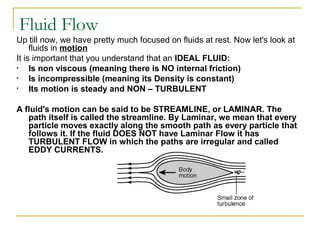
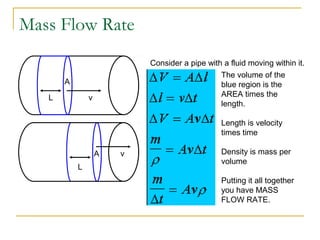
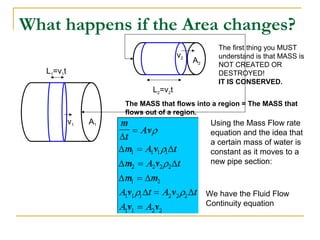
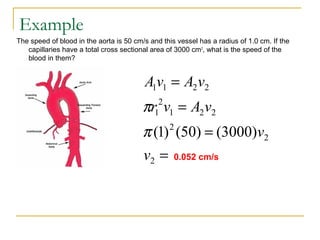
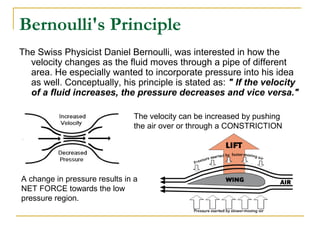
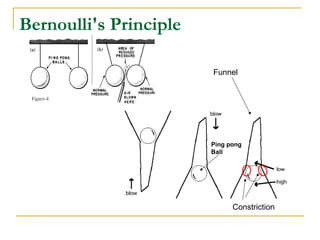
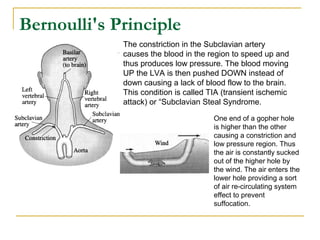
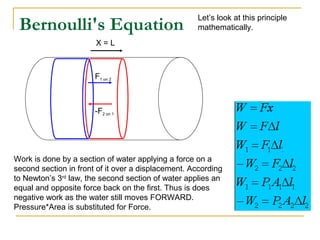
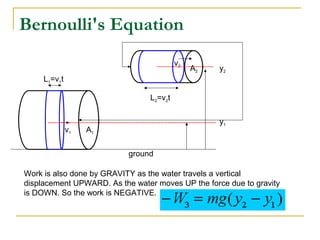
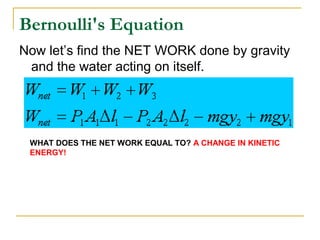
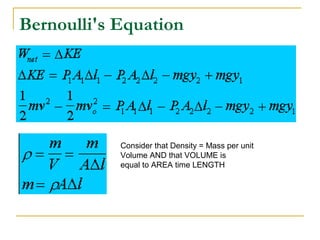
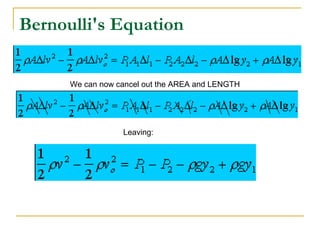
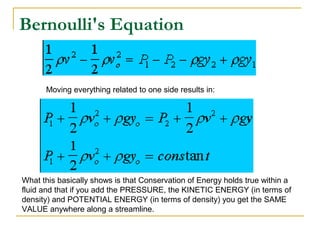
Fluid dynamics deals with fluids in motion. An ideal fluid is non-viscous, incompressible, and has steady, non-turbulent motion. Fluid motion can be laminar or turbulent. Mass flow rate is a measure of how much mass passes through an area over time. Bernoulli's principle states that as fluid velocity increases, pressure decreases, and vice versa. Bernoulli's equation represents this relationship mathematically using conservation of energy concepts. It relates pressure, velocity, density, and elevation in a fluid stream.