This document defines and classifies various sexual offences under Indian law. It discusses natural offences like rape, adultery and incest. It also discusses unnatural offences per section 377 IPC, which criminalizes carnal intercourse against the order of nature. Further, it provides detailed definitions and explanations of rape, including the old and amended legal definitions. It also outlines the process for examining victims and suspects of sexual assault.


![Classification of Sexual offences:
A] Natural Sexual Offences
1. Rape 2. Adultery
3. Incest
B] Unnatural Sexual Offences
1. Sodomy 2. Lesbianism
3. Bestiality 4. Buccal Coitus
C] Sexual deviations/perversions
1. Fetishism 2. Transvestism
3. Sadism 4. Pedophilia etc.
D] Sex linked offences
1. Indecent Assault
2. Offences under Immoral Traffic Act](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/270083297-sexual-offences-161229190550/85/sexual-offences-3-320.jpg)





















![1] Consent:
- Age >12 years
- Witnessed, written and informed
consent is required
- In absence of consent, examination
cannot be undertaken](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/270083297-sexual-offences-161229190550/85/sexual-offences-25-320.jpg)
![2] History:
1. Menstrual History
2. Marital Status
3. Obstetric History ( If relevant)
4. History of venereal diseases
5. History of the incident
6. Resistance offered
7. Bath or local washing done?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/270083297-sexual-offences-161229190550/85/sexual-offences-26-320.jpg)






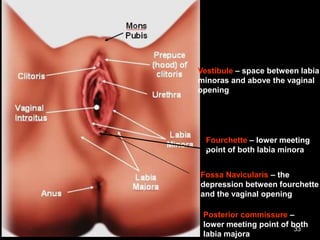





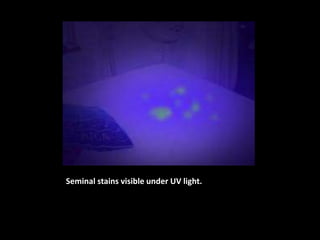







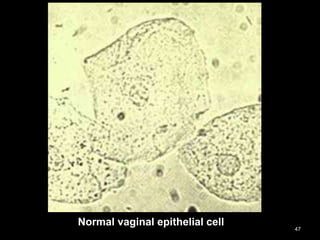
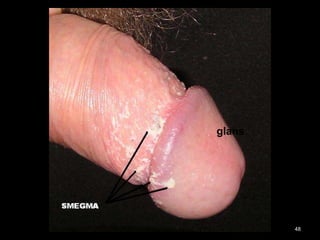





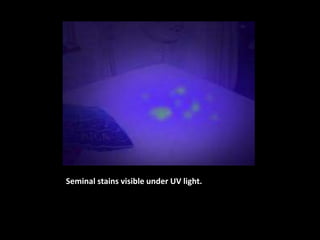





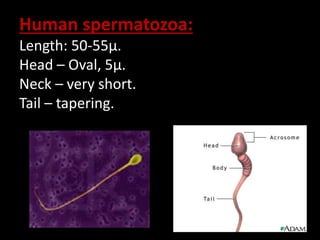
































![Medical Examination:
A] Active partner:
- abrasions
- Amylase detected in penile swabs
B] Passive partner:
Spermatozoa in oral cavity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/270083297-sexual-offences-161229190550/85/sexual-offences-94-320.jpg)



![Animals used:
A] By males: cows, female sheep, goat, she
ass etc.
B] By female: dogs, horses etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/270083297-sexual-offences-161229190550/85/sexual-offences-98-320.jpg)
![Medical Examination:
A] Accused:
1. Stains over clothes
2. Injuries over body
3. Stains & foreign material on penis
4. Transmitted infections.
B] In Animal:
1. Injuries to genitals
2. Presence of human spermatozoa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/270083297-sexual-offences-161229190550/85/sexual-offences-99-320.jpg)
