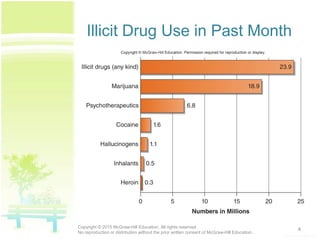
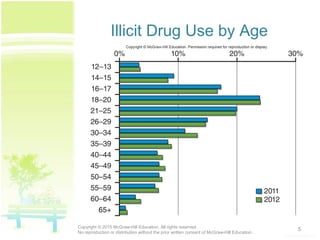
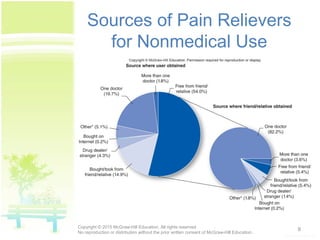
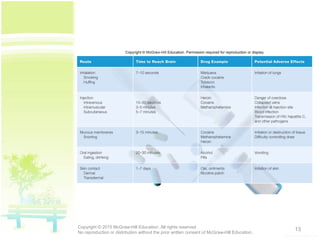
The document discusses patterns of illicit drug use in the United States. It finds that over 47% of Americans aged 12 or older have used an illicit drug in their lifetime, with marijuana being the most commonly used. It also notes a substantial rise in misuse of prescription drugs like pain relievers, stimulants, tranquilizers, and sedatives among college students between 1993 and 2005. The document classifies and describes different types of drugs like stimulants, depressants, opioids, hallucinogens, inhalants, and cannabinoids. It explains how drugs affect the brain's reward and pleasure centers, as well as factors influencing their effects.