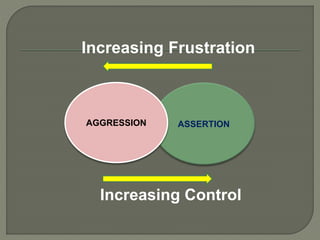
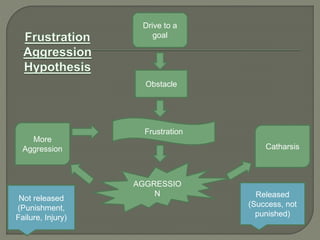
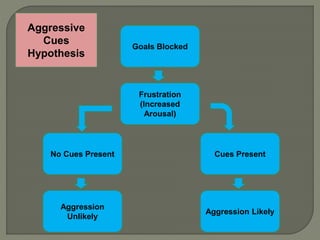
This document discusses different types of aggression in sports, including hostile aggression which aims to harm opponents outside the rules of the game, and instrumental aggression which aims to successfully execute skills while also intending harm. Potential causes of aggression include being fouled, poor refereeing, pressure of competition, and learning from role models. Theories discussed include the frustration-aggression hypothesis, which links frustration to aggression, and social learning theory, which posits that aggression can be learned through observation and reinforcement. Strategies to reduce aggression involve controlling arousal, punishing aggressive acts, rewarding non-aggressive behavior, and officials enforcing rules consistently.