The document discusses India's foreign trade and major organizations that promote trade. It provides information on:
1. Major organizations that promote Indian trade including the India Trade Promotion Organisation, Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, Indian Institute of Packaging, and Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority.
2. The roles and activities of these organizations such as organizing trade fairs, training programs, and assistance to exporters.
3. India's major exports including petroleum products, gems, machinery, and pharmaceuticals and major imports including crude oil, gold, industrial machinery, and medical apparatus.
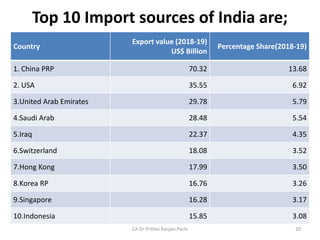
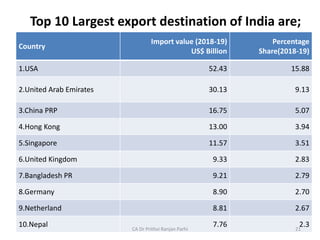
4. India's top 10 export destinations and import sources led by the USA for exports and China for imports