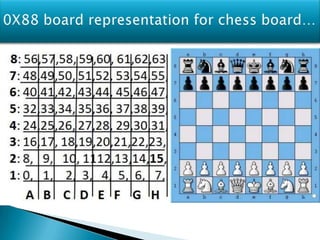
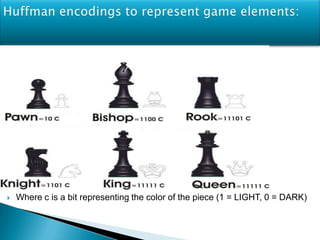
The document discusses game artificial intelligence and techniques used to generate intelligent behavior in non-player characters in computer and video games. It covers topics like machine learning, reinforcement learning, pathfinding algorithms, and different data structures used to represent game boards and chess positions. Game AI aims to create behavior that feels natural to the player while obeying the rules of the game. Various computer science disciplines are required to develop effective game AI, and different types of games require different AI techniques.