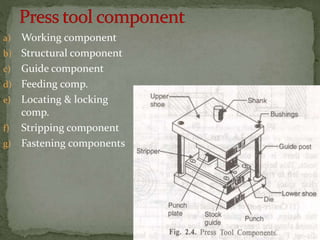
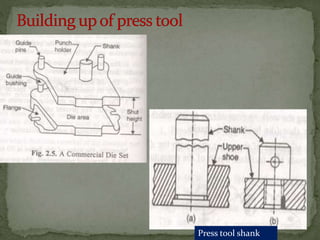
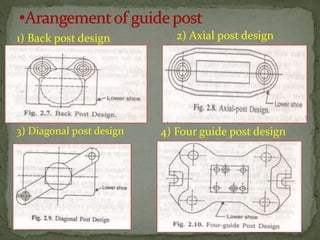
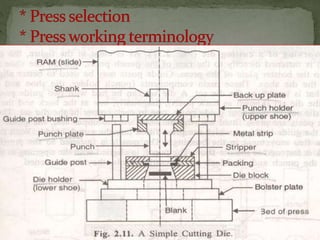
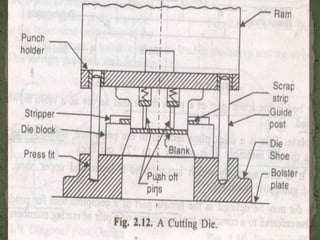
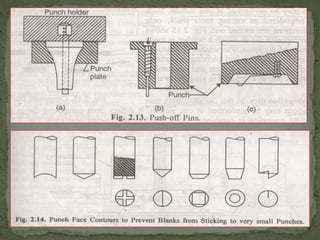
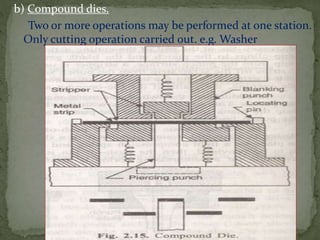
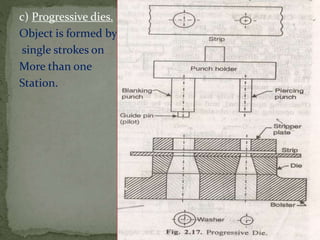
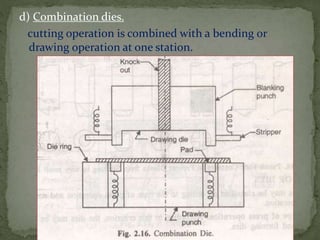
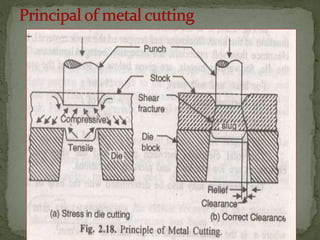
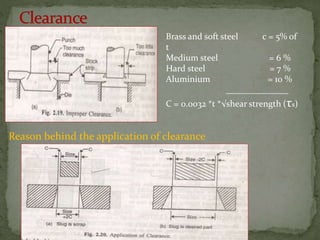
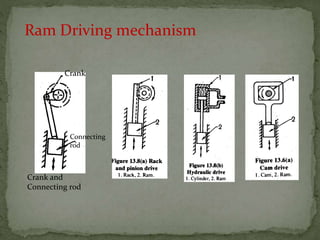
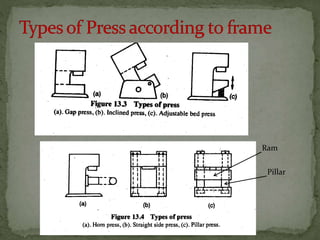
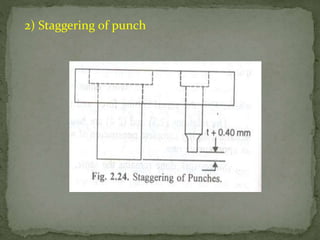
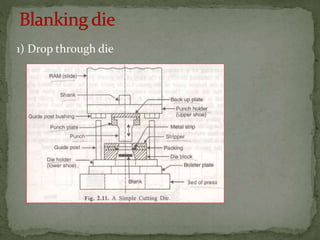
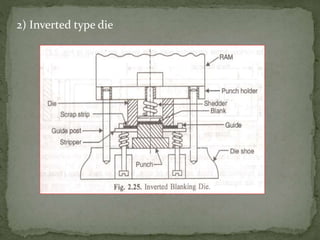
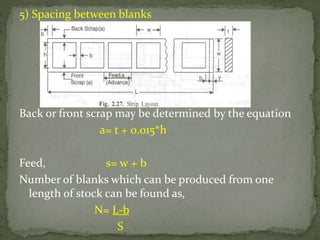
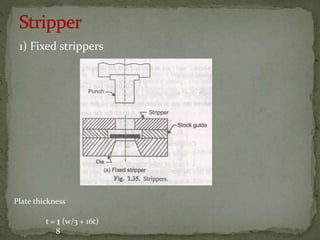
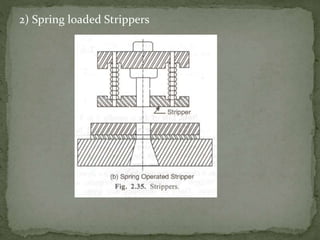
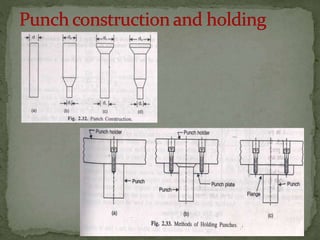
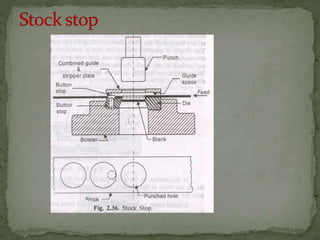
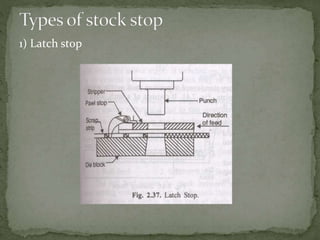
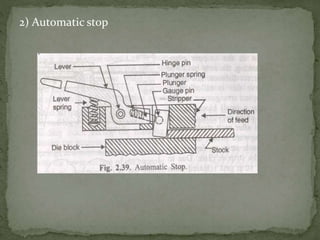
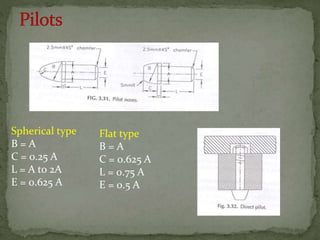
This document discusses metal stamping processes and press working equipment. It describes various cutting and forming operations used in stamping like blanking, punching, and bending. Advantages of stamping include small weight, high productivity, accuracy and low cost. Press tools require components for working, structuring, guiding, feeding, locating and stripping the metal piece. Hydraulic presses use oil pressure to actuate the ram while mechanical presses use a crankshaft. Press tools are designed based on the required operation and method of working like simple, compound or progressive dies. Clearance is required between the punch and die to allow for material flow.