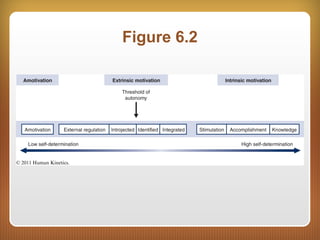
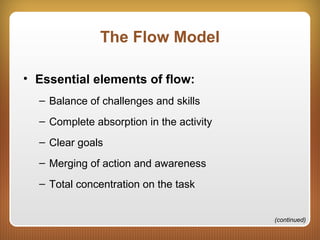
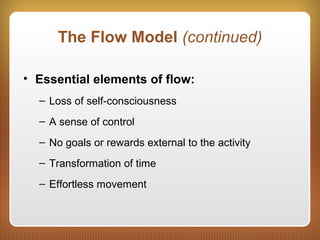
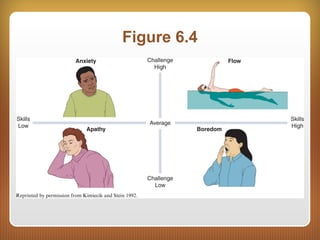
This chapter discusses feedback, reinforcement, and intrinsic motivation. It outlines principles of reinforcement including how reinforcement and punishment can influence future behaviors. The chapter also discusses approaches to positively and negatively influencing behavior and guidelines for using punishment. Intrinsic motivation and how extrinsic rewards can impact it are explored through cognitive evaluation theory. The chapter also defines the concept of "flow" as a special case of intrinsic motivation and lists elements that characterize being in a state of flow.