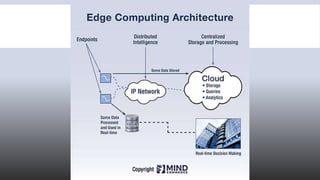
Edge computing is a method of optimizing cloud computing systems by performing data processing near the data source rather than sending all data to a central cloud. This reduces bandwidth usage and latency. Edge computing involves leveraging devices like sensors, smartphones and tablets that may not always be connected to perform localized analytics and knowledge generation before sending data to cloud storage.