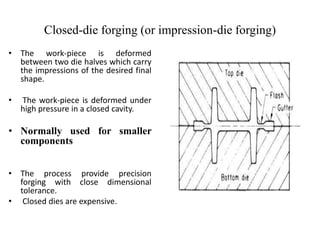
This document discusses the selection of forging equipment and stock size for open and closed die forging. It begins by classifying forging equipment into work-restricted and stroke-restricted machines such as hammers, presses, and hydraulic presses. It then explains open and closed die forging processes and considerations for die design such as flash, gutter, draft angles, and variation of stroke with load. The document concludes by providing design considerations for blocker, finisher, trim tools, and punches.