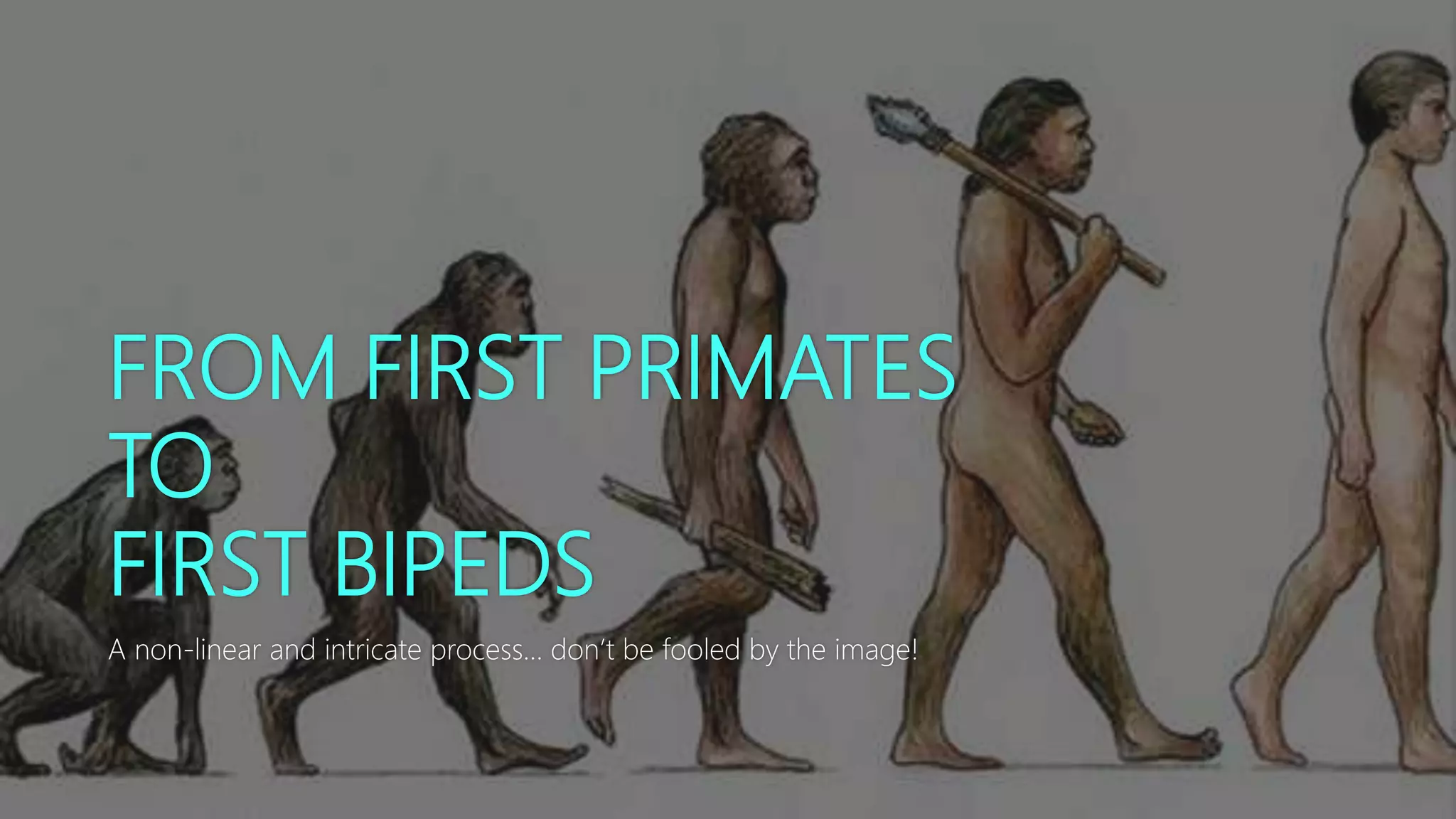
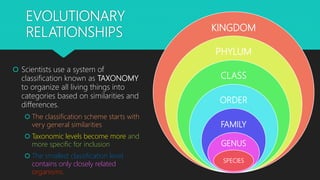
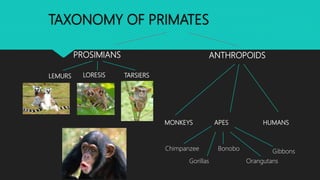
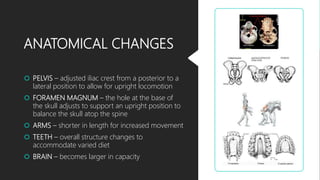
This document discusses human evolution from early primates to the first bipedal hominins. It outlines the taxonomic classification system used to categorize living things and shows where humans fit within this system. Key events in human evolution are described such as the emergence of the first primates 55 million years ago and the earliest evidence of bipedalism between 6-7 million years ago. Anatomical changes required for bipedalism are also summarized. The timeline of human ancestors is reviewed, showing the progression from early hominins like Australopithecus to the later emergence of the genus Homo.