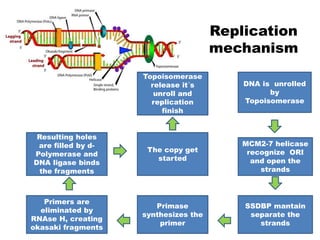
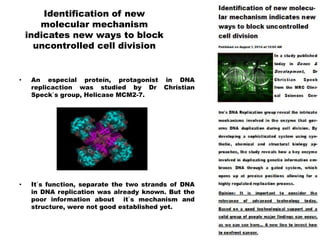
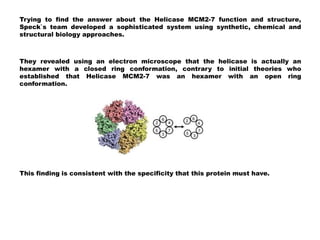
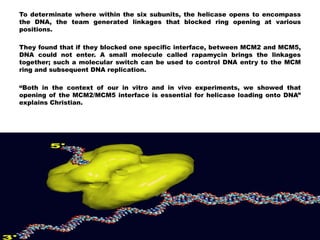
The document discusses the discovery of a new molecular mechanism involving the mcm2-7 helicase, crucial for DNA replication, revealing its function as a closed ring structure contrary to previous beliefs. This finding offers insights into how to inhibit uncontrolled cell division, a significant aspect of cancer research. Understanding the precise mechanics of DNA replication could lead to new cancer treatments by targeting this crucial process.