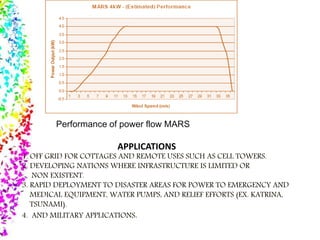
The document discusses the flying windmill technology, specifically the Magenn Air Rotor System (MARS), which uses tethered buoyant turbines to generate electricity at high altitudes, offering advantages such as low-cost electricity and the ability to operate in various wind speeds. MARS can be deployed rapidly for off-grid applications, disaster relief, and in regions with limited infrastructure, while facing limitations like installation restrictions near airports and the need for disassembly in extreme winds. Overall, this system presents a novel approach to harnessing wind energy where traditional turbines may not be feasible.