Embed presentation
Download to read offline


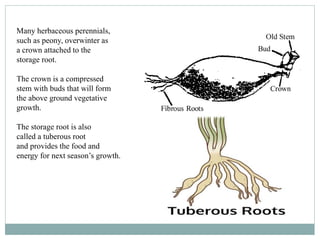
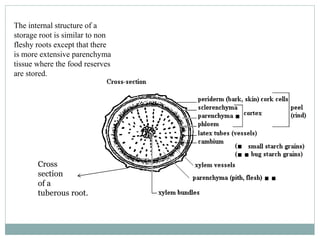
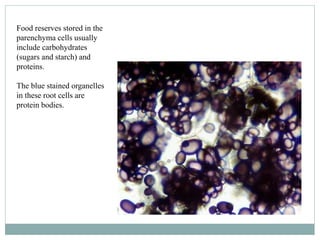
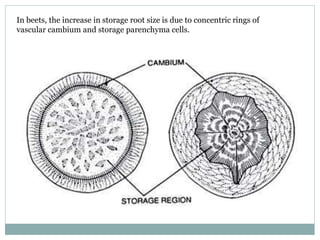
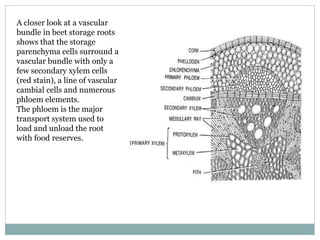
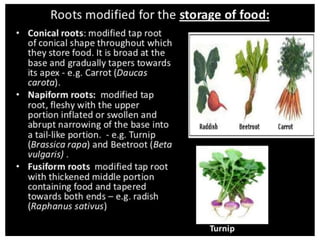


1) Many plant roots have the ability to store food reserves, and in some species the root is further modified into a fleshy storage organ like carrots, sweet potatoes, and beets. 2) These storage roots provide food and energy for the plant's next season of growth, and have internal structures similar to normal roots but with more extensive parenchyma tissue for storing carbohydrates, sugars, starches, and proteins. 3) In beets specifically, the storage root increases in size through concentric rings of vascular cambium and storage parenchyma cells, with the phloem being the major system for transporting food reserves into and out of the root.









