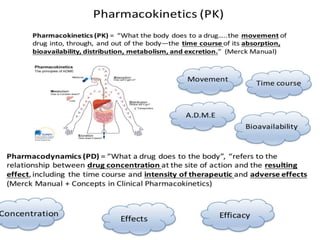
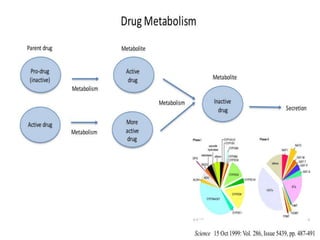
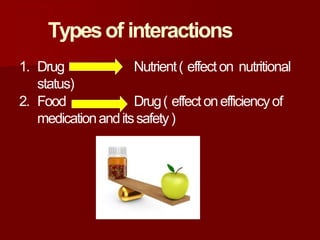
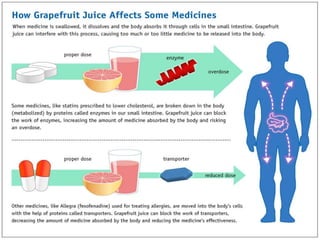
This document discusses food-drug interactions, defining them as situations where nutrients affect how a medication works or where drugs affect nutrient metabolism. It describes several types of interactions, including how drugs can decrease nutrient absorption or nutrient production. Foods are also described as potentially interfering with drug absorption, metabolism, or action in the body. Specific examples are given of foods that can interact with medications like anticoagulants, digoxin, antibiotics, statins, and those affected by grapefruit. Those at highest risk of interactions are identified. The document concludes with recommendations around monitoring high risk patients and considering interactions between food and drugs.