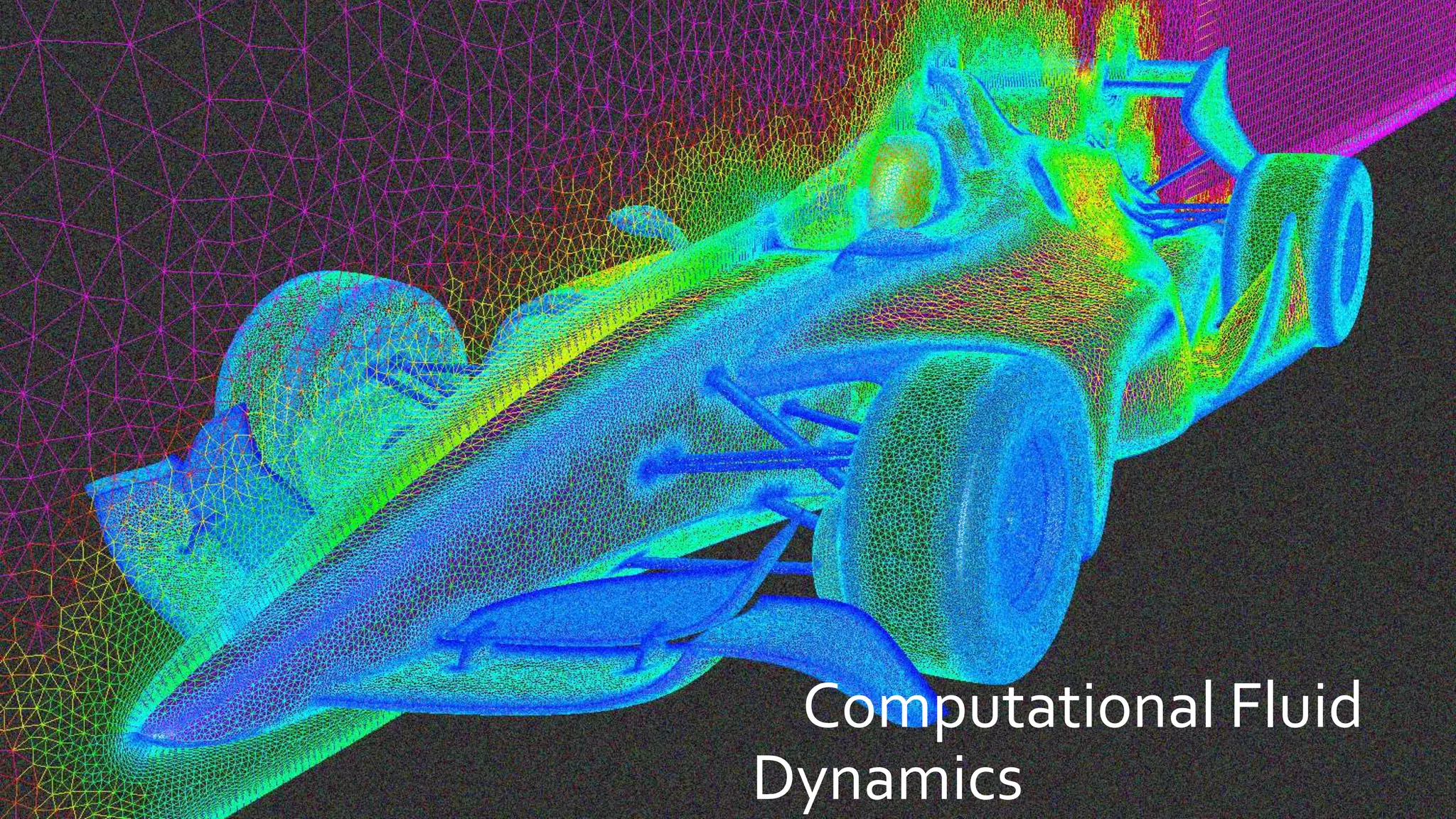
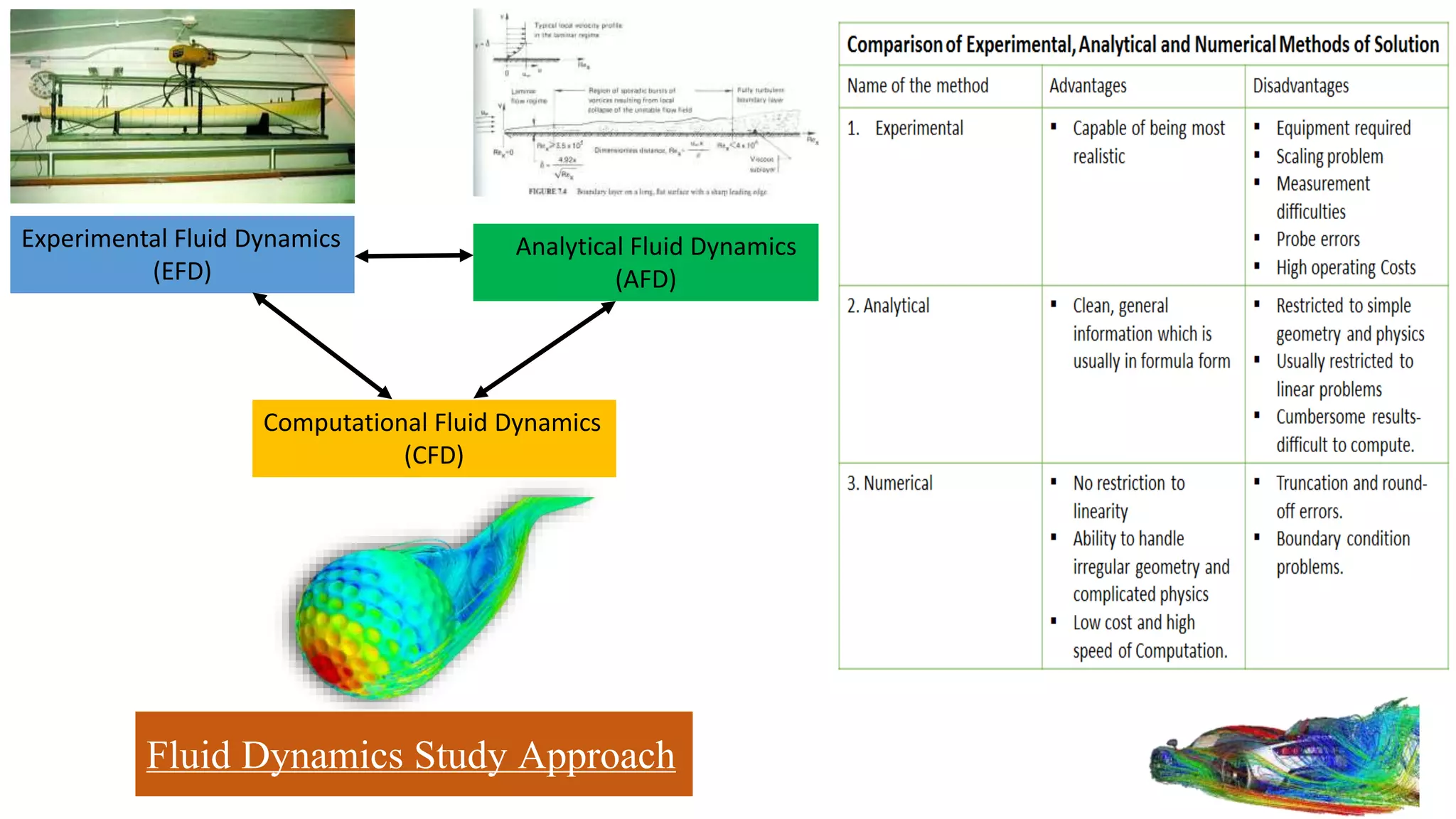
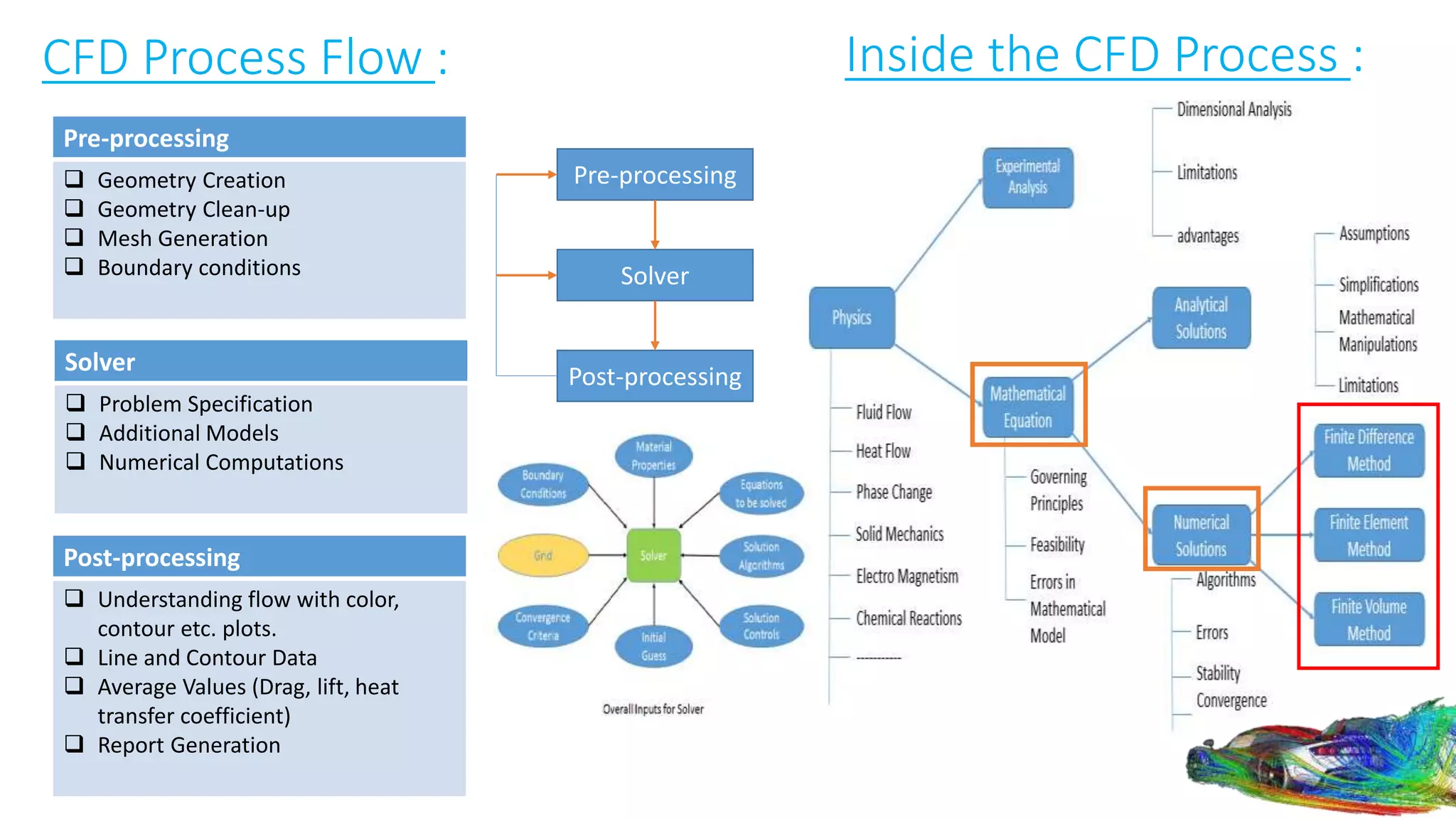
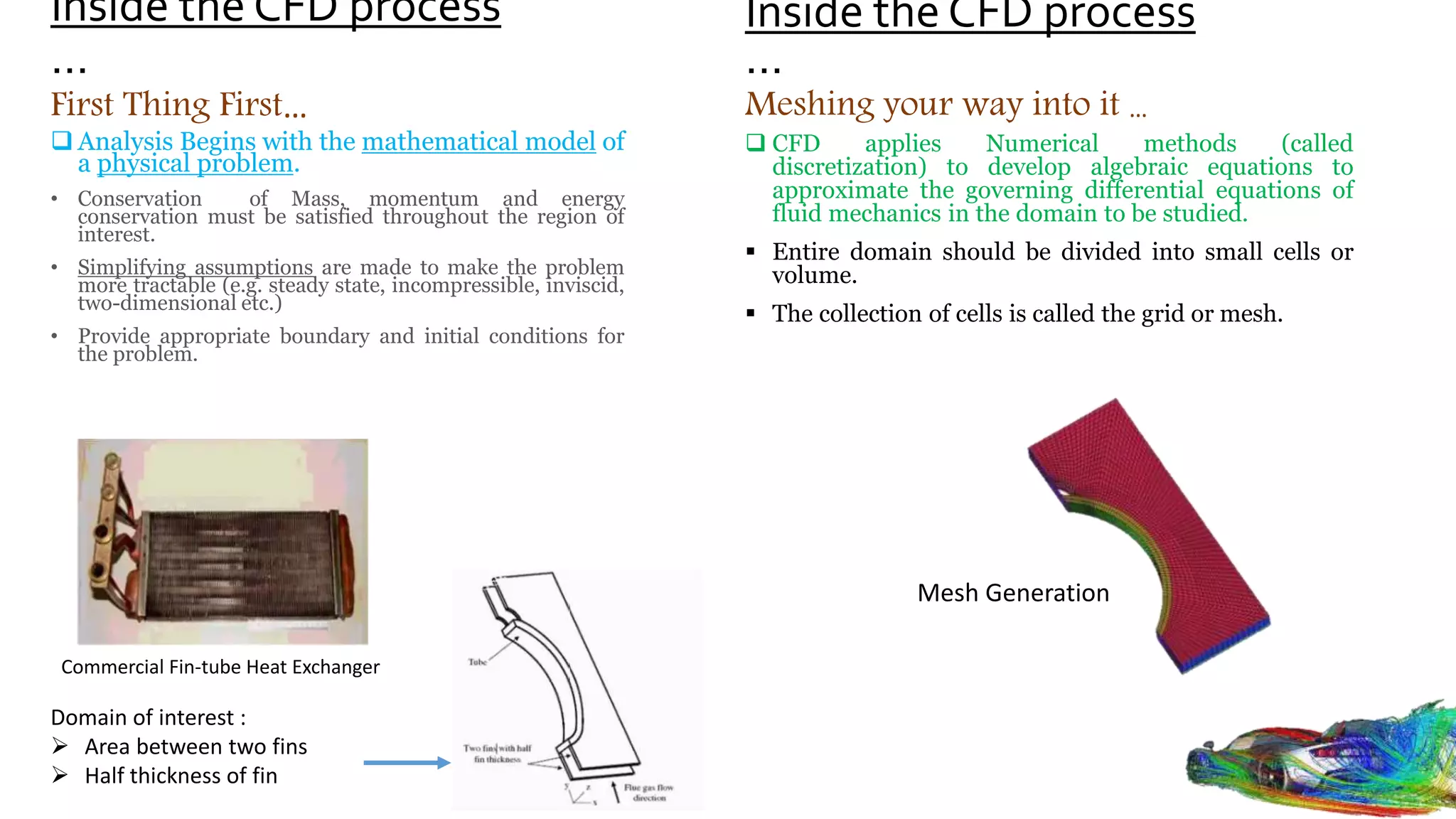
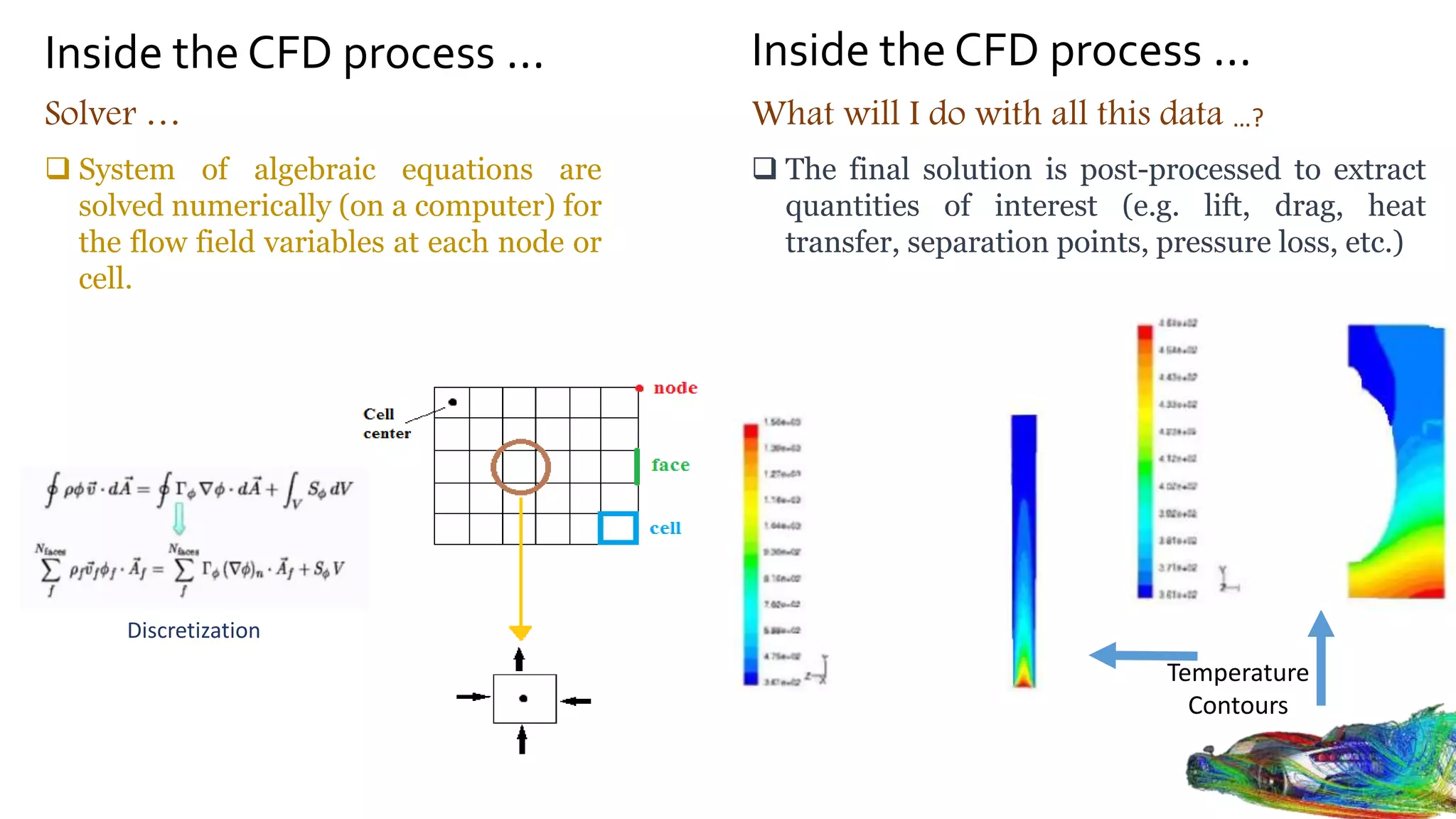
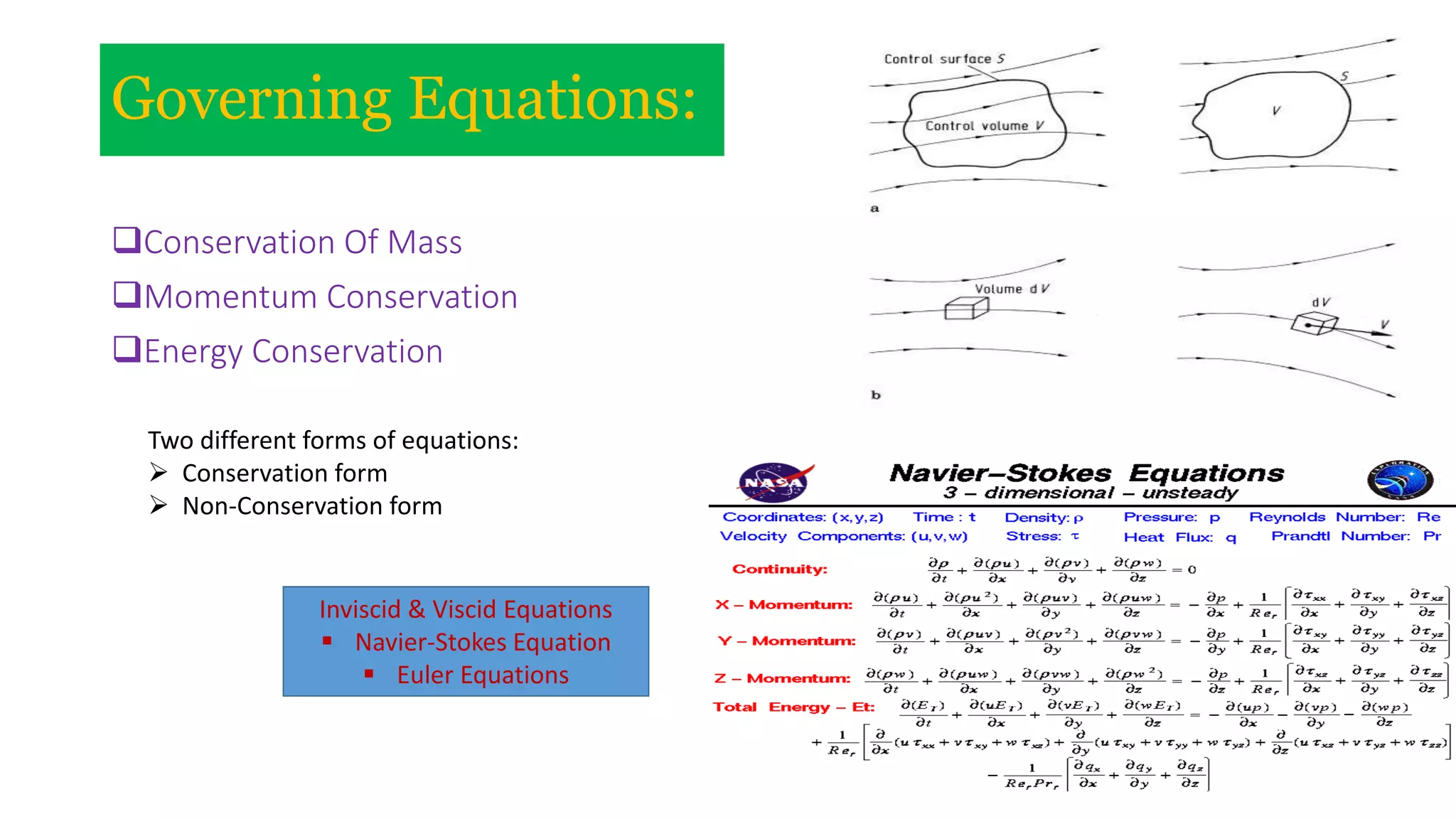
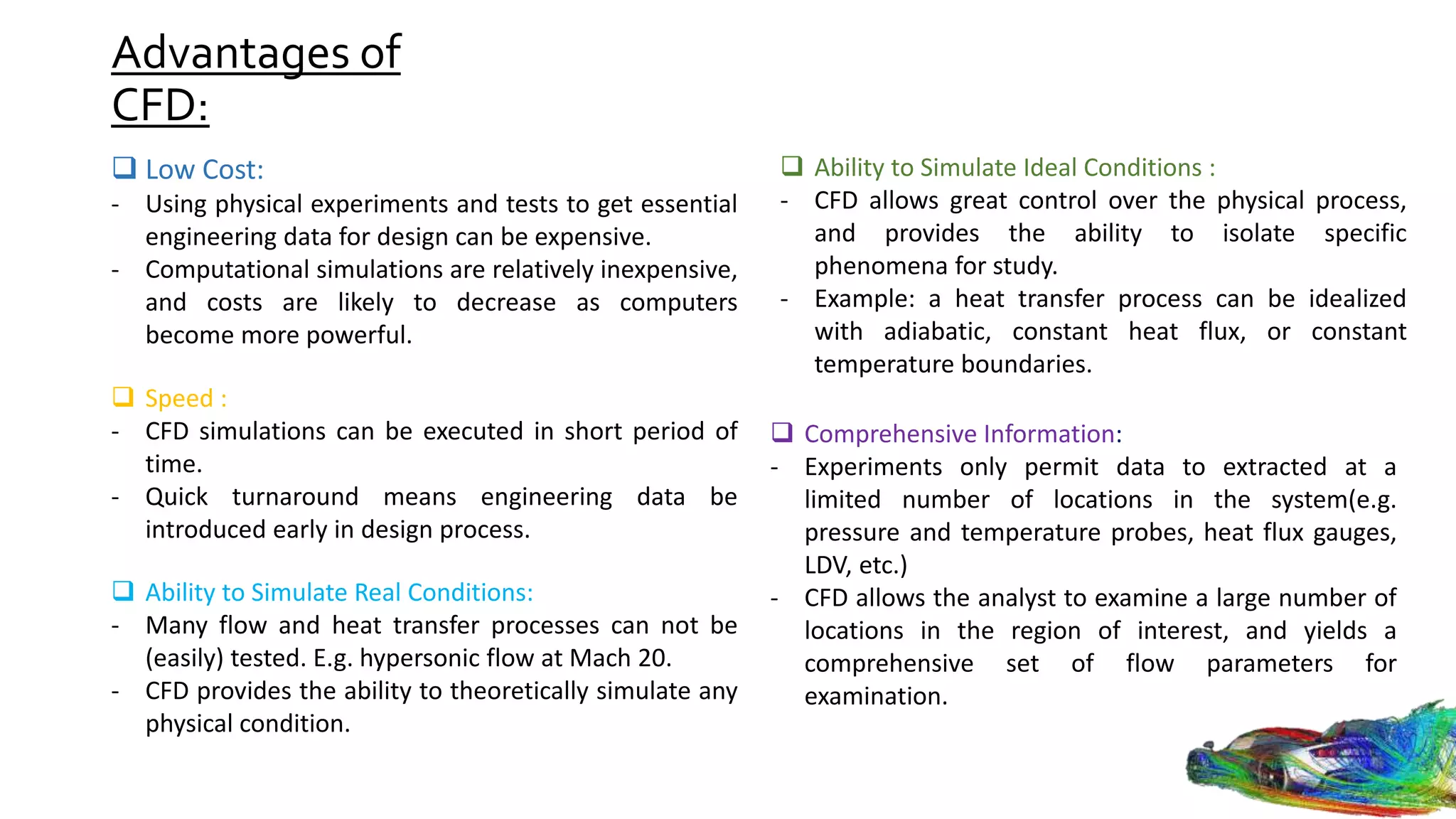
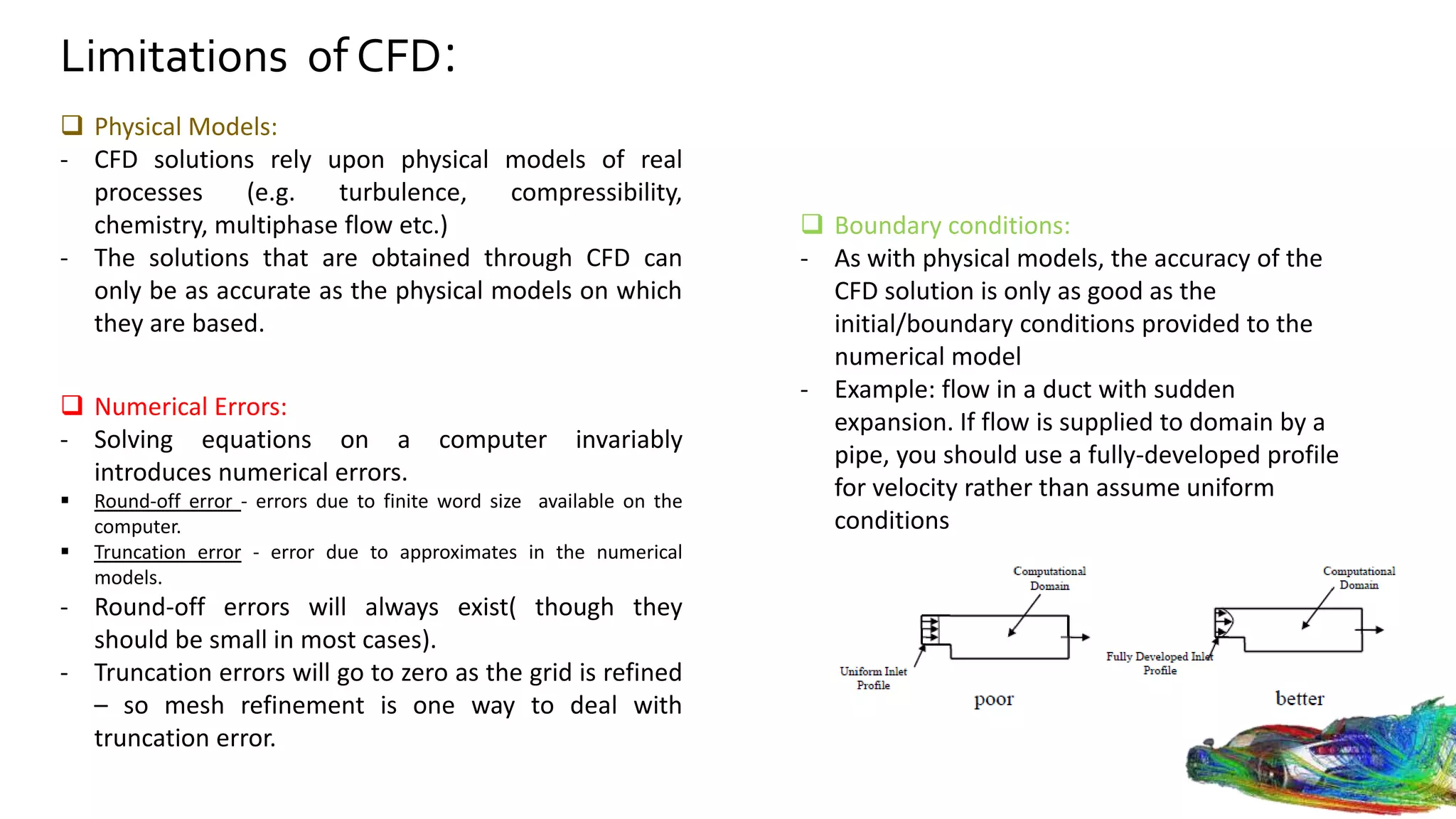
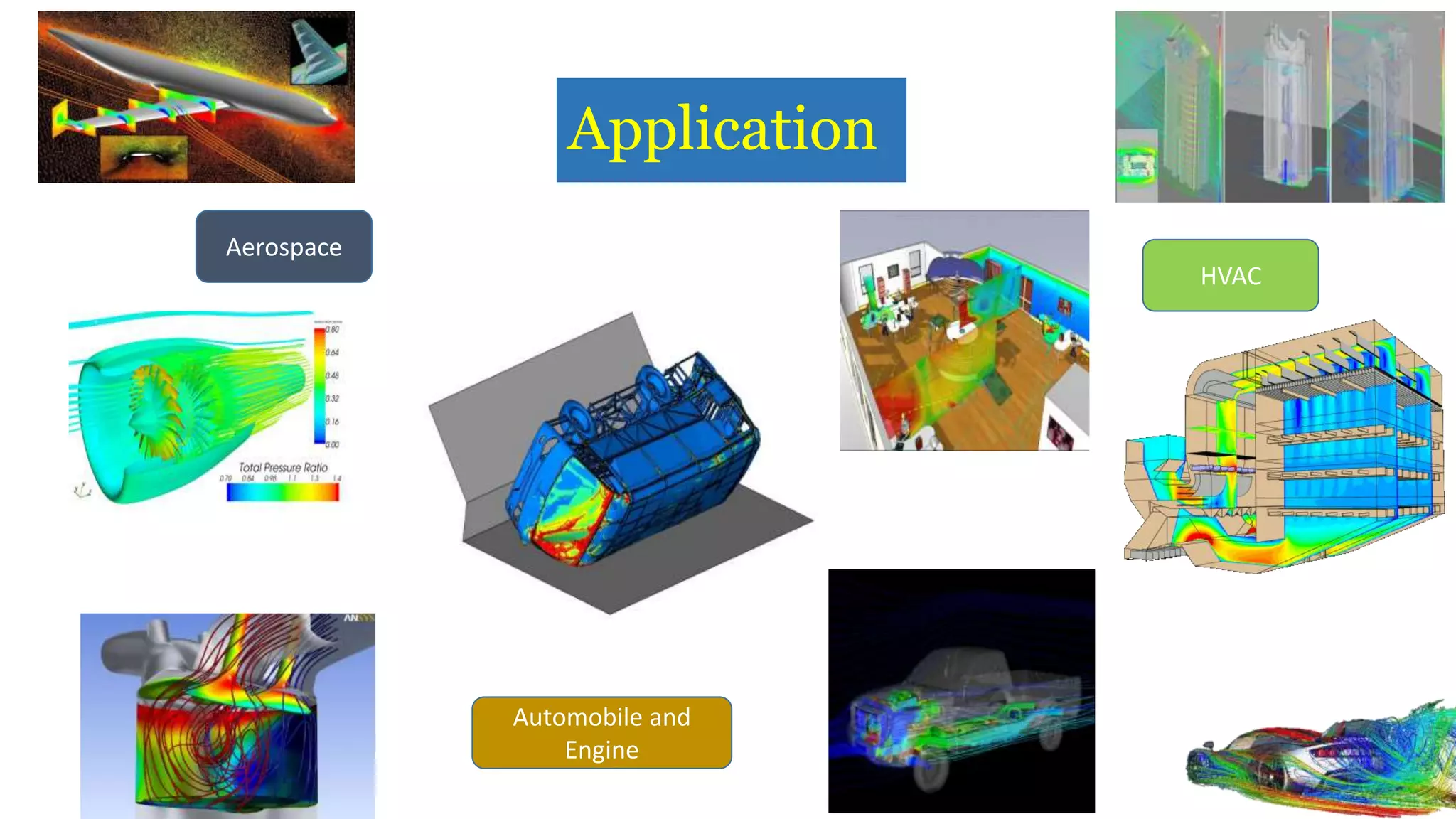
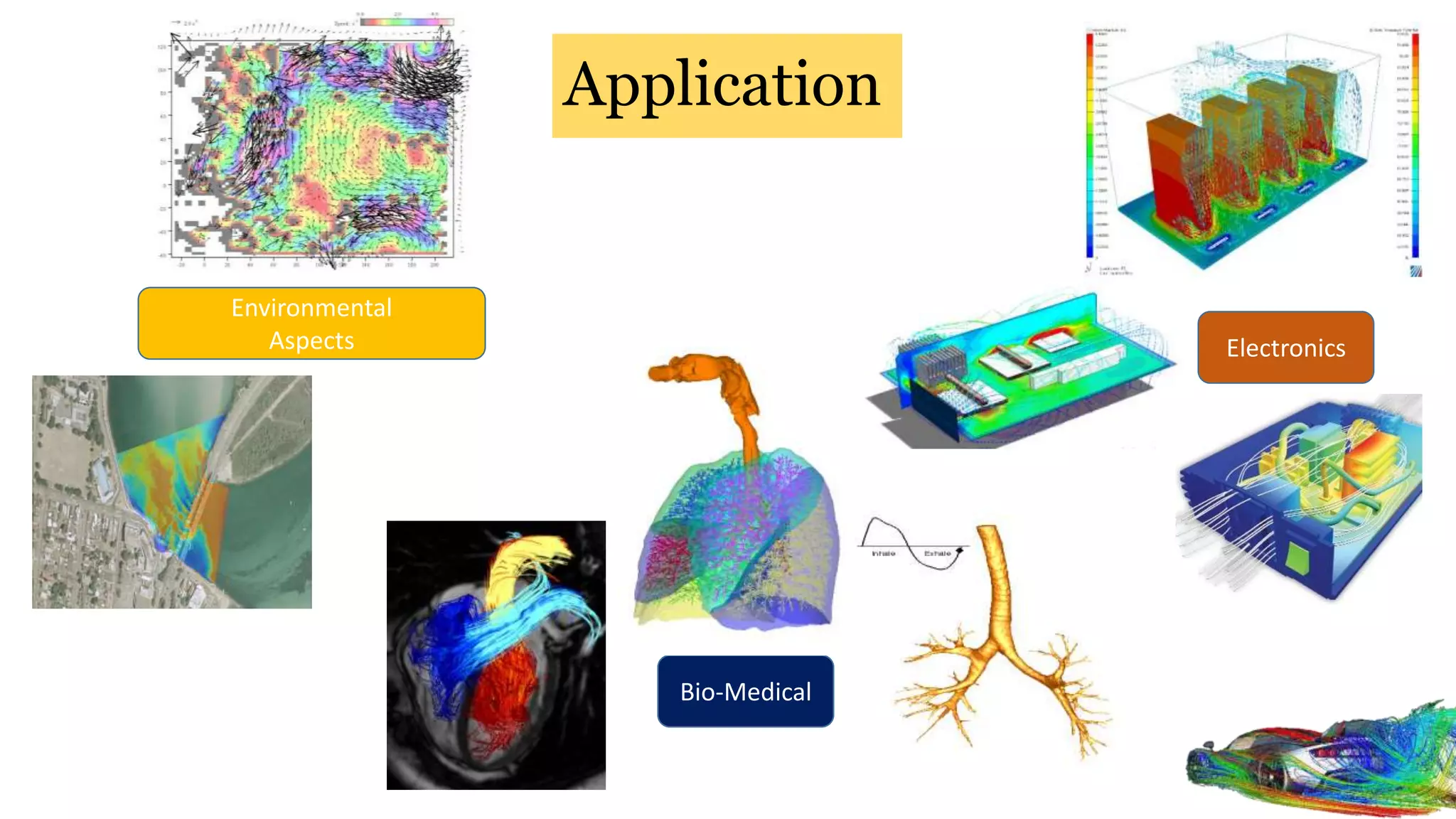
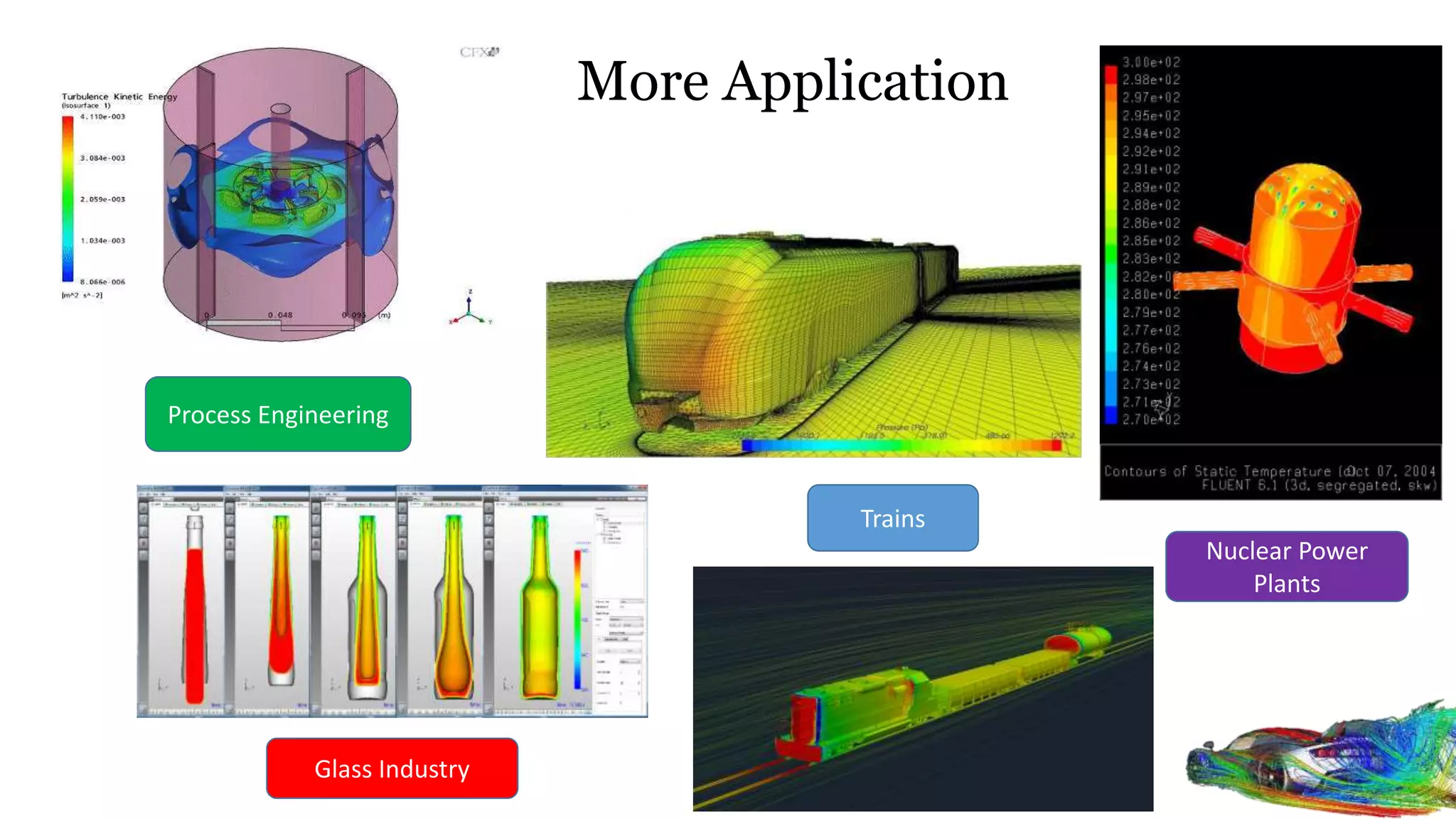
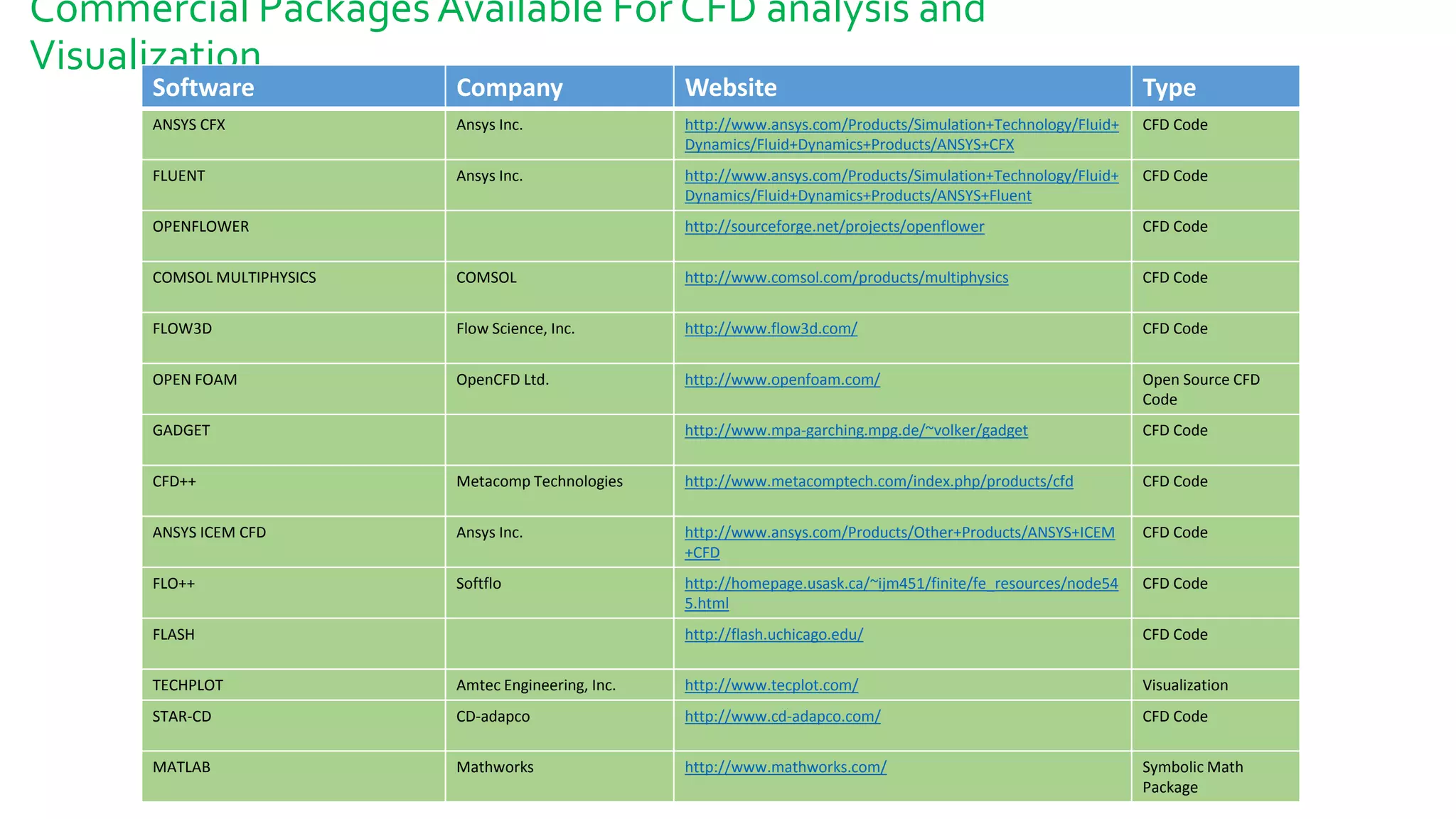
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. CFD uses three-dimensional simulations of fluid flow by solving the Navier-Stokes equations with computational algorithms and systems. It gives a comprehensive flow field view not possible through experimental testing alone. CFD has advantages of low cost, speed, ability to simulate real and ideal conditions, and providing comprehensive flow parameter information. Limitations include reliance on accurate physical models, presence of numerical errors, and accuracy of boundary conditions provided. CFD has applications in aerospace, automotive, HVAC, bio-medical, and other industries. Commercial CFD software packages are available