Unique challenges arise for manufacturing smart, connected IoT devices including power efficiency, compatibility across different interfaces, and migration to new processors. However, FPGAs can help address these challenges in three ways. First, their low power consumption and programmability allows for more efficient power management. Second, FPGAs support various interfaces through customizable IP cores, improving interoperability. Third, a companion FPGA can augment processors to expand I/O and interfaces without requiring a new processor. In this way, FPGAs provide a low-cost, small-sized solution suitable for overcoming common IoT design problems.


![Fundamental Idea
Web services based on FPGA hardware have already been realized and defined [2], [3]. Their embedded nature
permits the developers to simply adjust those services to energetically interrelate with their surroundings and collect
Real-time measurement data or control various actuators [4]. These entities can be called environment-aware Web
services in difference to classical Web services that work on remote physical or virtual machines. In the modern era
IP address is added to the targeted VHDL Code design in order to make Internet of things (IOTs) enable VLSI Design.
Reference :- Ajay Rupani1 , Gajendra Sujediya2, A Review of FPGA implementation of Internet of Things](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaiotpresentation-190614042018/85/FPGA-using-IoT-3-320.jpg)


![Possible approach to solve this matter :-
1. Make the IoT device in sleep state and wait for any human interacting or human stimuli to make the device active again.
2. FPGA will determine depending on User command when to turn on or off the processors and display.
3. As per Xilinx if we use Artix-FPGA which consumes low power then it will be easy for us to develop power efficient IoT
Devices[6].
4. Power consumption comparison table for implementation of Secure hash Algorithm-3 on Xilinx FPGA[6].
Reference:-
Muzaffar Rao, Thomas Newe and Ian Grout, Secure Hash Algorithm-3(SHA-3) implementation on Xilinx FPGAs, Suitable for IoT Applications
Artix-7 FPGA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaiotpresentation-190614042018/85/FPGA-using-IoT-6-320.jpg)
![Challenge 2 :- Incompatible Interfaces
IEEE 1451 protocol focuses on those low-speed devices in IoT such as sensors, actuators, and transducers, while ignoring
other high-speed devices or equipment. To solve this issue FPGA was introduced[8].
With the continuous development of IoT applications, the IEEE 1451 is no longer suitable to handle the novel high-speed
devices, such as digital camera and USB devices.[8]
Market doesn’t fully accept IEEE 1451 because of the high resource cost and complexity for adopting the protocol. Normally, it
needs two physical processors for NCAP module and TIM module, as well as the 10-line TII interface is also difficult to be
implemented.[7]
Reference:- IEEE P1451.2, http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/1451/2 (2003, accessed 10 May 2015).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaiotpresentation-190614042018/85/FPGA-using-IoT-7-320.jpg)
![FPGA can be configured to be multi-core processors and deployed to process different modules in the whole system in
comparison to micro control unit (MCU).Along with that FPGA can support various low-speed and high-speed interfaces
through custom-designed intellectual property (IP) core. With the characteristics of re-programmability, the system
implemented by FPGA can be reused and extended for other applications[8].
Architecture of Smart Interface
Reference :- Shulong Wang1,2, Yibin Hou1,2, Fang Gao1,2 and Xinrong Ji, A reconfigurable smart interface based on IEEE 1451 and
field](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaiotpresentation-190614042018/85/FPGA-using-IoT-8-320.jpg)
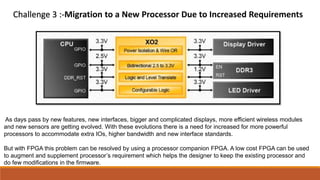


![References
[2] https://www.edn.com/electronics-blogs/eye-on-iot-/4442318/FPGAs-solve-challenges-at-the-core-of-IoT-implementation
[1] Ajay Rupani1 , Gajendra Sujediya2, A Review of FPGA implementation of Internet of Things
[3] A. Ruta, R. Brzoza-Woch, and K. Zieli ´nski, “On fast developmentof FPGA-based SOA services—machine vision case study,”
Available:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10617-012-9084-z
[4] R. Brzoza-Woch, A. Ruta, and K. Zieli´nski, “Remotely reconfigurable hardware software platform with web service interface
for automated video surveillance,” Journal of Systems Architecture, vol. 59, no. 7, pp. 376 – 388, 2013.
DOI: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2013.05.007. [Online]. Available:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S138376211300074X
[5] Robert Brzoza-Woch, PiotrNawrocki, “Reconfigurable FPGA-based embedded Web services as distributed computational
nodes,” Position Papers of the FEDCSIS. ŁO´ DZ´, Vol. 6, pp-159-164, 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaiotpresentation-190614042018/85/FPGA-using-IoT-12-320.jpg)
![[6]Muzaffar Rao, Thomas Newe and Ian Grout, Secure Hash Algorithm-3(SHA-3) implementation on Xilinx FPGAs, Suitable for
IoT Applications.
[7] IEEE P1451.2, http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/1451/2 (2003, accessed 10 May 2015).
[8] Shulong Wang1,2, Yibin Hou1,2, Fang Gao1,2 and Xinrong Ji, A reconfigurable smart interface based on IEEE 1451 and field
programmable gate array for multiple Internet of Things devices.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaiotpresentation-190614042018/85/FPGA-using-IoT-13-320.jpg)
