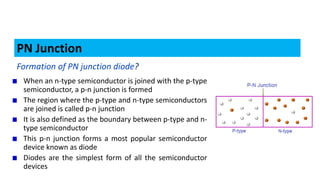
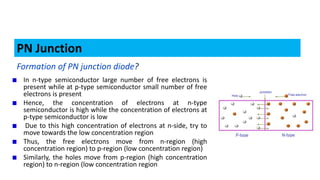
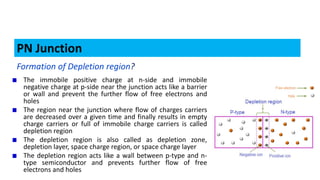
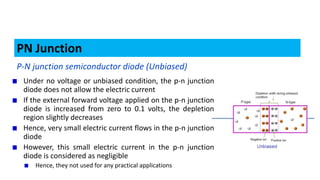
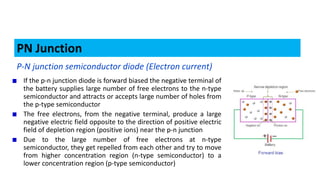
When a p-type and n-type semiconductor are joined, electrons flow from the n-side to the p-side, leaving positive ions in the n-side and negative ions in the p-side. This forms an electric field called a depletion region that acts as a barrier. When a voltage is applied in the forward direction, it reduces the depletion region, allowing electrons and holes to flow more easily across the junction. This forms the basis of a p-n junction diode, which allows current to flow easily in one direction but blocks it in the other.