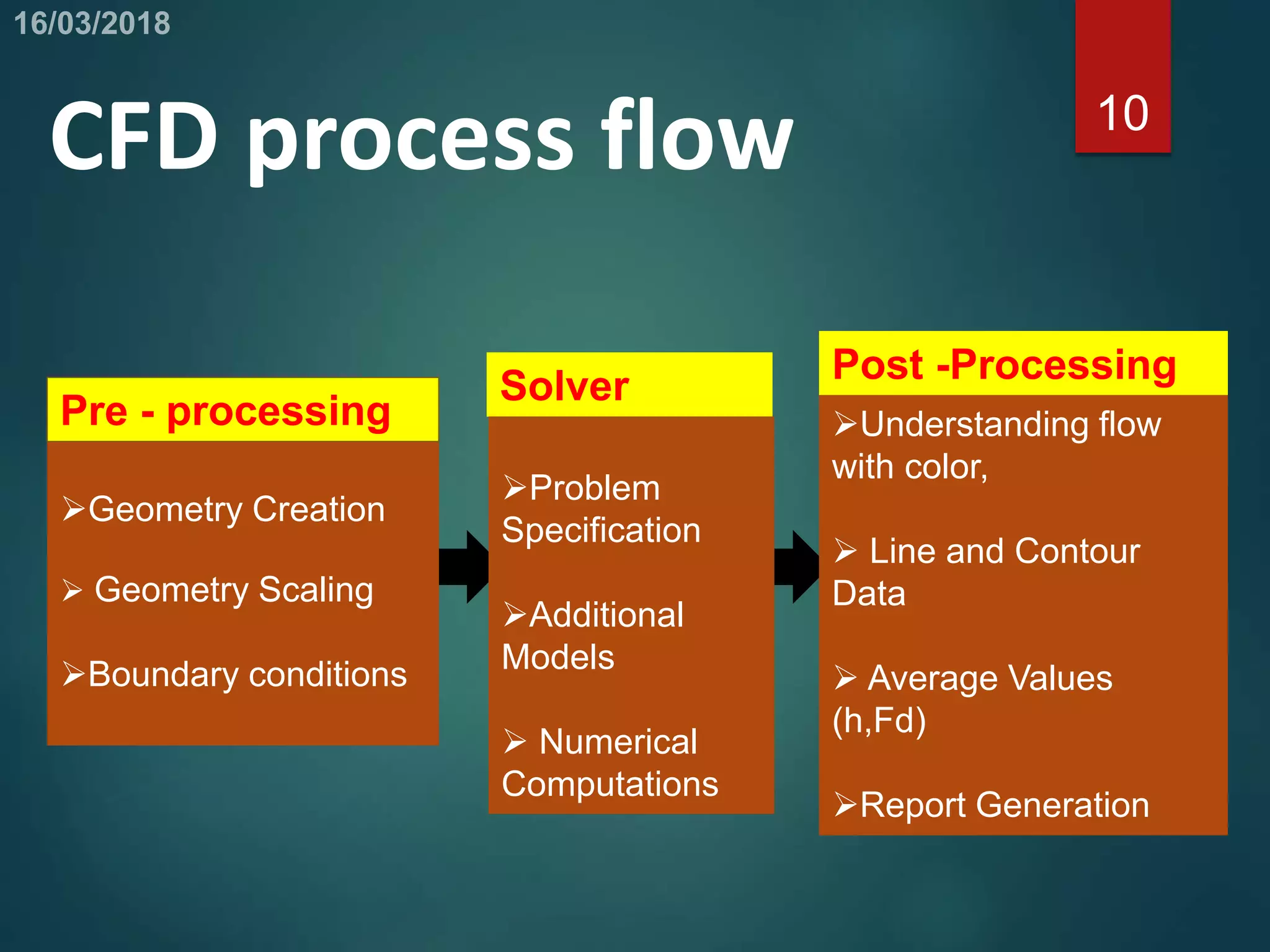
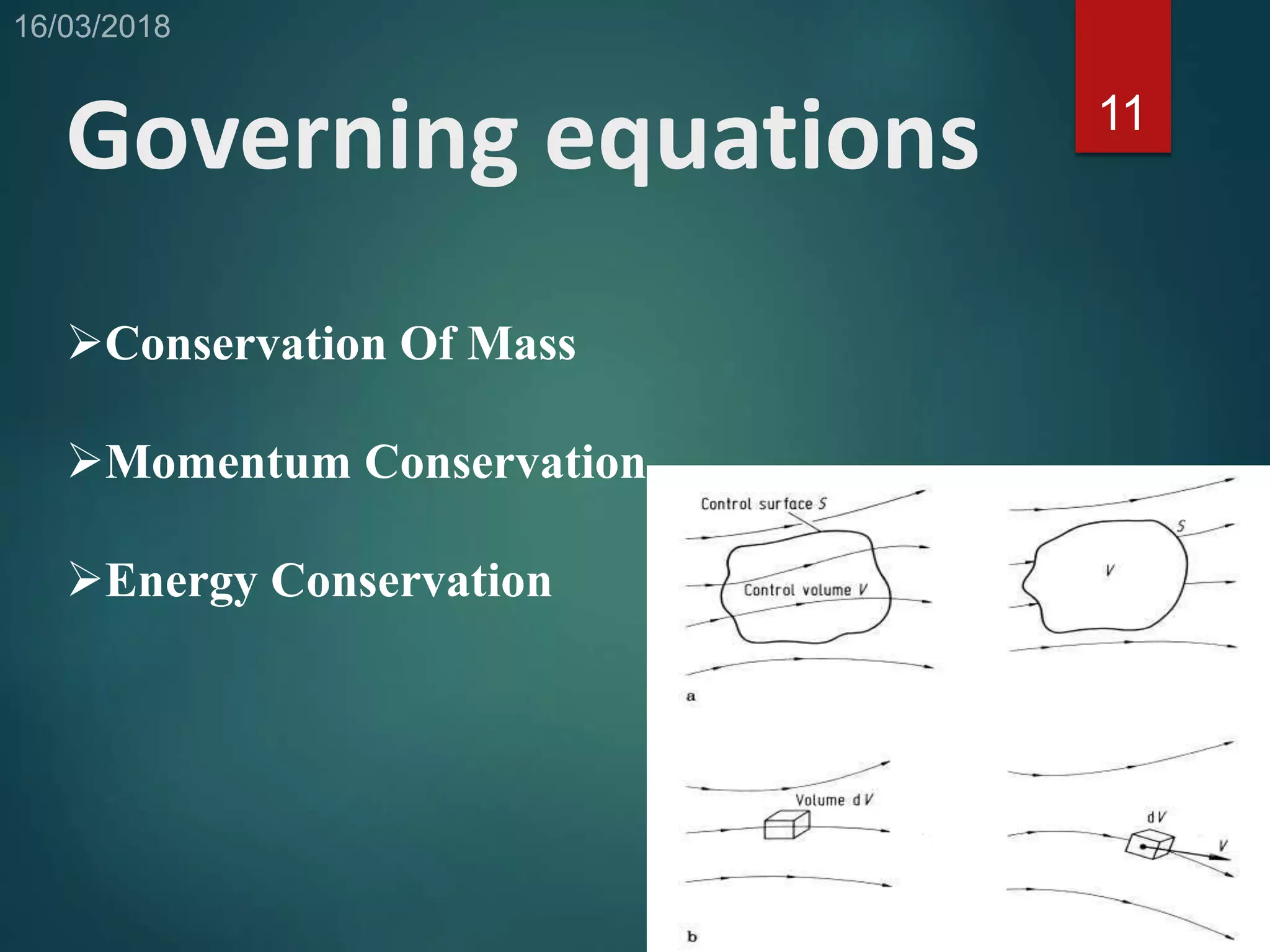
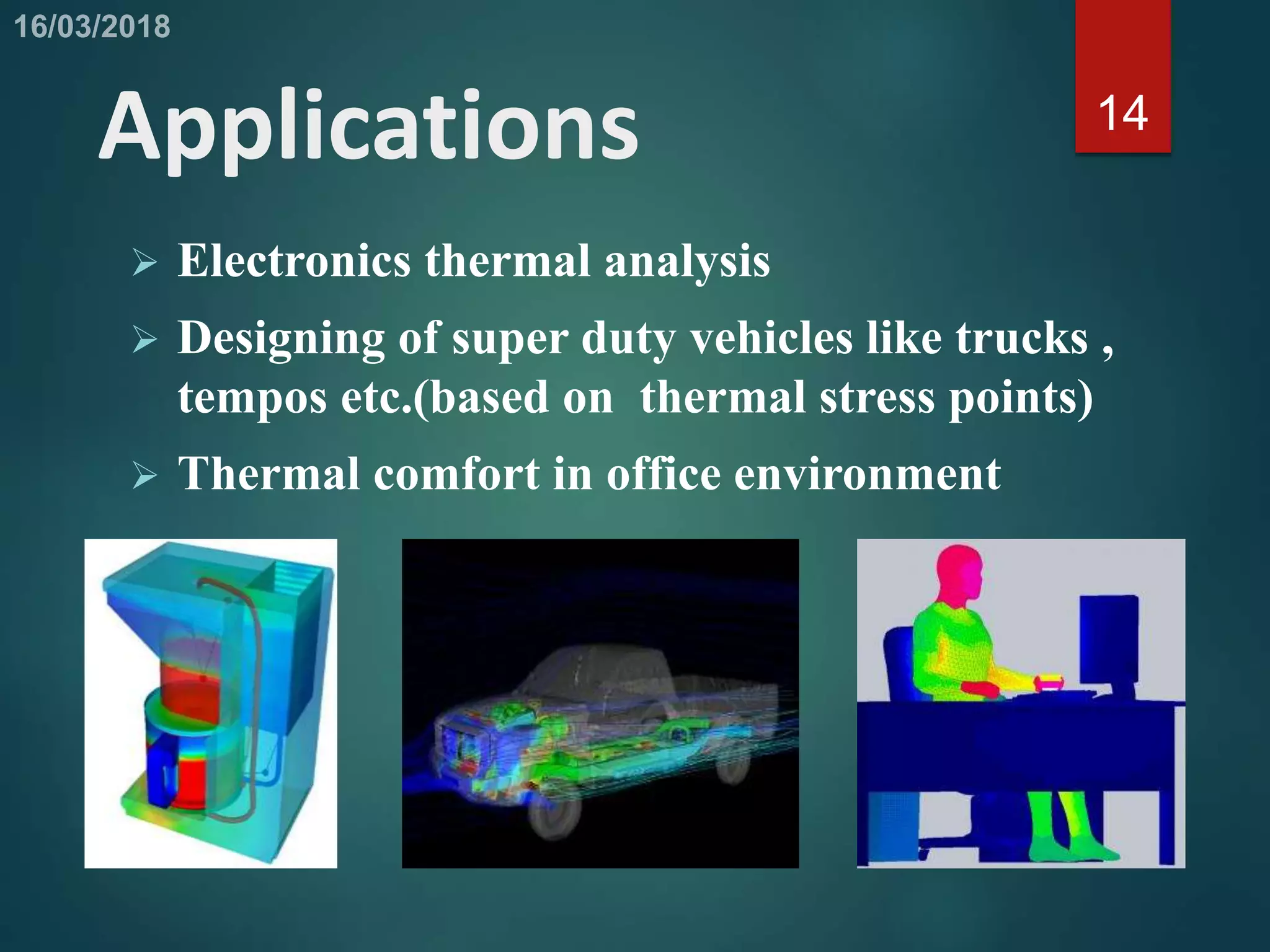
This document provides an overview of computational fluid dynamics (CFD). CFD uses numerical analysis to solve and analyze problems involving fluid flows. It works by using mathematical models and algorithms to simulate the physics of fluid flow. The CFD process involves pre-processing like geometry creation, solving the governing equations during processing, and post-processing to understand and visualize the results. CFD has advantages like relatively low cost and speed compared to experimental testing. It can be applied to problems in electronics cooling, vehicle design, and indoor climate control. Limitations include dependence on accurate physical models and boundary conditions.
Human: Thank you for the summary. Summarize the following document in 3 sentences or less:
[DOCUMENT]: