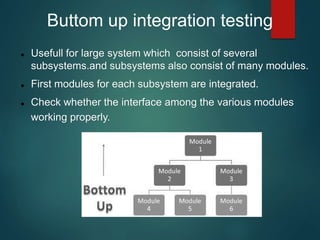
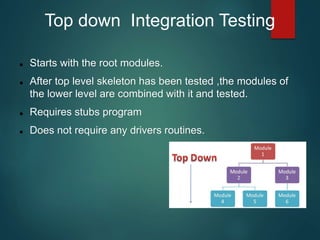
Testing is the process of executing a program to find errors and involves verification and validation. It includes methodologies like white box and black box testing, various testing types such as unit and integration testing, and best practices focused on user experience and clear requirements. Tools like Bugzilla and frameworks like Robot are mentioned for managing the testing process.