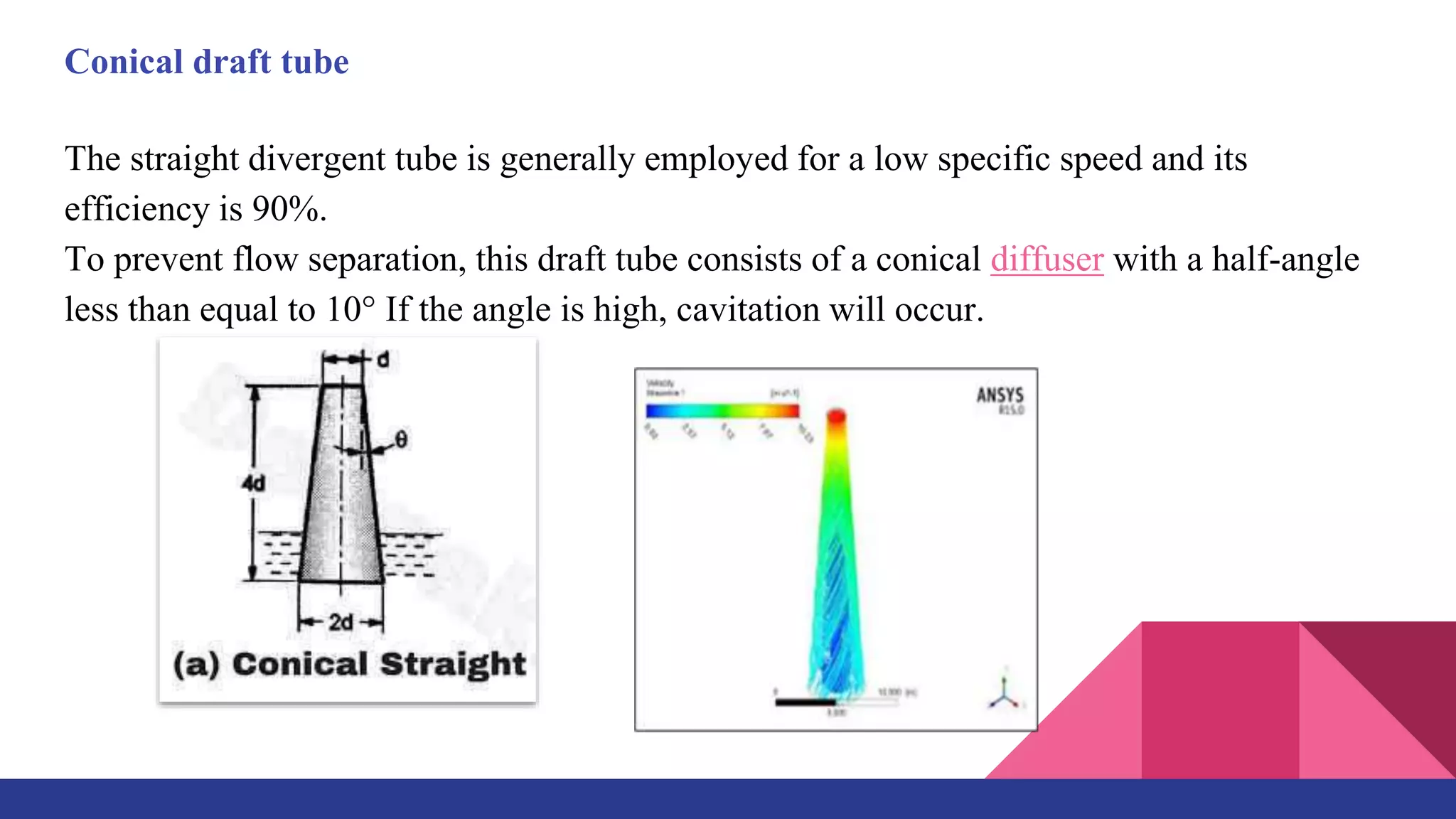
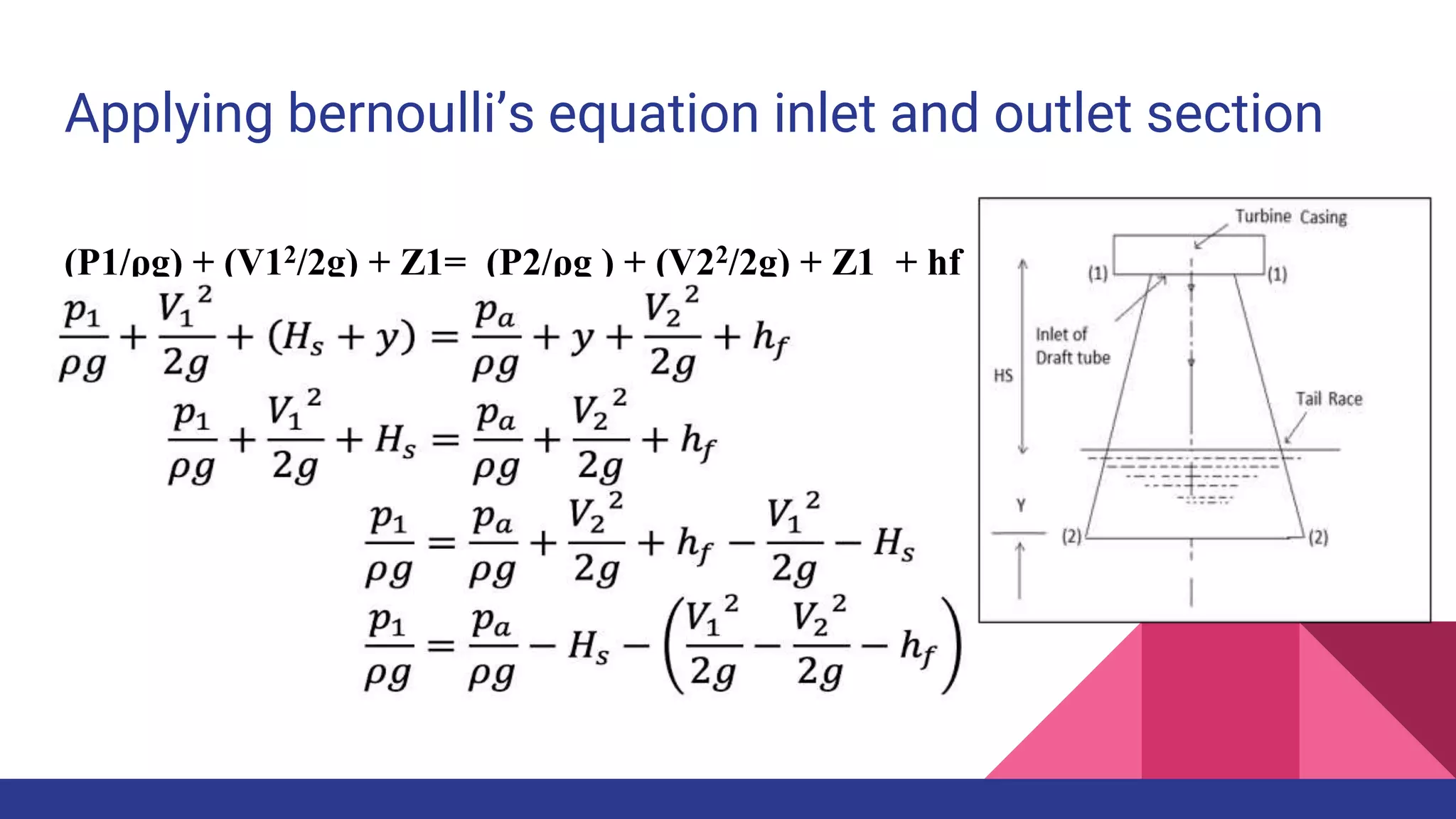
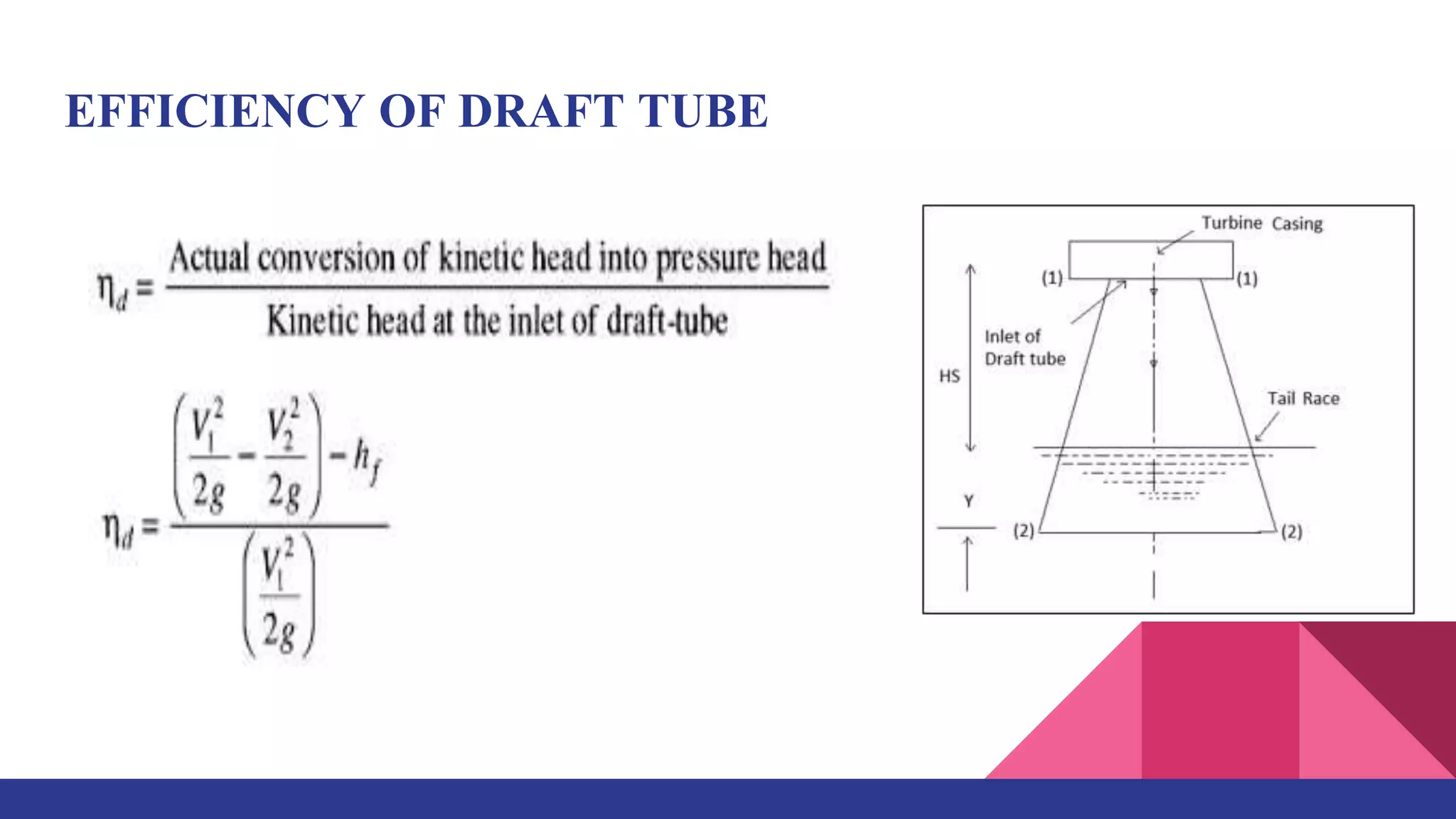
This document provides information about a presentation on the topic of studying draft tubes. It includes an introduction describing what a draft tube is and its purposes. It then discusses four main types of draft tubes: conical, Moody spreading, simple elbow, and elbow with varying cross-section. It provides details on the design and efficiency of each type. The document also includes examples of calculations using Bernoulli's equation as applied to draft tubes. It lists advantages and disadvantages of draft tubes and discusses potential future areas of study such as CFD analysis and multi-disciplinary design optimization.