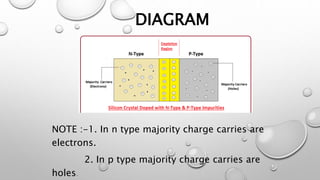
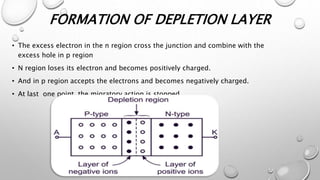
When a p-type semiconductor is joined with an n-type semiconductor, a p-n junction is formed. Electrons from the n-type region diffuse across the junction and combine with holes from the p-type region, forming a depletion layer devoid of charge carriers. The diffusion of charge carriers continues until an electric field is produced that prevents further diffusion. When a voltage is applied across the junction, current can flow as the majority charge carriers are encouraged to diffuse in one direction.