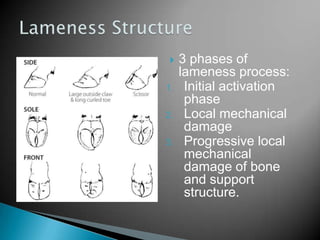
This document discusses lameness in dairy cattle. It begins by introducing the topic and outlining the structure of lameness, which involves 3 phases: initial activation, local mechanical damage, and progressive local damage of bone. It then discusses prevention methods like locomotion scoring and foot trimming programs. Lameness negatively impacts productivity by reducing milk production and causing late pregnancy. The conclusion emphasizes that lameness can be prevented through proper management strategies as it significantly affects animal health and production.