This document provides an overview of game theory, including:
1) Game theory is the study of strategically interdependent decision-making between players in a game. It examines why competitors behave similarly and how players in the Cold War determined nuclear weapon levels.
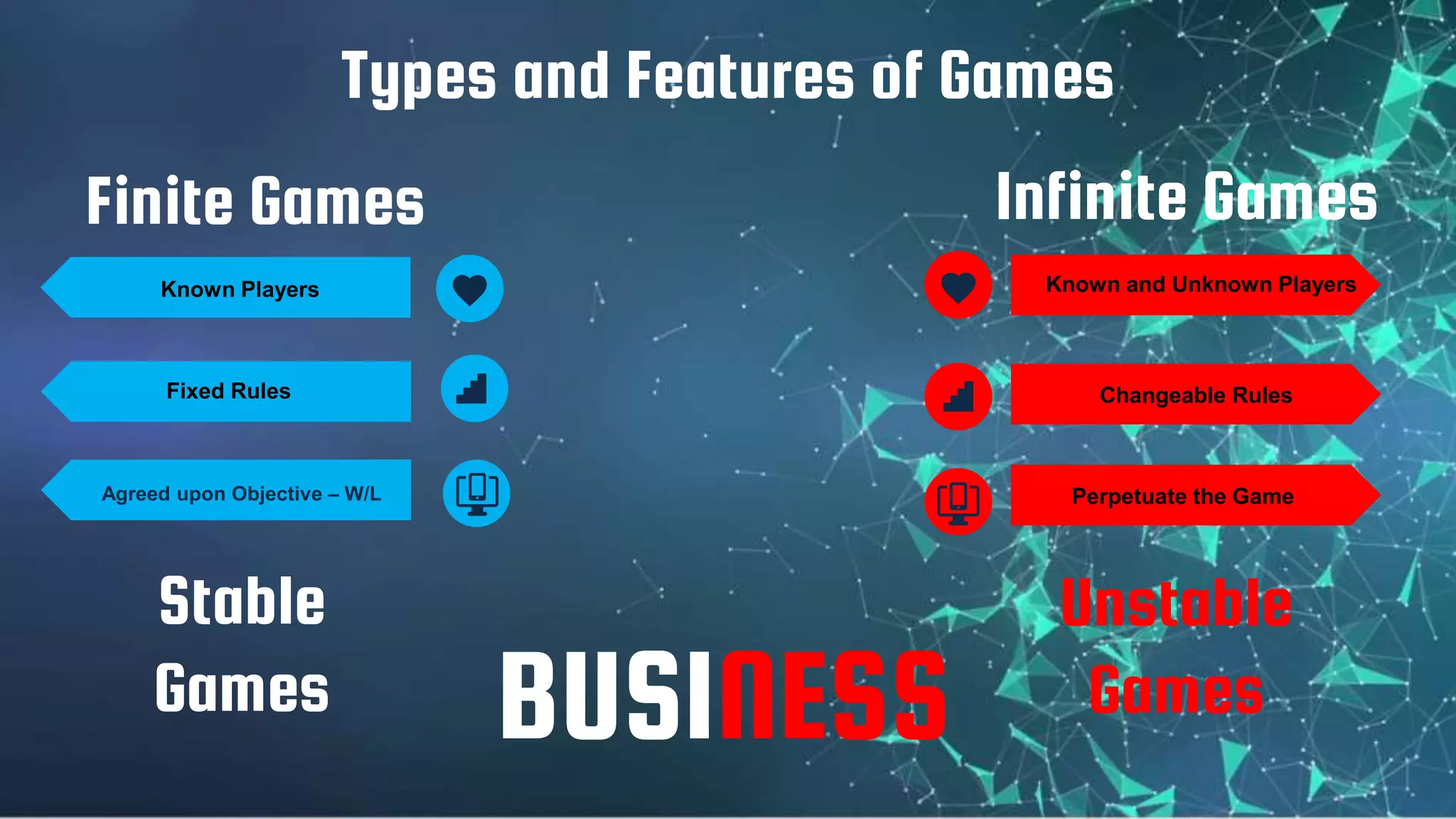
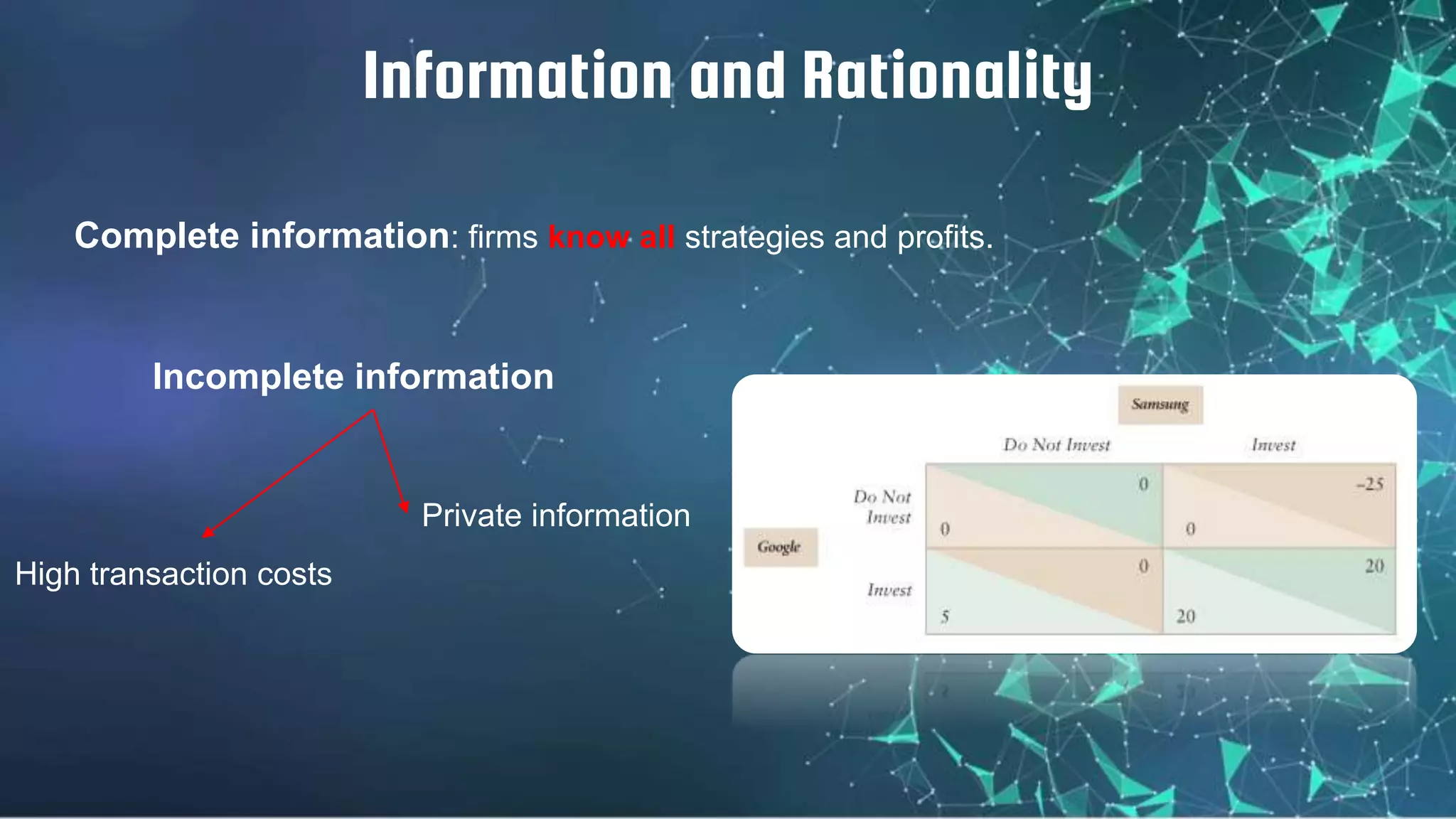
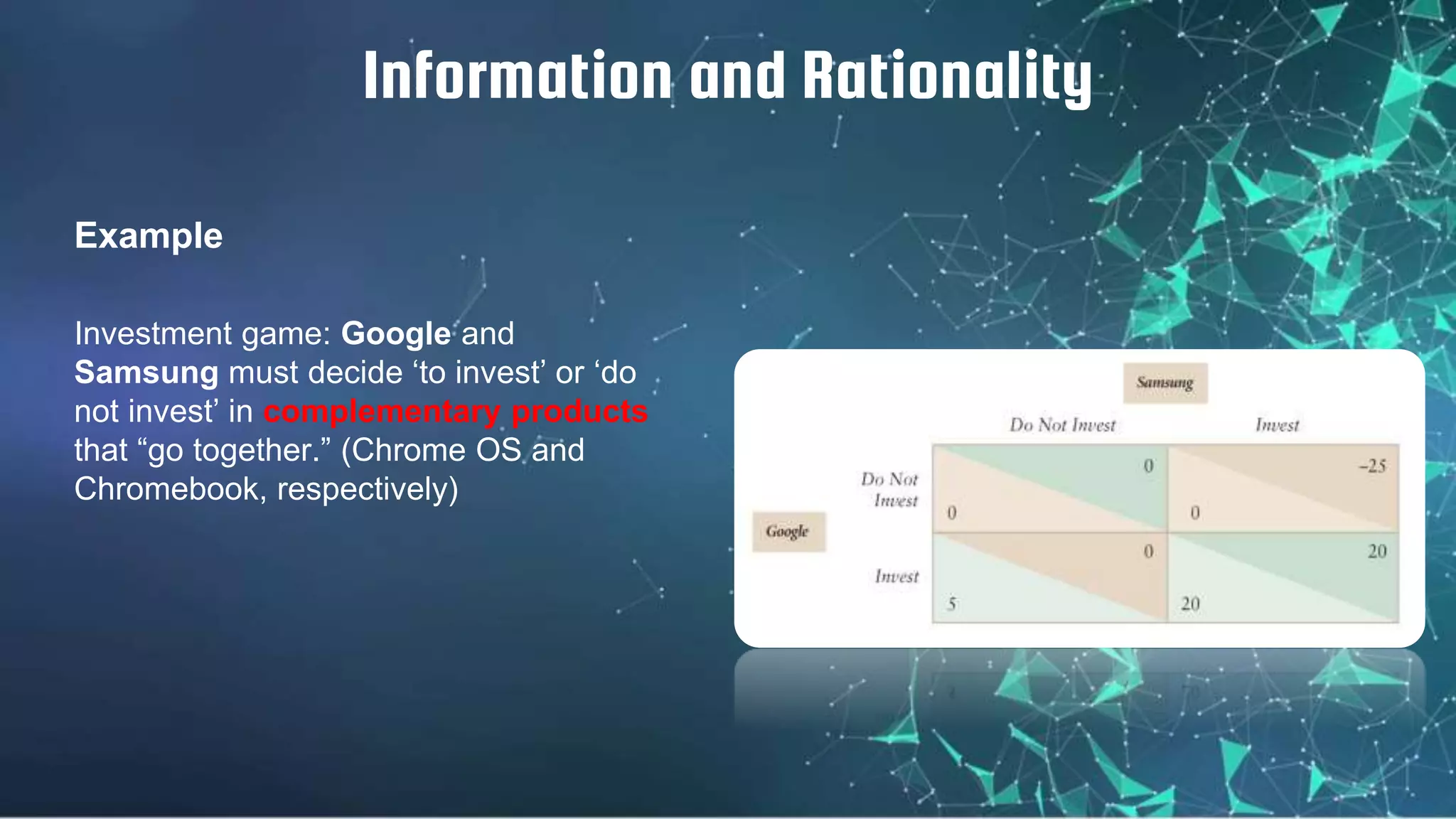
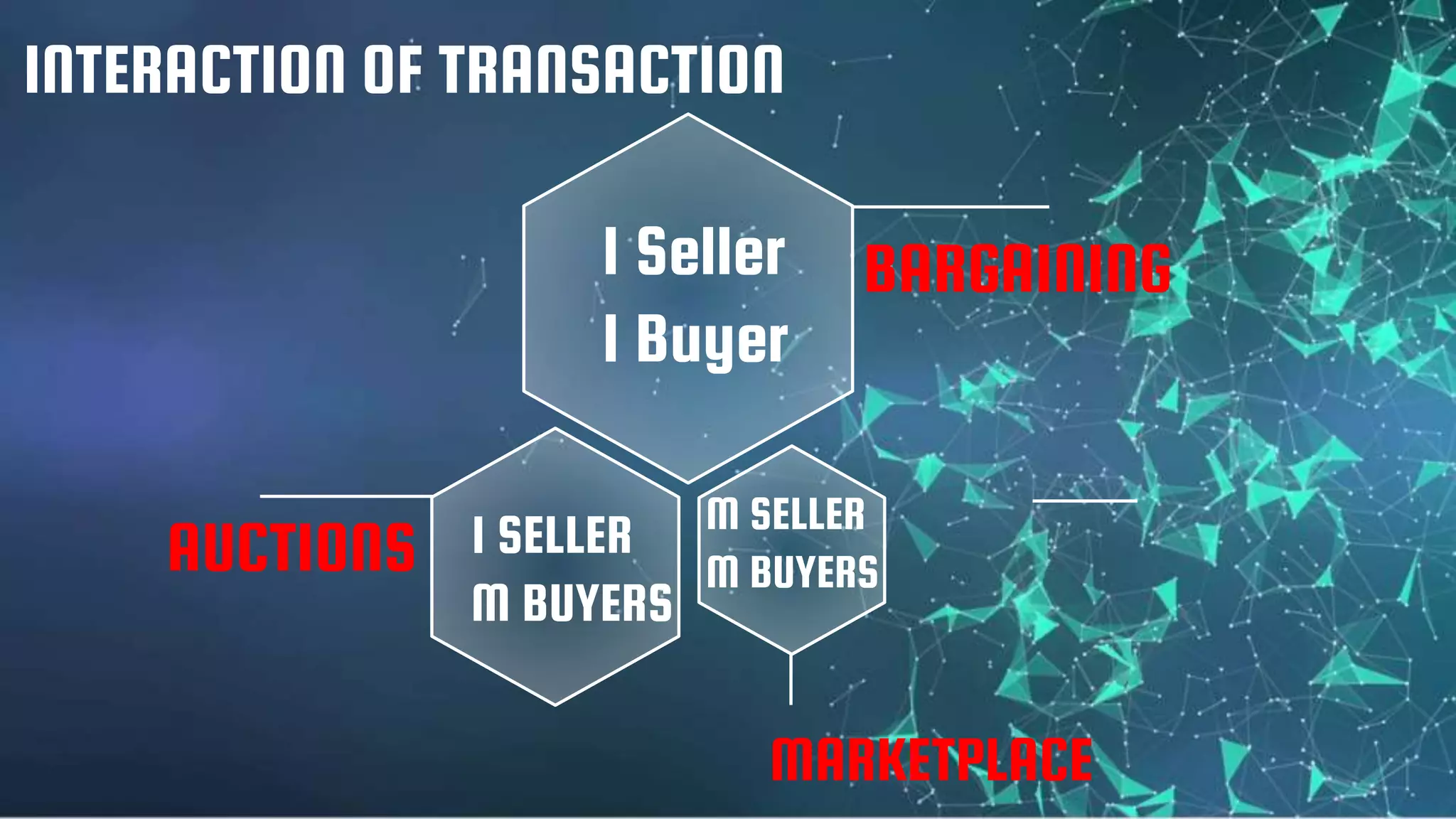
2) A game has players, strategies, payoffs, and outcomes. It can be finite or infinite, stable or unstable. Players can have complete or incomplete information.
3) Nash equilibrium describes situations where players lack incentive to deviate from their strategy given another player's strategy. The prisoner's dilemma exemplifies this.