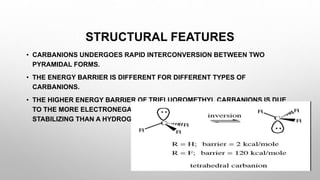
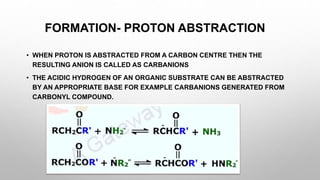
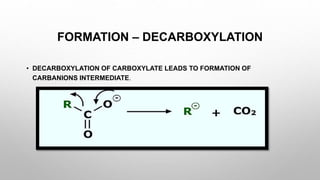
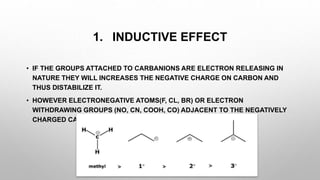
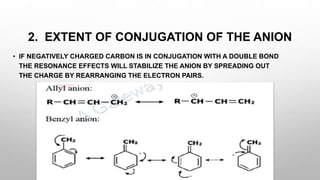
The document discusses carbanions, which are reactive intermediates in organic chemistry characterized by a carbon with an unshared electron pair and a negative charge. It covers their structure, formation methods, stability factors, and synthetic applications in various chemical reactions. Key highlights include the significance of inductive effects, conjugation, hybridization, and aromaticity in stabilizing carbanions.