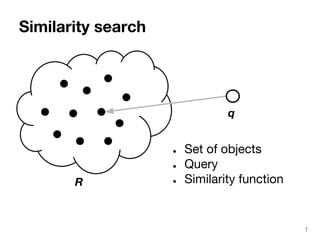
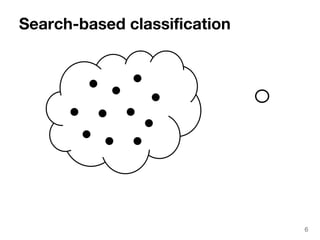
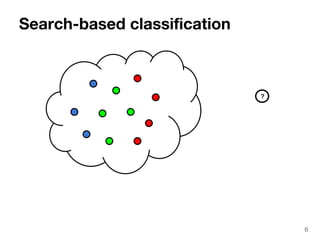
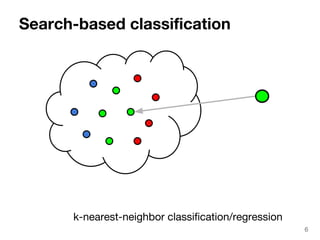
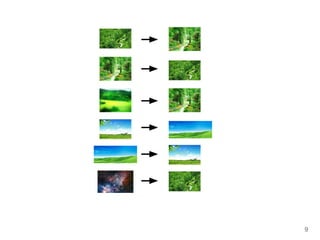
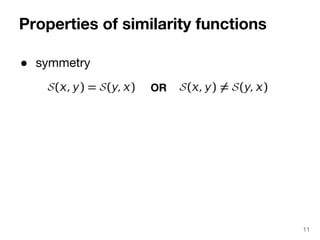
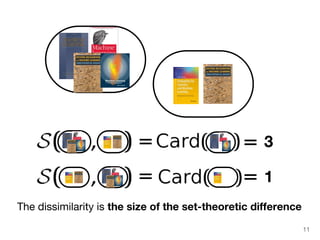
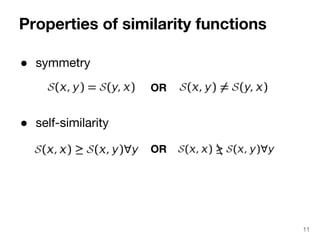
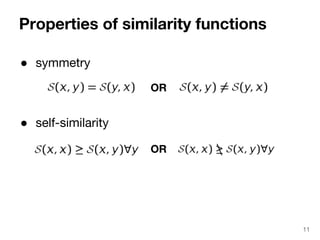
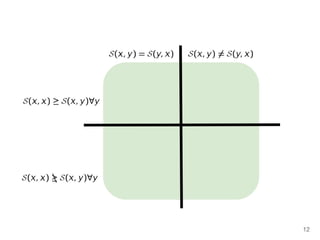
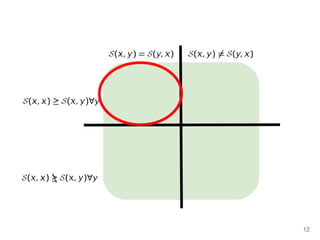
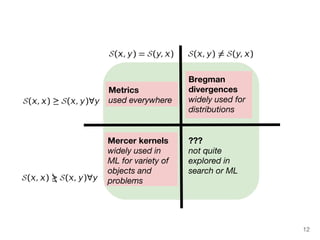
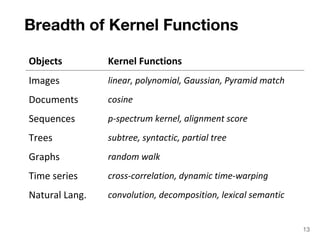
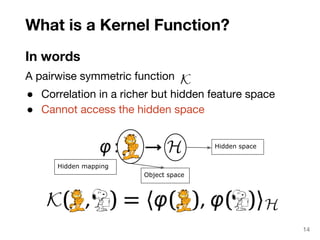
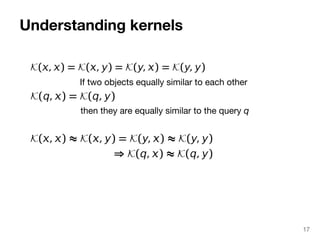
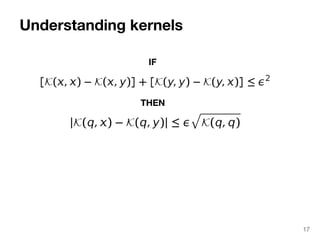
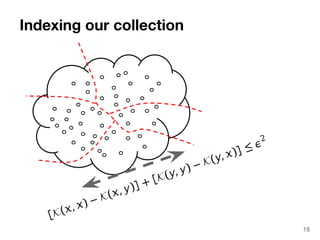
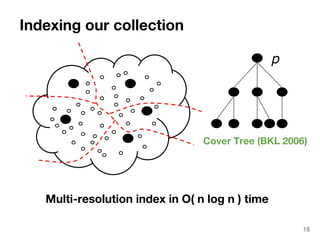
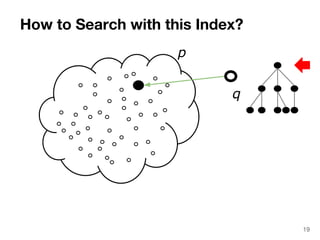
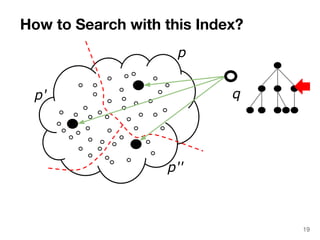
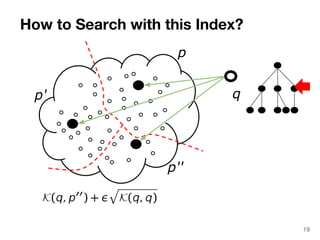
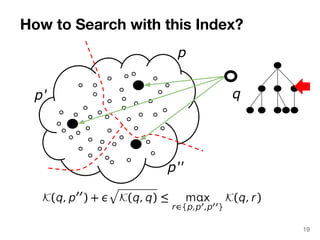
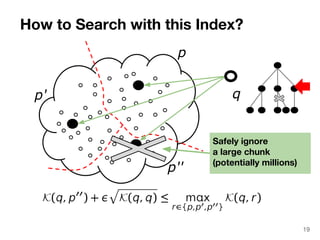
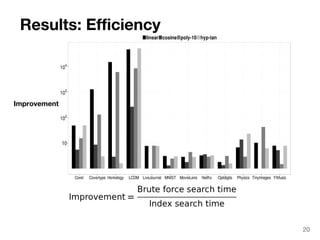
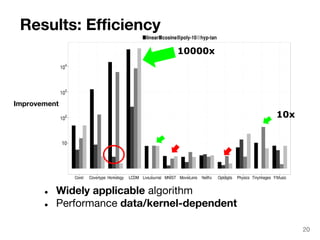
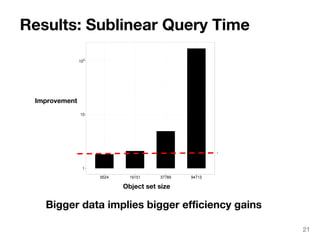
The document discusses max-kernel search as a method for efficiently finding similar objects based on various similarity functions, highlighting its applications in fields such as machine learning and computer vision. It outlines key concepts including the importance of kernel functions, metrics used, and the efficiency improvements gained through indexing techniques. The document emphasizes the relevance of search in machine learning and provides resources for further exploration of fast max-kernel search algorithms.