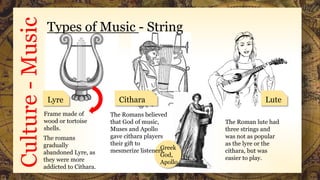
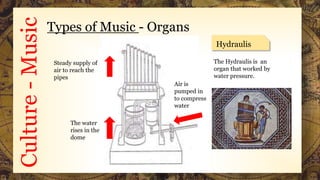
This document summarizes aspects of Roman culture from 105 BCE to 404 CE, including their government which transitioned from kings to a republic to an empire, music which was mainly monophonic and used in military, religious, and entertainment settings, gladiatorial games which featured armed combatants and animals, and their religion which included gods like Jupiter, Neptune, and Mars. It provides information on these topics in both text and images.