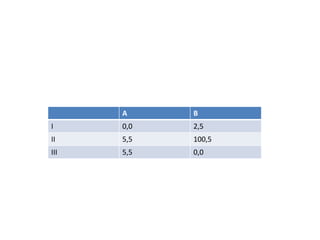
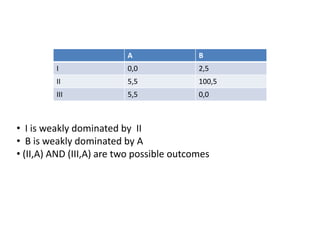
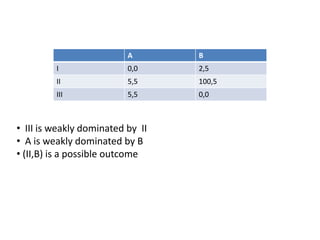
The document discusses Nash equilibrium, best responses, coordination games, and iterated elimination of dominated strategies. A Nash equilibrium exists when each player's strategy is a best response to the other players' strategies, meaning no player has an incentive to unilaterally change their strategy. Iterated elimination of dominated strategies involves repeatedly removing strategies that are strictly or weakly dominated until no further dominated strategies remain. The order of elimination matters for weakly dominated strategies but not strictly dominated strategies.