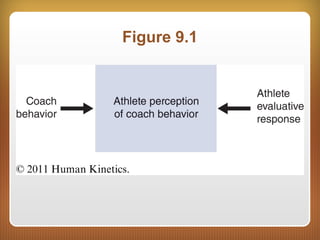
This document discusses leadership in sport. It defines leadership and distinguishes between leaders and managers. Leaders provide vision and direction while managers focus on organization and logistics. Leaders can be appointed or emerge naturally from a group. Effective leaders ensure goals are met and group needs are satisfied. Approaches to studying leadership include traits, behaviors, situations, and their interactions. The multidimensional model of sport leadership proposes that leader effectiveness depends on athlete and situational characteristics. Research shows that coaching style influences outcomes like athlete satisfaction, team cohesion, and performance. Developing high skill, work ethic, relationships, and knowledge are outcomes of athlete leadership development through sport.